Intro to values and hofstede
- 1. Introduction to values and Hofstede CommunicationKnowledgeCenter@Outlook.com
- 2. Values: inside-out/ outside-in S x R Values of Values of Sender Receiver Express Link to own values: like/ dislike Values of Brand/ product/ service EFFECT Analyze what is expressed: semiotics CommunicationKnowledgeCenter Influenced by cultural values (and other factors) 2
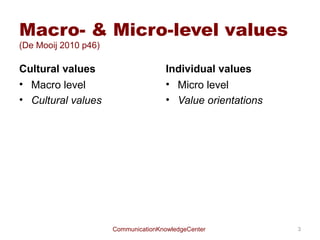
- 3. Macro- & Micro-level values (De Mooij 2010 p46) Cultural values ŌĆó Macro level ŌĆó Cultural values Individual values ŌĆó Micro level ŌĆó Value orientations CommunicationKnowledgeCenter 3
- 4. Influence of values on effect CommunicationKnowledgeCenter Values 4
- 5. Value: ŌĆó : ŌĆ£an enduring belief that one mode of conduct or end-state of existence is preferable to an opposing mode of conduct or end-state of existence.ŌĆØ(Rokeach 1973 in De Mooij 2010 p45) ŌĆó Examples of preferred alternatives: ŌĆō Clean ŌĆō dirty ŌĆō Happy ŌĆō sad ŌĆō Healthy ŌĆō sick (De Mooij 2010 p45) CommunicationKnowledgeCenter 5
- 6. Value system ŌĆó ŌĆ£learned organization of principles and rules to help one choose between alternatives, resolve conflicts, and make decisions.ŌĆØ(Rokeach 1973 in De Mooij 2010 p45) ŌĆó ŌĆ£In a value system, values are ordered in priority with respect to other values.ŌĆØ ŌĆó ŌĆ£For example, in North America, individual happiness is a value of high priority, (ŌĆ”) whereas in East Asia personal happiness has lower priority than perseverance and harmony.ŌĆØ (Rokeach 1973 in De Mooij 2010 p45) CommunicationKnowledgeCenter 6
- 7. Value priority, example North America 1. individual happiness 2. perseverance 3. harmony East Asia 1. perseverance 2. harmony 3. individual happiness CommunicationKnowledgeCenter 7
- 8. Target Market Incentive Statement (Schultz '96) ŌĆó To (user group), (name of brand) is the (product category) that (benefit of brand). ŌĆó To ambitious people, VSM is the toothpaste that prevents cavities and maintains clean, white teeth. ŌĆó Support: with fluoride & strong ŌĆó What consumer wants from product; psychographic attributes : security & self-confidence CommunicationKnowledgeCenter 8
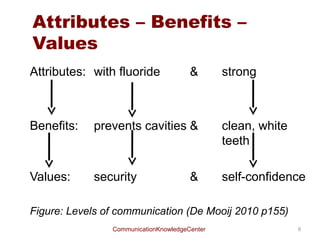
- 9. Attributes ŌĆō Benefits ŌĆō Values Attributes: with fluoride & strong Benefits: prevents cavities & clean, white teeth Values: security & self-confidence Figure: Levels of communication (De Mooij 2010 p155) CommunicationKnowledgeCenter 9
- 10. About values (De Mooij 2010 p46) ŌĆó At age of 10 most children have their basic value systems firmly in place. ŌĆó Learned implicitly (not consciously). ŌĆó Describe what people in general think the world ought to be. ŌĆó Are absolute (freedom, not a little bit of freedom). ŌĆó More stable than attitudes. ŌĆó We are not aware of our values; they operate like an automatic pilot. Knowledge ’āĀ Attitude ’āĀ Behavior Value CommunicationKnowledgeCenter 10
- 11. Assumptions about values (De Mooij 2010 p46) a) Total number of values that a person possesses is relatively small. b) All people everywhere possess the same values to different degrees. c) Antecedents of human values can be traced to culture, society, and its institutions. See shortlist of value priorities See Maslow pyramid of needs See Cultural Values ŌĆō Value Orientations CommunicationKnowledgeCenter 11
- 12. MaslowŌĆÖs hierarchy of needs CommunicationKnowledgeCenter 12
- 13. Instrumental values: Rokeach ŌĆś73 in: De Mooij ŌĆś98 p97 1 Ambitious 2 Broad-minded 3 Capable 4 Cheerful 5 Clean 6 Courageous 7 Forgiving 8 Helpful 9 Honest 10 Imaginative 11 Independent 12 Intellectual 13 Logical 14 Loving 15 Obedient 16 Polite 17 Responsible 18 Self-controlled CommunicationKnowledgeCenter 13
- 14. Terminal values: Rokeach ŌĆś73 in: De Mooij ŌĆś98 p97 1 A comfortable life 2 An exciting life 3 A sense of accomplishment 4 A world at peace 5 A world of beauty 6 Equality 7 Family security 8 Freedom 9 Happiness 10 Inner harmony 11 Mature love 12 National security 13 Pleasure 14 Salvation 15 Self-respect 16 Social recognition 17 True friendship 18 Wisdom CommunicationKnowledgeCenter 14
- 15. Onion model of culture = Expressions of values : observable CommunicationKnowledgeCenter 15
- 16. Hofstede ŌĆó Engineer ŌĆó Worked for IBM (HR) ŌĆó Tried to find values in different cultures that he could compare CommunicationKnowledgeCenter 16
