International financial reporting standards and India's Response
- 1. SAKSHI VARSHNEY NIKITA MANGAL Presented By: INTERNATIONAL FINANCIAL REPORTING STANDARDS AND INDIAŌĆÖS RESPONSE
- 2. CONTENTS ŌĆó What? ŌĆó The IFRS: History ŌĆó The IFRS : Objectives ŌĆó Advantages & Disadvantages of Adopting IFRS ŌĆó IFRS adoption procedure in India ŌĆó Utility for India in Adopting IFRS ŌĆó Challenges in the Process of Adoption of IFRS in India ŌĆó Conclusion
- 3. WHAT? International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) are a set of accounting standards developed by the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) that is becoming the global standard for the preparation of public company financial statements.
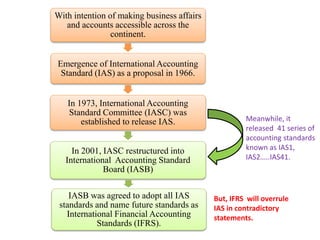
- 5. With intention of making business affairs and accounts accessible across the continent. Emergence of International Accounting Standard (IAS) as a proposal in 1966. In 1973, International Accounting Standard Committee (IASC) was established to release IAS. In 2001, IASC restructured into International Accounting Standard Board (IASB) IASB was agreed to adopt all IAS standards and name future standards as International Financial Accounting Standards (IFRS). Meanwhile, it released 41 series of accounting standards known as IAS1, IAS2ŌĆ”..IAS41. But, IFRS will overrule IAS in contradictory statements.
- 6. The IFRS: Objective ŌĆó To develop, in the public interest, a single set of high quality, understandable, enforceable and globally accepted financial reporting standards based upon clearly articulated principles. ŌĆó To promote the use and rigorous application of those standards. ŌĆó To promote and facilitate adoption of International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRSs), being the standards and interpretations issued by the IASB. ŌĆó In fulfilling the above objectives and to help entities in diverse economic settings.
- 7. ADVANTAGES ŌĆó Greater comparability ŌĆó Beneficial to new and small investors
- 9. DISADVANTAGES ŌĆó High costs ŌĆó Prone to Manipulation
- 10. ŌĆó Not globally accepted
- 13. IFRS Adoption Procedure Established Institute of Chartered Accountant of India (ICAI) ICAI constituted Accounting Standard Board (ASB) Task force set up by ICAI 1949 1977 2006
- 14. 3 step process ŌĆō 1. IFRS Impact Assessment Assessment of impact of IFRS Identify key conversion dates Laid down training plan Identify loopholes b/w existing one & IFRS
- 15. 2. Preparation for IFRS Implementation Documentation of IFRS Accounting Manual Revamp internal reporting systems IFRS 1 act as a guide for first time adopter & provide exemptions
- 16. 3. Implementation Preparation of an Opening Balance Sheet Proper understanding of the impact required Continuous training of staff For smooth transition
- 17. Utility for India in Adopting IFRS Better Access to Global Capital Markets Easy Cross Border Listing Easier Global Comparability
- 18. Better Quality of Financial Reporting Elimination of Multiple Reporting
- 19. Challenges in the Process of Adoption of IFRS in India Awareness of International Financial Reporting Practices Training Amendments to the Existing Laws
- 20. Taxation Use of Fair Value as Measurement Base
- 21. CONCLUSION ŌĆó Ensuring a high quality corporate financial reporting environment depends on effective Control & Enforcement Mechanism. ŌĆó To ensure that all the Firms are complying with adoption procedure, Indian lawmakers and Accounting Body (ICAI) should have a Financial Reporting Compliance Monitoring Board who will play an advisory and monitoring role for the firms on IFRS Adoption Procedure. ŌĆó Self regulation, awareness and proper training will also contribute in adopting IFRS.