Intro three occlusion
- 1. Introduction to Dentistry DA101 Lecture Three Occlusion Dr. Somaia Hasan Dashti 2017
- 2. SDASHTI. CHS,2017 2 Lecture Outlines Definitions Facial Profiles Angle’s Classification Malrelationships of Individual or Groups of Teeth Noncarious Dental Lesions
- 3. SDASHTI. CHS,2017 3 Definitions Occlusion is defined as the contact relationship between maxillary and mandibular teeth when the jaws are in fully closed position Malocclusion is malportioned relationship or deviation in relationship between maxillary and mandibular teeth when they are fully in closed position
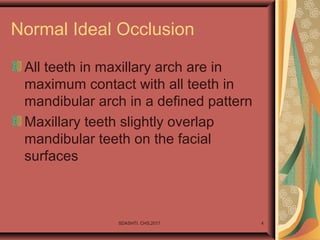
- 4. Normal Ideal Occlusion All teeth in maxillary arch are in maximum contact with all teeth in mandibular arch in a defined pattern Maxillary teeth slightly overlap mandibular teeth on the facial surfaces SDASHTI. CHS,2017 4
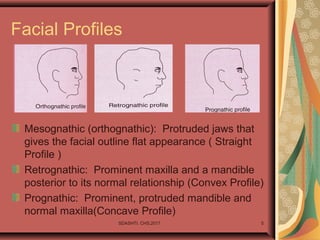
- 5. SDASHTI. CHS,2017 5 Facial Profiles Mesognathic (orthognathic): Protruded jaws that gives the facial outline flat appearance ( Straight Profile ) Retrognathic: Prominent maxilla and a mandible posterior to its normal relationship (Convex Profile) Prognathic: Prominent, protruded mandible and normal maxilla(Concave Profile)
- 6. SDASHTI. CHS,2017 6 Angle’s Classification Normal Occlusion Class I Malocclusion Class II Division 1 Class II Division 2 Class III
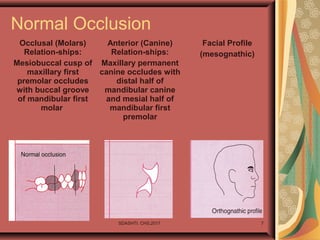
- 7. SDASHTI. CHS,2017 7 Normal Occlusion Occlusal (Molars) Relation-ships: Mesiobuccal cusp of maxillary first premolar occludes with buccal groove of mandibular first molar Anterior (Canine) Relation-ships: Maxillary permanent canine occludes with distal half of mandibular canine and mesial half of mandibular first premolar Facial Profile (mesognathic)
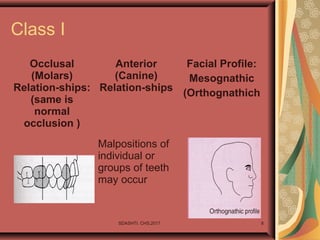
- 8. SDASHTI. CHS,2017 8 Class I Occlusal (Molars) Relation-ships: (same is normal occlusion ) Anterior (Canine) Relation-ships Facial Profile: Mesognathic (Orthognathich Malpositions of individual or groups of teeth may occur
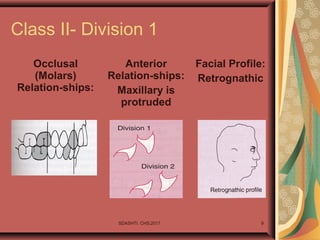
- 9. SDASHTI. CHS,2017 9 Class II- Division 1 Occlusal (Molars) Relation-ships: Anterior Relation-ships: Maxillary is protruded Facial Profile: Retrognathic
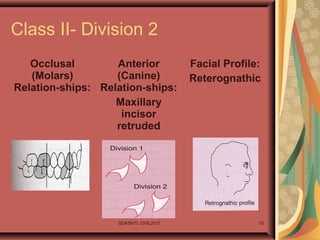
- 10. SDASHTI. CHS,2017 10 Class II- Division 2 Occlusal (Molars) Relation-ships: Anterior (Canine) Relation-ships: Maxillary incisor retruded Facial Profile: Reterognathic
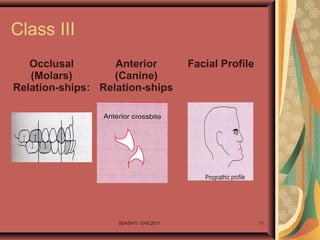
- 11. SDASHTI. CHS,2017 11 Class III Occlusal (Molars) Relation-ships: Anterior (Canine) Relation-ships Facial Profile