- 17. Exercise I choose for: I choose for: Make myself happy Make my family happy CommunicationKnowledgeCenter 17
- 18. Exercise Individualist Collectivist Make myself happy Make my family happy CommunicationKnowledgeCenter 18
- 19. Individualism ŌĆō Collectivism ŌĆó Looks at whether the interests of the group or the interests of the individual prevail in making choices. ŌĆō Individualism ŌĆō IndividualŌĆÖs interests prevail. ŌĆō Collectivism ŌĆō GroupŌĆÖs interests prevail. CommunicationKnowledgeCenter 19
- 20. Exercise I choose for: I choose for: Assertiveness Quality of life Success Personal relationships Competition Caring Career possibilities Better for my family We will tell you our qualities You will notice our qualities CommunicationKnowledgeCenter 20
- 21. Exercise Masculine values Feminine values Assertiveness Quality of life Success Personal relationships Competition Caring Career possibilities Better for my family We will tell you our qualities You will notice our qualities CommunicationKnowledgeCenter 21
- 22. Masculinity/Femininity ŌĆó The degree to which members of a given culture consider positive typically masculine or feminine traits. ŌĆō Masculinity : Value competition, ŌĆ£positive aggressionŌĆØ material gains ŌĆō Femininity: Value cooperation, helping position, affective relationships gains. CommunicationKnowledgeCenter 22
- 23. Exercise I choose for: I choose for: Adventure Safety I always try new things to eat. I only eat what I know. CommunicationKnowledgeCenter 23
- 24. Exercise Low uncertainty avoidance High uncertainty avoidance Adventure Safety I always try new things to eat I only eat what I know. . CommunicationKnowledgeCenter 24
- 25. Uncertainty Avoidance ŌĆó How do cultures handle their anxiety regarding the unknown. ŌĆō High uncertainty avoidance: unknown is seen as threatening, thus there is a strong desire to minimize uncertainty ŌĆō seen as dangerous. ŌĆō Low uncertainty avoidance: unknown is seen as manageable provoking less anxiety. CommunicationKnowledgeCenter 25
- 26. Exercise I choose for: I choose for: I do what my boss tells me what to do If I donŌĆÖt agree with my boss I will tell him The teacher knows every thing I will judge whether I believe what the teacher tells me CommunicationKnowledgeCenter 26
- 27. Exercise High power distance Low power distance I do what my boss tells me what to do If I donŌĆÖt agree with my boss I will tell him The teacher knows every thing I will judge whether I believe what the teacher tells me CommunicationKnowledgeCenter 27
- 28. Power Distance ŌĆó How people in a given culture handle inequality and differences in power. ŌĆō High Power Distance: Inequality is assumed to be normal and just for a functioning society. ŌĆō Low Power Distance: Inequality is considered undesirable. CommunicationKnowledgeCenter 28
- 29. Exercise I choose for: I choose for: If I earn money, I spend it on nice things. If I earn money, I safe a considerable amount for later. I have to act now. DonŌĆÖt do stupid things and eventually everything will be OK. CommunicationKnowledgeCenter 29
- 30. Exercise Short term orientation Long term orientation If I earn money, I spend it on nice things. If I earn money, I safe a considerable amount for later. I have to act now. DonŌĆÖt do stupid things and eventually everything will be OK. CommunicationKnowledgeCenter 30
- 31. HofstedeŌĆÖs 5 Dimensions 1. Collectivism ŌĆō Individualism 2. Femininity ŌĆō Masculinity 3. Uncertainty Avoidance (High/Low) 4. Power Distance (High/Low) 5. Long-term orientation ŌĆō Short-term orientation http://www.geert-hofstede.com/ CommunicationKnowledgeCenter 31
- 33. Think from perspective of organization & of consumer OrganizationŌĆÖs problem: ŌĆō Need more money to pay own employees, suppliers, etc. ŌĆō We want to help all refugees, but we help only a few. Communication problem: ŌĆō Change Know / Feel / Do of receiver. (= Domino-model of communication effects) Problem of receiver ŌĆō Fulfilling Wants & Needs (MaslowŌĆÖs Pyramid) ŌĆō Influenced by values CommunicationKnowledgeCenter 33
Editor's Notes
- #4: Individuals have values. If groups of individuals share the same values, this group has this values. Example of such a group: culture, society, organization. Value orientation that becomes manifest in the actions of a group is a cultural value.
