IGCSE Biology 0610 - Introduction to Biology - Characteristics of living organisms - Binomial Nomenclature - Kingdoms
- 2. ŌŚÅ Biology is the science of life. Its name derives from the Greek words "bios" (life) and "logos" (study). ŌŚÅ Biologists study the structure, function, growth, origin, evolution and distribution of living organisms. ŌŚÅ The study of life and all living organisms along with their characteristics, environment and evolution
- 3. Characteristics of living organisms Living organisms have the following characteristics in common: ŌŚÅ Movement - they can move and change their position. ŌŚÅ Reproduction ŌĆō they can make more of the same kind of organism as themselves. ŌŚÅ Sensitivity ŌĆō they can detect or sense stimuli and respond to them. ŌŚÅ Growth - they can permanently increase their size or dry mass by increasing the number or size of their cells. ŌŚÅ Respiration ŌĆō they can create chemical reactions that break down nutrient molecules in living cells to release energy. ŌŚÅ Excretion ŌĆō they can excrete toxic materials, waste products of metabolism, and excess substances ŌŚÅ Nutrition - they can take in and absorb nutrients such as organic substances and mineral ions. These nutrients contain the raw materials or energy needed for growth and tissue repair.
- 4. The Binomial System The Binomial System of scientifically naming organisms was developed by Carolus Linnaeus of Sweden. It consists of the organismŌĆÖs Genus and species name, and thus it is called as Binomial. It consists of 7 levels: Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species
- 5. Now, letŌĆÖs take up a simple example: Humans Kingdom- Animal Phylum- Vertebrates Class- Mammalia Order- Primate Family- Hominidae Genus- Homo Species- Sapiens
- 6. Key definitions A species is a group of organisms that can reproduce to produce fertile offspring. The binomial systemis an internationally agreed system in which the scientific name of an organism is made up of two parts showing the genus and the species Rules for writing scientific names: The first letter of the genus is ALWAYS capitalised e.g. Homo sapiens The first letter of the species is NEVER capitalised Scientific names of organisms are always italicized or underlined
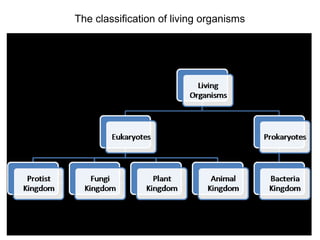
- 7. The classification of living organisms
- 8. ŌŚÅ Protoctista: are organisms with a nucleus, and many flexible organelles amongst their species (for example, some have chloroplasts and cell walls like plants and some like animal cells without these distinguishing characteristics). Their main characteristics include: ŌŚÅ ŌŚÅ unicellular or multi-cellular bodies ŌŚÅ cells with or without cell wall and chloroplasts ŌŚÅ some species are autotrophic, rest are heterotrophic ŌŚÅ all species have cells with nucleus
- 9. ŌŚÅ Fungi: are organisms which do not have chlorophyll, thus are heterotrophic and feed on dead organic matter parasitically. The most common known is the edible mushroom; others include fungi causing diseases like athleteŌĆÖs foot, ringworm etc. Their characteristics include: ŌŚÅ Multicellular bodies (very few are unicellular) ŌŚÅ Have nuclei ŌŚÅ Reproduce by spore production ŌŚÅ Are heterotrophic ŌŚÅ DonŌĆÖt have chloroplasts ŌŚÅ Feed by parasitic or saprophytic means on organic dead matter
- 10. ŌŚÅ The Plant Kingdom ŌŚÅ ŌŚÅ Phylum Angiosperm: ŌŚÅ Have root, stem and leaves ŌŚÅ Have xylem and phloem ŌŚÅ Reproduce by seed production ŌŚÅ Seeds are produced inside the ovary of the flower ŌŚÅ Phloem: Transports sugar ŌŚÅ Xylem: Transports water and minerals
- 11. Viruses is a small infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of other organisms. Viruses can infect all types of life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Entirely microscopic Consisting of a single nucleic acid surrounded by a protein coat Capable of replication only within living cells of bacteria, animals or plants. Example of Viruses: Human Immunodeficiency Virus, Tuberculosis, etc. Prokaryotes Bacteria are prokaryotic and unicellular. they have cell walls and circular DNA called plasmids. They are Heterotrophs or Autotrophs. Example: L.bulgaricus