International monetary fund
- 2. Main mission: International Monetary System stability The International Monetary Fund, or IMF, promotes international financial stability and monetary cooperation. It also facilitates international trade, promotes employment and sustainable economic growth, and helps to reduce global poverty. Bretton Woods on July 1944 v December 27, 1945 Articles of Agreement v Great Depression World Wars Harry Dexter White and John Maynard Keynes v
- 3. Headquarter 1: located on 720 19th street Headquarter 2: 1900 Pennsylvania Avenue Washington, DC Headquarter: Washington, D.C. Offices: Paris, Tokyo, New York and Geneva
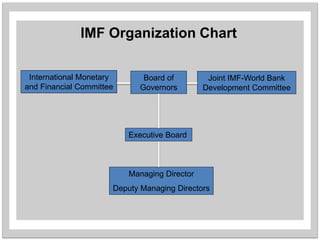
- 4. IMF Organization Chart International Monetary and Financial Committee Joint IMF-World Bank Development Committee Executive Board Managing Director Deputy Managing Directors Board of Governors
- 5. List of Managing Directors 1946 ŌĆō 1951 Belgium 1951 ŌĆō 1956 Sweden 1956 ŌĆō 1963 Sweden 1963 ŌĆō 1973 France 1973 ŌĆō 1978 Netherlands 1978 ŌĆō 1987 France 1987 ŌĆō 2000 France 2000 ŌĆō 2004 Germany 2004 ŌĆō 2007 Spain 2007 ŌĆō 2011 France 2011 ŌĆō present France
- 6. (The Present Managing Director) Christine Lagarde Christine Lagarde is the Managing Director of the International Monetary Fund. She was appointed on June 2011. She was re- appointed in July 2016 for a second term.
- 7. 1. Belgium 2. Bolivia 3. Canada 4. China 5. Colombia 6. Czechoslovakia 7. Egypt 8. Ethiopia 9. France 10. Greece 11. Honduras 12. Iceland 13. India 14. Iraq 15. Luxembourg 16. Netherlands 17. Norway 18. Philippines 19. South Africa 20. United Kingdom 21. United States 22. Dominican Republic Member Countries 23. Ecuador 24. Guatemala 25. Paraguay 26. Iran 27. Chile 28. Mexico 29. Peru 30. Costa Rica 31. Brazil 32. Uruguay 33. El Salvador 34. Nicaragua 35. Panama 36. Denmark 37. Venezuela 38. Turkey 39. Italy 40. Syria 41. Lebanon 42. Australia 43. Finland 44. Austria 45. Thailand 46. Pakistan 47. Sri Lanka 48. Sweden 49. Myanmar 50. Japan 51. Germany 52. Jordan 53. Haiti 54. Israel 55. Afghanistan 56. Korea 57. Argentina 58. Vietnam 59. Ireland 60. Saudi Arabia 61. Sudan 62. Ghana 63. Malaysia 64. Tunisia 65. Morocco 66. Spain 67. Libya 68. Portugal 69. Nigeria 70. Lao 71. New Zealand 72. Nepal 73. Cyprus 74. Liberia 75. Togo 76. Senegal 77. Somalia 78. Sierra Leone 79. Tanzania 80. Kuwait 81. Jamaica 82. Cote dŌĆÖ Ivoire 83. Niger 84. Burkina Faso 85. Cameroon 86. Central African Republic 87. Chad 88. Republic of Congo 89. Benin 90. Gabon 91. Mauritania
- 8. 92. Trinidad and Tobago 93. Madagascar 94. Algeria 95. Mali 96. Uganda 97. Burundi 98. Democratic Republic of Congo 99. Guinea 100.Rwanda 101.Kenya 102.Malawi 103.Zambia 104.Singapore 105.Guyana 106.Indonesia 107.The Gambia 108.Botswana 109.Lesotho 110.Malta 111.Mauritius 112.Swaziland 113.Equatorial Guinea 114.Cambodia 115.Barbados 116.Fiji 117.Oman 118.Samoa 119.Bangladesh 120.Bahrain 121.Qatar 122.United Arab Emirates 123.Romania 124.The Bahamas 125.Grenada 126.Papua New Guinea 127.Comoros 128.Guinea-Bissau 129.Seychelles 