- #5: Value can prevent attitude from influencing behavior.
- #7: ? Why are value systems relevant for influencing people? = Helps communication professionals understand WHY people choose something. => construct message that will help to develop a positive attitude (associated with value). ? Do you recognize these value priorities in USA & East Asia? Value System: several values, some values are more relevant than others.
- #8: ? If you had to sell toothpaste to North Americans, what would be your message? SEE NEXT SLIDES = VSM makes you happy. ? Idem: East Asia? = VSM is good for your long lasting relationships.
- #11: More stable than attitudes. Attitude towards brand can change, but your values stay the same.
- #12: Value priorities: SLIDE USA ŌĆō Asia Individuals have values. If groups of individuals share the same values, this group has this values. Example of such a group: culture, society, organization.
- #13: Research can be done in order to find out which needs your target audience has. In different cultures the order might be different. ? If you know the needs, what can you do with it in order to construct a message that will influence the target audience? = focus on attributes & benefits & values that belong to what the target audience needs PLUS that can be associated with the product.
- #16: Symbols: most superficial: language, clothing, food. => Speaking English does not make you British : you will still have the Dutch bluntness / Asian focus on perseverance & harmony / etc. Wearing baseball-cap & baggy trousers does not make you a Brooklyn hoody. a woman told that she is very intercultural, because she goes to a Chinese restaurant, twice a year. Heroes: teenagers try to find identity and put posters on the room wall of Tupac / Notorios BIG / Rihanna / Dennis Bergkamp / etc. Later: picture of husband / wife/ children / Obama / etc. Rituals: bring coffee for roommates / celebrate birthday To what ŌĆśtribeŌĆÖ do you belong? We need a CODE in order to understand these expressions: if you do not belong to this culture you will not fully understand all of them : different Realms Of Understanding/ Field of Experience => you will feel excluded, members of the (sub) culture will feel a strong insider feeling. We vs. They. PICTURE Snoop Dogg = Hero Symbols, what do they mean?: boxing dress ; ? What does the logo mean? ; jewellery; small cigar? Ritual: hand shake ; smoking cigar ? What do all these Symbols & Rituals mean? What values do they represent? ? What values does Snoop Dogg represent? = street values: Afro Americans rule ; money is most important ; drugs and violence are acceptable (because they are needed to earn much money). => Versus values that the dominant white society tries to enforce. (peace, harmony, long-term relationships; by education, good job).
- #18: Stand up. Walk to the side of the class-room that fits your choice.
- #19: Stand up. Walk to the side of the class-room that fits your choice.
- #21: Stand up. Walk to the side of the class-room that fits your choice.
- #22: ? Does this correlate with gender? ? Cultural background?
- #24: Stand up. Walk to the side of the class-room that fits your choice.
- #25: Stand up. Walk to the side of the class-room that fits your choice.
- #27: Stand up. Walk to the side of the class-room that fits your choice.
- #28: Stand up. Walk to the side of the class-room that fits your choice.
- #30: Stand up. Walk to the side of the class-room that fits your choice.
- #31: Stand up. Walk to the side of the class-room that fits your choice.
- #33: A person is not just his/her nationality! People are also influenced by: their family culture, their religion, their class-mates, their team-mates, etc.
- #34: Key for solving the problem is that you will construct the right message. The message will be constructed in the basis of the BRIEFING. (Also you will have to think about the media by which you will disseminate the message: S ’āĀ [x] ’āĀ R x = message ; [] = medium