Introducing User Experience Design
- 1. Introducing User Experience design By: Claire Sherrington
- 2. What I am talking about today ŌŚÅ What is User Experience design ŌŚÅ Why it is important ŌŚÅ The moving parts of User Experience design ŌŚÅ New challenges ŌŚÅ What about.... ?
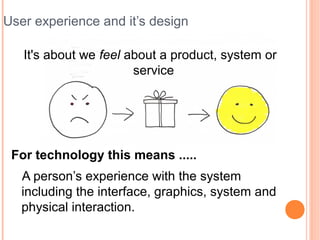
- 3. User experience and itŌĆÖs design It's about we feel about a product, system or service For technology this means ..... A personŌĆÖs experience with the system including the interface, graphics, system and physical interaction.
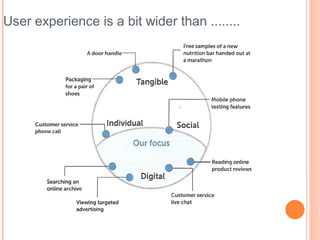
- 4. User experience is a bit wider than ........
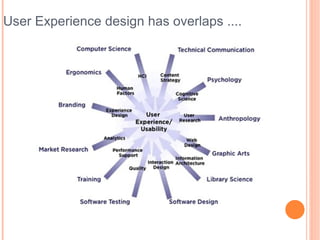
- 5. User Experience design has overlaps ....
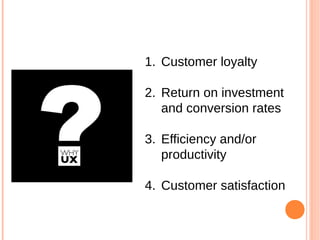
- 6. 1. Customer loyalty 2. Return on investment and conversion rates 3. Efficiency and/or productivity 4. Customer satisfaction
- 7. Principles ŌŚÅ Understandable ŌŚÅ Actionable ŌŚÅ Engaging ŌŚÅ Efficient
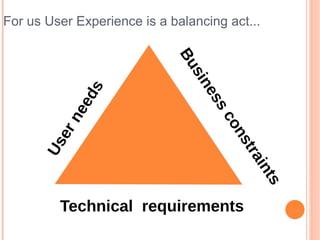
- 8. For us User Experience is a balancing act... Bu sin ds es ee sc n on er st Us ra in ts Technical requirements
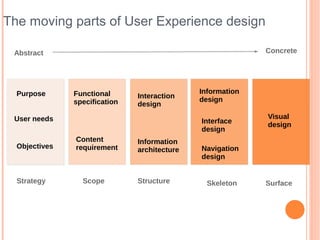
- 9. The moving parts of User Experience design Abstract Concrete Purpose Functional Information Interaction design specification design User needs Visual Interface design design Content Information Objectives requirement architecture Navigation design Strategy Scope Structure Skeleton Surface
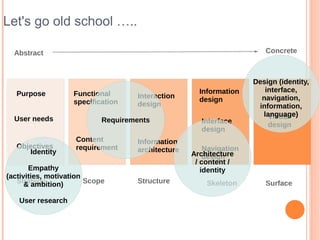
- 10. Let's go old school ŌĆ”.. Abstract Concrete Design (identity, Information interface, Purpose Functional Interaction design navigation, specification design information, language) Visual User needs Requirements Interface design design Content Information Objectives requirement architecture Navigation Identity Architecture design / content / Empathy identity (activities, motivation Strategy & ambition) Scope Structure Skeleton Surface User research
- 11. New kettle of fish? ŌŚÅ Responsive design; how does this impact process? ŌŚÅ Internet of things....... ŌŚÅ What about accessibility needs?
- 12. What about ? Usability: ŌŚÅ Paper prototyping/ walk-though ŌŚÅ Remote testing ŌŚÅ Observation labs ŌŚÅ Focus groups? Service design: ŌŚÅ Experience maps ŌŚÅ Dependence on technology ŌŚÅ End to end design ŌŚÅ The way forward....
