Internet (introduce)
- 1. INTERNET
- 2. Session Objective ïŪ ïŪ ïŪ ïŪ What is INTERNET ? Brief History of Internet. Services provided by Internet. Impact of Internet. âĒ Education. âĒ Health Care. âĒ Business.
- 3. What is I N T E R N E T ? ïŪ The largest network of networks in the world.
- 4. What is I N T E R N E T ? ContinueâĶâĶ ïŪ A network of networks, joining many government, university and private computers together and providing an infrastructure for the use of E-mail, bulletin boards, file archives, hypertext documents, databases and other computational resources.
- 5. What is I N T E R N E T ? ContinueâĶâĶ ïŪ The vast collection of computer networks which form and act as a single huge network for transport of data and messages across distances which can be anywhere from the same office to anywhere in the world.
- 6. Brief History of Internet ïŪ ïŪ ïŪ ïŪ ARPA â Advanced Research Project Agency. 1969 January 2 â started an experimental Computer Network. Concept â No Server, but equal importance/participation to every computer in the Network. Even if, one or two node destroyed that will not affect the Network.
- 7. Paul Baran ïŪ Paul Baran developed the field of packet switching networks while conducting research at the historic RAND organization.
- 8. Vinton Cerf ïŪ ïŪ Father of Internet Co-designer of the TCP/IP networking protocol.
- 9. Brief History of Internet ContinueâĶâĶ ïŪ First named as ARPANET ïŪ This is renamed as INTERNET âĒ TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol)
- 10. Internet Growth Trends ïŪ ïŪ ïŪ ïŪ ïŪ ïŪ ïŪ ïŪ ïŪ ïŪ ïŪ 1977: 111 hosts on Internet 1981: 213 hosts 1983: 562 hosts 1984: 1,000 hosts 1986: 5,000 hosts 1987: 10,000 hosts 1989: 100,000 hosts 1992: 1,000,000 hosts 2001: 150 â 175 million hosts 2002: over 200 million hosts By 2010, about 80% of the planet will be on the Internet
- 11. How to Connect to Internet
- 12. Internet Services ïŪ ïŪ ïŪ ïŪ ïŪ ïŪ ïŪ ïŪ Electronic Mail (e-mail) World Wide Web Telnet File Transfer Protocol (FTP) Internet Telephone Web TV/Radio Internet Relay Chat News Groups
- 13. Electronic Mail (e-Mail) ïŪ ïŪ Distributes e-mail messages and attached files to one or more electronic mailboxes. Eg:- e-mail addresses âĒ thomas@mes.edu.in âĒ murugan@mesmarampally.org
- 14. Electronic Mail (e-Mail) ContinueâĶâĶ thomas Name of Person murugan @ mes Organization @ . edu . in Type of Organization mesmarampally . Country org
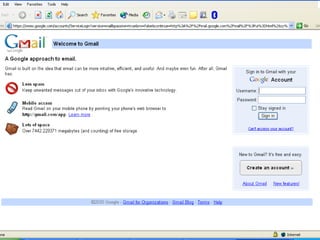
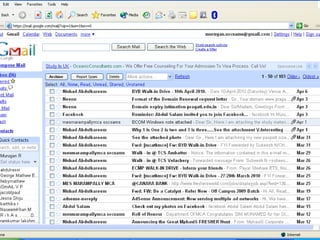
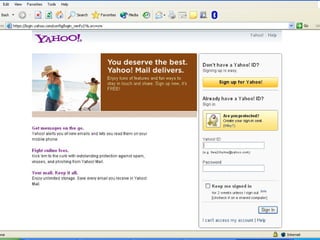
- 15. Electronic Mail (e-Mail) ContinueâĶâĶ ïŪ Different e-mail service providers âĒ G-Mail âĒ Yahoo Mail âĒ Hot Mail
- 21. World Wide Web (W W W) ïŪ ïŪ ïŪ Most important service provided by Internet. An internet-based hypermedia initiative for global information sharing. Developed in 1989 by Tim Berners-Lee of the European Particle Physics Lab (CERN) in Switzerland.
- 22. Tim Berners-Lee ïŪ Father of W W W. ïŪ The inventor of HTML. ïŪ Invented W W W while working at CERN, the European Particle Physics Laboratory.
- 23. Search Engines ïŪ For searching information on the Internet. âĒ Google âĒ Yahoo âĒ Altavista
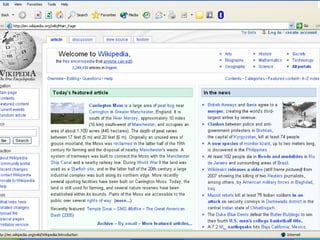
- 30. WIKIPEDIA ïŪ ïŪ ïŪ A wiki is a publishing platform on which many people can contribute new content and revise existing content. The content benefits from the collective knowledge of the contributors, so wikis can be very beneficial for group projects. Some businesses and organizations use wikis to maintain documents.
- 34. Impact of Internet ïŪ Education ïŪ Health Care ïŪ Business