Introduction about Tablets Dosage form.pptx
- 2. What is Tablet??? ŌĆó Tablets may be defined as solid pharmaceutical dosage forms containing drug substances prepared either by compression or molding methods. ŌĆó Although it is possible to manufacture in a wide range of shape, official tablets are defined as circular sizes with either flat or convex faces.
- 3. Advantages of Tablets 1.Large scale manufacturing is feasible in comparison to other dosage forms. Therefore, economy can be achieved. 2. Accuracy of dose is maintained since tablet is a solid unit dosage form. 3. Tailor made release profile can be achieved. 4. Longer expiry period and minimum microbial spillage owing to lower moisture content. 5. As tablet is not a sterile dosage form, stringent environmental conditions are not required in the tablet department. 6. Ease of packaging (blister or strip) and easy handling.
- 4. Disadvantages of tablets 1. Drugs not absorbed or extensively degraded into GI tract cannot be made into tablets. 2. It is difficult to convert a high dose poorly compressible API into a tablet of suitable size for human use. 3. Difficult to formulate a drug with poor wettability, slow dissolution into a tablet. 4. Slow onset of action as compared to parenterals, liquid orals and capsules. 5. The amount of liquid drug (e.g. Vitamin E, Simethicone) that can be trapped into a tablet is very less. 6. Difficult to swallow for kids, terminally ill and geriatric patients. 7. Patients undergoing radiotherapy cannot swallow tablet.
- 5. Essential qualities of a good tablet They should be accurate and uniform in weight. The drugs should be uniformly distributed throughout the tablets. The size and shape should be reasonable for easy administration. The tablets should not be too hard that it may not be disintegrate in the stomach. After administration it should disintegrate readily. They should be attractive in appearance. They should not have any manufacturing defects like cracking, capping or discoloration.
- 6. Absorption of drug from tablets ŌĆó The most common mechanism of absorption for drugs is passive diffusion. ŌĆó This process can be explained through the Fick law of diffusion, in which the drug molecule moves according to the concentration gradient from a higher drug concentration to a lower concentration until equilibrium is reached.
- 7. Tablet excipients ŌĆó Compressed tablets usually consist of active medicaments mixed with a number of inert substances known as excipient or additives i.e. all non ŌĆō drug components of a formula are termed excipients or additives. ŌĆó Although these additives are termed as inert but they have a great influence on stability, bioavailability and the process by which the dosage forms are prepared.
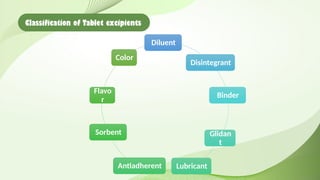
- 8. Classification of Tablet excipients Diluent Disintegrant Binder Glidan t Lubricant Antiadherent Sorbent Flavo r Color
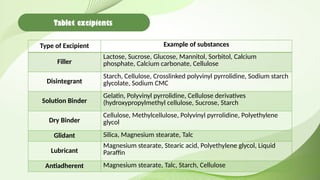
- 9. Tablet excipients Type of Excipient Example of substances Filler Lactose, Sucrose, Glucose, Mannitol, Sorbitol, Calcium phosphate, Calcium carbonate, Cellulose Disintegrant Starch, Cellulose, Crosslinked polyvinyl pyrrolidine, Sodium starch glycolate, Sodium CMC Solution Binder Gelatin, Polyvinyl pyrrolidine, Cellulose derivatives (hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose, Sucrose, Starch Dry Binder Cellulose, Methylcellulose, Polyvinyl pyrrolidine, Polyethylene glycol Glidant Silica, Magnesium stearate, Talc Lubricant Magnesium stearate, Stearic acid, Polyethylene glycol, Liquid Paraffin Antiadherent Magnesium stearate, Talc, Starch, Cellulose
- 10. Tablet Manufacturing ŌĆó Tablets are prepared by forcing particles into close proximity to each other by powder compression, which enables the particles to cohere into a porous, solid specimen of defined geometry. ŌĆó The compression takes place in a die by the action of two punches, the lower and the upper, by which the compressive force is applied. ŌĆó Powder compression is defined as the reduction in volume of a powder owing to the application of a force.
- 11. Tablets Types ŌĆó Swallowable tablets ŌĆó The most common types of tablets are swallowed whole. These tablets dis-integrate and release their contents in the GI tract. ŌĆó Effervescent tablets ŌĆó These tablets are formulated to allow dissolution or dispersion in water prior to administration and should not be swallowed whole. In addition to the DS, these tablets contain sodium carbonate or bicarbonate and an organic acid such as tartaric acid.
- 12. Tablets Types ŌĆó Sugar Coated Tablets ŌĆó The compressed tablets having a sugar coating are called sugar coated tablets. ŌĆó It masks the bitter and upleasant odour and improves the taste of the tablets. ŌĆó Film Coated Tablets ŌĆó Film Coated Tablets are compressed tablets having a thin layer of polymer capable of forming a skin like film
- 13. Tablets Types ŌĆó Enteric Coated Tablets ŌĆó These are compressed tablets meant for administration by swallowing and are designed to bypass the stomach and get disintegrated in the intestines only. ŌĆó Sustained Release Tablets ŌĆó Sustained release tablets are designed to achieve prolonged therapeutic effect by continously releasing medication over an extended period of time after the administration of a single dose.
- 14. References ŌĆó AnselŌĆÖs Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms and Drug Delivery System ŌĆó AultonŌĆÖs Pharmaceutics- The science of Dosage Form