- 12. SDASHTI. CHS,2017 12 Malrelationships of Individual or Groups of Teeth Labioversion Linguoversion Buccoversion Supraversion Toriversion Infraversion Anterior & Posterior Crossbite Edge-to-Edge Bite Open Bite Over Jet Underjet Overbite
- 13. SDASHTI. CHS,2017 13 Labioversion: A tooth assumed a position labial to normal Linguoversion: Position lingual to normal Buccoversion: Position buccal to normal Supraversion: Elongated above the line of occlusion Tersoversion: Turned or rotated Infraversion: Depressed below the line of occlusion
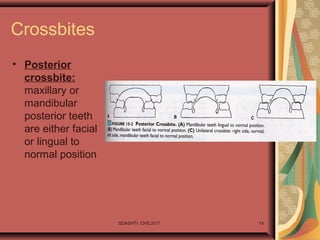
- 14. Crossbites • Posterior crossbite: maxillary or mandibular posterior teeth are either facial or lingual to normal position SDASHTI. CHS,2017 14
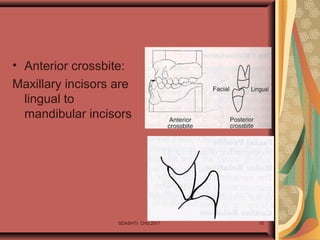
- 15. SDASHTI. CHS,2017 15 • Anterior crossbite: Maxillary incisors are lingual to mandibular incisors
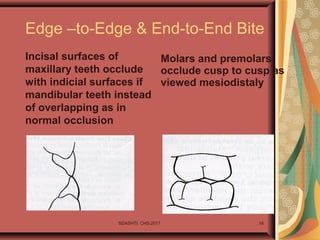
- 16. Edge –to-Edge & End-to-End Bite Incisal surfaces of maxillary teeth occlude with indicial surfaces if mandibular teeth instead of overlapping as in normal occlusion Molars and premolars occlude cusp to cusp as viewed mesiodistaly SDASHTI. CHS,2017 16
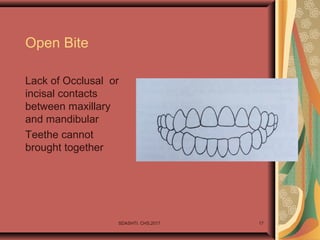
- 17. Open Bite Lack of Occlusal or incisal contacts between maxillary and mandibular Teethe cannot brought together SDASHTI. CHS,2017 17
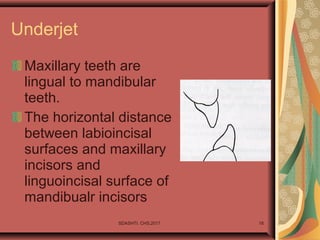
- 18. SDASHTI. CHS,2017 18 Underjet Maxillary teeth are lingual to mandibular teeth. The horizontal distance between labioincisal surfaces and maxillary incisors and linguoincisal surface of mandibualr incisors
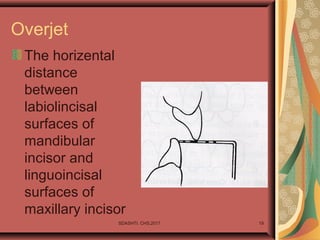
- 19. Overjet The horizental distance between labiolincisal surfaces of mandibular incisor and linguoincisal surfaces of maxillary incisor SDASHTI. CHS,2017 19
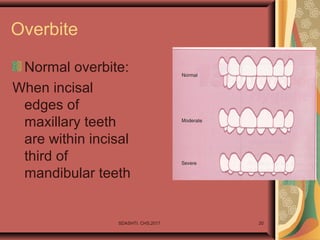
- 20. Overbite Normal overbite: When incisal edges of maxillary teeth are within incisal third of mandibular teeth SDASHTI. CHS,2017 20
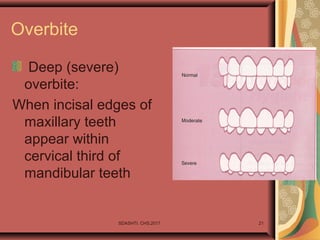
- 21. Overbite Deep (severe) overbite: When incisal edges of maxillary teeth appear within cervical third of mandibular teeth SDASHTI. CHS,2017 21
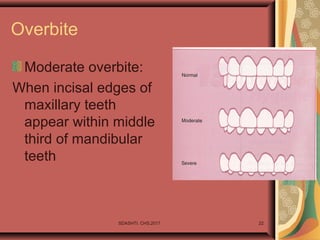
- 22. Overbite Moderate overbite: When incisal edges of maxillary teeth appear within middle third of mandibular teeth SDASHTI. CHS,2017 22
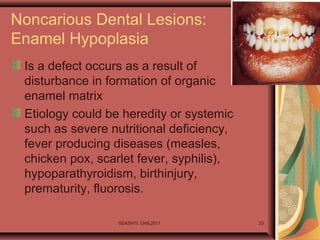
- 23. SDASHTI. CHS,2017 23 Noncarious Dental Lesions: Enamel Hypoplasia Is a defect occurs as a result of disturbance in formation of organic enamel matrix Etiology could be heredity or systemic such as severe nutritional deficiency, fever producing diseases (measles, chicken pox, scarlet fever, syphilis), hypoparathyroidism, birthinjury, prematurity, fluorosis.