- 13. Conclusion ŌŚÅ Designing your experience ŌŚÅ Happy customers ŌŚÅ There are many steps to design a user's experience ŌŚÅ There are challenges
Editor's Notes
- On Thursday the 8th Nov is World Usability Day. I have been asked to brief our staff ( I work Catalyst IT) at the monthly gathering about what is User Experience design, why it is important and what are the parts for User Experience design.
- Include things that the user can hear / touch and smell User Experience design fully encompasses traditional Human-Computer Interaction (HCI) design and extends it by addressing all aspects of a product or service as perceived by users.
- Human-Computer Interaction (HCI) design
- 1 Customer Loyalty In the simplest terms possible, if your users have a bad experience on your website, they wonŌĆÖt come back 2. Return on Investment and Conversion Rates Having a really good user experience ensures that your company gets a return on its investment 3. Efficiency and/or Productivity A great user experience improves efficiency as well ŌĆō by either helping your users to do things faster or by helping them make fewer mistakes 4. Customer satisfaction Your customers are your users. When it is easy, pleasant and natural for users to be able to achieve a given task, users are likely to do the task more often. User adoption of solution or change mngt
- The importance of user experience, how will a real user feel after interacting with the software, website, animation, design or graphics created by the designers, how usability can bring a smile to the user; these questions were raised which evoked thought provoking responses from the students.
- Jess Garth in the early 2000s USER NEEDS Goal: To gather external derived goals for the site. How: Identified through user research Techniques: User interviews/focus groups Observes the users at work Surveys Usability testing ( existing solution) Outputs: Affinity diagramming Personas OBJECTIVE & PURPOSE Goal: To gather business, creative, or other internally derived goals/purpose for the site. How: workshops & information gathering Techniques: Met with project stakeholders Met with the customer facing teams Read SOI or strategies documents FUNCATIONAL SPEC Goal: To gather the "feature set". How: workshops/interview/heuristic analysis. Build on previous outputs. Outputs: Detailed requirements documentation UML Diagrams (structure - class/object/component or behaviour - user case/sequence/ activity) CONTENT REQS Goal: To gather the needs of the content. How: Triangulation requirements & content strategy & user research Outputs: Detailed requirements documentation UML workflow/activity/sequence diagrams User case descriptions & diagrams IA Information architecture is the art and science of structuring and organizing the information in products and services, supporting usability and findability. Goal: To develop the structural design of the information space to facilitate intuitive access to content How: Information gathering & collation Techniques: Analytic reviews Card sorting Competitive review Outputs: Site map / navigation model Content model ( content specification ) INFORMATION DESIGN Goal: To design the presentation of information to facilitate understanding INTERACTION DESIGN There are many key factors to understanding Interaction Design and how it can enable a pleasurable end user experience. It is well recognized that building great user experience requires interaction design to play a pivotal role in helping define what works best for the users. Goal: To develop the application flows to facilitate user tasks How: Model the user actions and trigger required. Balance with the user needs(cases) & the given technology Technique: Use user cases to design. Talk to users. Prototyping ? Outputs: Flow diagrams Storyboarding Annotated wireframes UML behaviour diagrams INTERFACE DESIGN Goal: To design of interface elements to facilitate user interface with functionality How: Balance the interaction design against functional specification. And remember your users ! Technique: Iteration design. Test the usability Outputs: Prototyping Mockups NAVIGATION DESIGN Goal: To design the visual treatment of text, graphic page elements and navigational components. How: Analysis the height & depth of site. Review the user search needs. Outputs: Prototyping Design guideline VISUAL DESIGN Visual design, also commonly known as graphic design, communication design or visual communication, represents the aesthetics or ŌĆ£look-and-feelŌĆØ of the front end of any User Interface. Graphic treatment of interface elements, such as the ŌĆ£lookŌĆØ in the term look- and-feel is often perceived as the visual design
- Jess Garth in the early 2000s
- Though User Experience Design is closely allied with Usability Testing and other User-Centered Design methods, which focus on human performance enhancement, one of its distinguishing aspects is inclusion of emotional aspects of human experience. E.g. happiness as a worthy pursuit in itself
- This event has inspire to share something is important to me and that is user experience design. My objective for this presentation is for you to recognise and appreciate an user experience and the place for user experience design in our development projects.