Internet of things
- 1. INTERNET OF THINGS IOT By - Palak Sood Makhija M.Tech CSE - I
- 2. AGENDA  Introduction  Origin of IoT  What is IoT?  Architectures  Working of IoT  Controversies  References  Q/A
- 3. INTRODUCTION  Today the Internet has become ubiquitous, has touched almost every corner of the globe, and is affecting human life in unimaginable ways. However, the journey is far from over. We are now entering an era of even more pervasive connectivity where a very wide variety of appliances will be connected to the web. We are entering an era of the “Internet of Things” (abbreviated as IoT).
- 4. ORIGIN OF IOT  1926 – Nikola Tesla in his interview talked about things like Smart Planet : when wireless will be perfectly applied  1999 – Term IoT was coined by Kevin Ashton, expert in technologist and digital transformation  Smart Refrigerator known as Internet Digital DIOS by LG with LCD Screen was first such example of IoT which showed inside temperature , freshness of stored food , nutrition info and recipes
- 5. WHAT IS IOT ?  IoT is a system of interrelated computing devices, mechanical and digital machines, objects, animals or people that are provided with unique identifiers (UIDs) and the ability to transfer data over a network without requiring human-to- human or human-to-computer interaction. or  It is a network of physical devices,vehicles,home appliances and other items embedded with electronics, software, sensors, actuators and connectivity which enables these things to connect and exchange data.
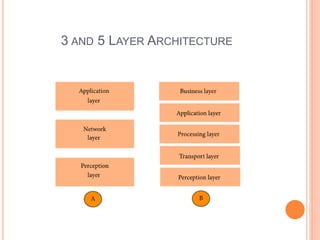
- 6. ARCHITECTURE OF IOT  There is no single consensus on architecture for IoT, which is agreed universally. Different architectures have been proposed by different researchers. Three- and Five-Layer Architectures  The most basic architecture is a three-layer architecture. It was introduced in the early stages of research in this area. It has three layers, namely, the perception, network, and application layers.  The perception layer is the physical layer, which has sensors for sensing and gathering information about the environment. It senses some physical parameters or identifies other smart objects in the environment.  The network layer is responsible for connecting to other smart things, network devices, and servers. Its features are also used for transmitting and processing sensor data.  The application layer is responsible for delivering application specific services to the user. It defines various applications in which the Internet of Things can be deployed, for example, smart homes, smart cities, and smart health.
- 7. 3 AND 5 LAYER ARCHITECTURE
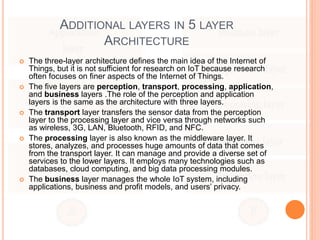
- 8. ADDITIONAL LAYERS IN 5 LAYER ARCHITECTURE  The three-layer architecture defines the main idea of the Internet of Things, but it is not sufficient for research on IoT because research often focuses on finer aspects of the Internet of Things.  The five layers are perception, transport, processing, application, and business layers .The role of the perception and application layers is the same as the architecture with three layers.  The transport layer transfers the sensor data from the perception layer to the processing layer and vice versa through networks such as wireless, 3G, LAN, Bluetooth, RFID, and NFC.  The processing layer is also known as the middleware layer. It stores, analyzes, and processes huge amounts of data that comes from the transport layer. It can manage and provide a diverse set of services to the lower layers. It employs many technologies such as databases, cloud computing, and big data processing modules.  The business layer manages the whole IoT system, including applications, business and profit models, and users’ privacy.
- 10. STEP BY STEP WORKING OF IOT
- 13. APPLICATIONS OF IOT  Consumer applications  Enterprise applications  Infrastructure applications  Infrastructure applications  Energy management  Environmental monitoring  Building and home automation  Healthcare  Metropolitan scale deployments -There are several planned or ongoing large-scale deployments of the IoT, to enable better management of cities and systems. For example, Songdo , South Korea, the first of its kind fully equipped and wired smart city, is gradually being built, with approximately 70 percent of the business district completed as of June 2018. Much of the city is planned to be wired and automated, with little or no human intervention.
- 14. CONTROVERSIES  Platform fragmentation - IoT suffers from platform fragmentation and lack of technical standards a situation where the variety of IoT devices, in terms of both hardware variations and differences in the software running on them, makes the task of developing applications that work consistently between different inconsistent technology ecosystems hard  Privacy, autonomy, and control - Internet of things offers immense potential for empowering citizens, making government transparent, and broadening information access. Privacy threats are enormous, as is the potential for social control and political manipulation.  Data storage - A challenge for producers of IoT applications is to clean, process and interpret the vast amount of data which is gathered by the sensors.  Security - Concerns have been raised that the Internet of things is being developed rapidly without appropriate consideration of the profound security challenges involved and the regulatory changes that might be necessary. Most of the technical security concerns are similar to those of conventional servers, workstations and smartphones, but security challenges unique to the IoT continue to develop, including industrial security controls, hybrid systems, IoT-specific business processes, and end nodes.
- 15. REFERENCES  https://www.hindawi.com/journals/jece/2017/932403 5/  https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Internet_of_things  /MohanKumarG/interneto fthings-iot-aseminar-ppt-by-mohankumarg
- 17. Thanks