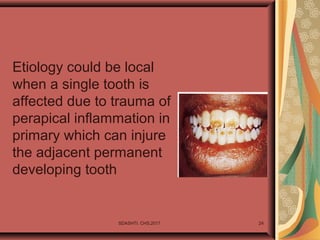
- 24. Etiology could be local when a single tooth is affected due to trauma of perapical inflammation in primary which can injure the adjacent permanent developing tooth SDASHTI. CHS,2017 24
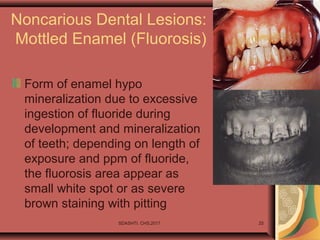
- 25. SDASHTI. CHS,2017 25 Noncarious Dental Lesions: Mottled Enamel (Fluorosis) Form of enamel hypo mineralization due to excessive ingestion of fluoride during development and mineralization of teeth; depending on length of exposure and ppm of fluoride, the fluorosis area appear as small white spot or as severe brown staining with pitting
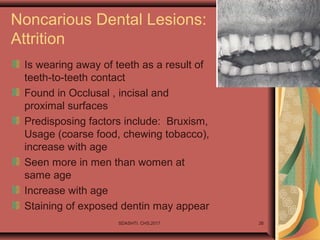
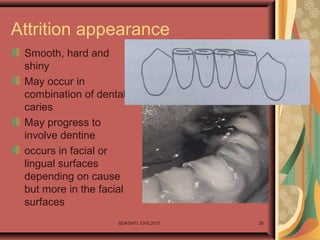
- 26. SDASHTI. CHS,2017 26 Noncarious Dental Lesions: Attrition Is wearing away of teeth as a result of teeth-to-teeth contact Found in Occlusal , incisal and proximal surfaces Predisposing factors include: Bruxism, Usage (coarse food, chewing tobacco), increase with age Seen more in men than women at same age Increase with age Staining of exposed dentin may appear
- 27. SDASHTI. CHS,2017 27 Noncarious Dental Lesions Erosion Is the loss of tooth substance by a chemical process that does not involve known bacterial action. Predisposing factors include chronic vomiting (bulimia, pregnancy), dietary (carbonated drinks, lemon juice) or idiopathic Usually involve several teeth
- 28. Attrition appearance Smooth, hard and shiny May occur in combination of dental caries May progress to involve dentine occurs in facial or lingual surfaces depending on cause but more in the facial surfaces SDASHTI. CHS,2017 28
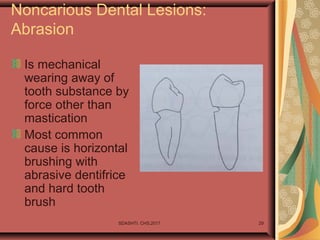
- 29. SDASHTI. CHS,2017 29 Noncarious Dental Lesions: Abrasion Is mechanical wearing away of tooth substance by force other than mastication Most common cause is horizontal brushing with abrasive dentifrice and hard tooth brush
- 30. Holding pens of pipe between teeth, usually people with this habit utilize same tooth Occupational causes such as carpenters, and dressmaker SDASHTI. CHS,2017 30
- 31. SDASHTI. CHS,2017 31 Noncarious Dental Lesions: Fractured teeth Trauma to face may involve fractured bones and teeth in addition to soft tissue injuries Caused by: Falls Blows while fighting Contact sports without mouth protectors Automobile, bicycle, and diving accidents