130.Sao Tome and Principe 131.Maldives 132.Suriname 133.Solomon Islands 134.Cape Verde 135.Dominica 136.Djibouti 137.St. Lucia 138.St. Vincent and the Grenadines 139.Zimbabwe 140.Bhutan 141.Vanuatu 142.Antigua and Barbuda 143.Belize 144.Hungary 145.St Kitts and Nevis 146.Mozambique 147.Tonga 148.Kiribati 149.Poland 150.Angola 151.Bulgaria 152.Namibia 153.Mongolia 154.Albania 155.Lithuania 156.Georgia 157.Kyrgyzstan 158.Latvia 159.Marshall Islands 160.Estonia 161.Armenia 162.Switzerland 163.Russian Federation 164.Belarus 165.Kazakhstan 166.Moldova 167.Ukraine 168.Azerbaijan 169.Uzbekistan 170.Turkmenistan 171.San Marino 172.Bosnia and Herzegovina 173.Croatia 174.Macedonia 175.Slovenia 176.Serbia 177.Czech Republic 178.Slovak Republic 179.Tajikistan 180.Federated States of Micronesia 181.Eritrea 182.Brunei Darussalam 183.Palau 184.Timor-Leste 185.Montenegro 186.Kosovo 187.Tuvalu 188.South Sudan 189.Nauru
- 9. Functions 1. Economic surveillance and monitoring ŌĆó Country Surveillance ŌĆó Global surveillance ŌĆó Regional Surveillance 2. Capacity Building ŌĆó Technical Assistance and Training 3. Lending ŌĆó Conditionality of Loans
- 10. SDR 477 billion (US $692 billion) $ Total Quota Greece, Ukraine, Pakistan, Egypt Largest Borrowers Articles of Agreement ’āś Article II, Section 2 ’āś Article XXVI Membership
- 11. Washington Consensus Ten Principles (John Williamson in 1989): 1. Fiscal discipline 2. Public expenditure priorities 3. Tax reform 4. Financial liberalization 5. Exchange rates 6. Trade liberalization 7. Increasing foreign direct investment 8. Privatization 9. Deregulation 10. Secure intellectual property rights
- 12. PHILIPPINES and the IMF ŌĆ£IMF sees sustained Philippine growth.ŌĆØ ŌĆ£IMF lifts 2017 PH growth.ŌĆØ ŌĆ£IMF has ŌĆśvery optimisticŌĆÖ growth outlook over PHLŌĆÖs impressive economic performance.ŌĆØ
- 13. IMF sees sustained PH growth The International Monetary Fund (IMF) expects the Philippines to sustain its growth momentum up to at least 2018, banking on increased fiscal spending and a recovery of global demand, as well as a reform agenda seen broadly on track to boost the local economy.
- 14. IMF has ŌĆśvery optimisticŌĆÖ growth outlook over PHLŌĆÖs impressive economic performance The International Monetary Fund (IMF) has relayed to the countryŌĆÖs economic managers the multilateral institutionŌĆÖs ŌĆ£very optimisticŌĆØ growth outlook on the Philippines owing to the economyŌĆÖs continued ŌĆ£impressiveŌĆØ performance.
- 15. IMF lifts 2017 PH growth The International Monetary Fund (IMF) has raised its growth forecast for the Philippines this year to 6.8 percent, faster than the previous estimate of 6.7 percent, on strong domestic demand. The latest IMF mission report said the domestic economy continued to be favorable despite external headwinds.
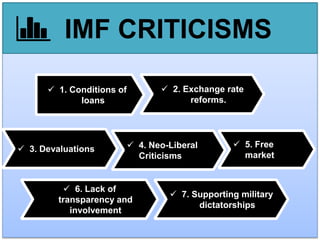
- 16. IMF CRITICISMS ’ā╝ 1. Conditions of loans ’ā╝ 2. Exchange rate reforms. ’ā╝ 3. Devaluations ’ā╝ 4. Neo-Liberal Criticisms ’ā╝ 5. Free market ’ā╝ 6. Lack of transparency and involvement ’ā╝ 7. Supporting military dictatorships