Introduction to Rhetoric
- 1. An introduction to key terms and elements. Note Taking Guide Rhetoric
- 2. We study rhetoric because: ïĻ it helps us to better appreciate appeals to our ethos, pathos, & logos. ÂĐ 2013 IndieReader
- 3. ïĻ it helps us to become more effective persuasive speakers and writers. ÂĐ Alex Cates
- 4. Rhetoric Defined ïĻ Rhetoric (n) - the art of effective expression (speaking & writing) and the persuasive use of language (Burton, 2007) George Doyle/Stockbyte/Getty Images
- 5. ïĻ Rhetoric requires understanding a fundamental division between what is communicated through language and how this is communicated. (Burton, 2007) ÂĐ 2010 Grip Limited
- 6. ïĻ Aristotle stated that an arguer must state a claim, or a proposition, and prove it. ïĻ Click Aristotle to learn more. ÂĐ Creative Commons
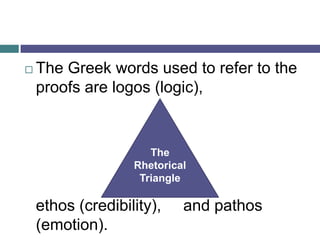
- 7. ïĻ The Greek words used to refer to the proofs are logos (logic), ethos (credibility), and pathos (emotion). The Rhetorical Triangle
- 8. Logos ïĻ Logical proof appeals to peopleâs reason, understanding, and common sense. (Weida & Stolley, 2013)
- 9. ïĻ Two main types of logos (logical proofs) are deduction and induction.
- 10. ïĪIncludes facts, reasons and opinions that are based on reality. ïĪExample: ïŪiHome ïŪCheerios ÂĐ iHome Audio
- 11. Ethos ïĻ The ethical appeal is based on the character, credibility, or reliability of the writer. (Weida & Stolley, 2013)
- 12. ïĪIncludes credible sources, accurate opposition, common ground between the writer and the audience. ïĪExample: ïŪGivenchy ïŪMacintosh ÂĐ Givenchy Paris
- 13. Pathos ïĻ Emotional appeal, appeals to the audienceâs needs, values, and emotional sensibilities. (Weida & Stolley, 2013)
- 14. ïĪIncludes personal accounts or interviews ïĪOnly use an emotional appeal if it supports the claim of an argument. ïĪExample: ïŪUMDNJ ïŪBC SPCA ÂĐ Copyright 2012 SGWMcGuggan
- 15. Karios ïĻ The opportune occasion for speech. (Burton, 2007) ÂĐ1996-2013 Madison Metropolitan School District
- 16. Audience ïĻ Rhetorical analysis always takes into account how an audience shapes the composition of a text or responds to it. (Burton, 2007) ÂĐ 2013 Entrepreneur Podcast Network
- 17. Decorum ïĻ One's words and subject matter must aptly fit together, to kairos, the audience, and the speaker. (Burton, 2007) ÂĐ 2013 Wikia, Inc
- 18. Practice Based on the each add determine: ïĻ Ethos, Pathos or Logos? ïĻ Whatâs the Karios? ïĻ Whoâs the audience? ïĻ Whatâs the decorum?
- 19. Scheme ïĻ A scheme is any artful deviation from the typical arrangement of words in a sentence (Burton, 2007)
- 20. ïĪ Words preserve their literal meaning, but are placed in a significant arrangement of some kind.
- 21. Active Voice ïĻ In a sentence using active voice, the subject of the sentence performs the action expressed in the verb. (Toadvine, Brizee, & Angeli, 2011)
- 22. Passive Voice ïĻ In a sentence using passive voice, the subject is acted upon; he or she receives the action expressed by the verb. (Toadvine, Brizee, & Angeli, 2011)
- 23. Active Voice versus Passive Voice ïĻ Active Voice- The boy hit the ball. ïĻ Passive Voice- The ball was hit by the boy. ÂĐ Copyright 2009-2013 real-world-physics-problems.com
- 24. Rhetoric uses Active Voice ïĻ This makes the meaning clear for readers, and keeps the sentences from becoming too complicated. (Toadvine, Brizee, & Angeli, 2011)
- 25. Works Cited ïĻ Burton, G. O. (2007, Feburary 26). Schemes and Tropes. Retrieved September 29, 2013, from Silva Rhetoricae: http://rhetoric.byu.edu/figures/Schemes%20and%20Tropes .htm ïĻ Toadvine, A., Brizee, A., & Angeli, E. (2011, July 13). Active and Passive Voice. Retrieved September 29, 2013, from Purdue Online Writing Lab: https://owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/539/1/ ïĻ Weida, S., & Stolley, K. (2013, March 11). Using Rhetorical Strategies for Persuasion. Retrieved September 29, 2013, from Perdue Online Writing Lab: https://owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/588/04/
Editor's Notes
- According to Aristotle, rhetoric is "the ability, in each particular case, to see the available means of persuasion." He described three main forms of rhetoric: Ethos, Logos, and Pathos
- When the mother reads the facts off the box she is appealing to reason.
- The Mac presents himself as a reliable source and shows the faults in the PCâs argument making the PC an uncredible source.
- Some say that there should be no appeals to emotion or attempts to arouse the emotions of the audience in an argument. The idea is that an argument should appeal only to reason.Emotional proofs (pathos) are appropriate in argument when the subject itself is emotional and when it creates strong feelings.
- Some say that there should be no appeals to emotion or attempts to arouse the emotions of the audience in an argument. The idea is that an argument should appeal only to reason.Emotional proofs (pathos) are appropriate in argument when the subject itself is emotional and when it creates strong feelings.-The music and images appeal to pathos because of the emotional response of the audience.