Internal hardware
- 1. Internal Hardware Gina 10A
- 2. What is Internal Hardware? Internal Hardware is mean the hardware that is inside the computer case. For example: ï― C.P.U ï― R.A.M ï― R.O.M ï― Graphics Card ï― Motherboard ï― Sound Card ï― Network Interface Card ï― Internal Fan
- 3. C.P.U Central Processing Unit ï― The âbrainâ of the computer that carries out software instructions. An Example: Pentium processor ï― It connect to the âmotherboardâ (main circuit board). Measure the speed: Hertz. ï― 1 Megahertz (MHz) = 1,000,000 (1 million) Hertz ï― 1 Gigahertz (GHz) = 1,000,000,000 (1 billion) Hertz
- 4. R.A.M Random Access Memory (RAM) ï― the part of the computer that temporarily stores and the data it is processing. ï― volatile storage device- turned power off the everything disappear, lost. ï― put in to sockets on the motherboard.
- 5. R.O.M Read-Only Memory ï― hold a small, special piece of software: the 'boot up' program. ï― non-volatile storage- never lost, even if the power is switched off. ï― In the motherboard
- 6. Graphics Card ï― produce high quality displays for your monitor. ï― controlling each pixel on the screen. ï― Make the computer chip hot.
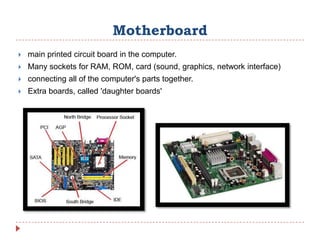
- 7. Motherboard ï― main printed circuit board in the computer. ï― Many sockets for RAM, ROM, card (sound, graphics, network interface) ï― connecting all of the computer's parts together. ï― Extra boards, called 'daughter boards'
- 8. Sound Card ï― Where the sound come out. ï― 'Mic' input for microphone ï― 'Line' input for general purpose connections ï― 'Speaker' socket for headphones.
- 9. Network Interface Card ï― allow the signal from the network to be transmitted to the machine or allow to connect to other network(s). ï― via a fixed cable, infra red or radio waves. ï― slot into the Motherboard.
- 10. Internal Fan ï― Cool the monitor down.