Introduction to Computer Science and hardware.ppt
- 1. WELCOME TO THE PRESENTATION ON INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTERS NOT IN 2022 1
- 2. WHAT IS A COMPUTER? A computer is an electronic device, operating under the control of instructions (software) stored in its own memory unit, that can accept data (input), manipulate data (process), and produce information (output) from the processing. Generally, the term is used to describe a collection of devices that function together as a system. 2
- 3. HISTORY OF COMPUTERS Can be divided into generations. ’éä First Generation (1945 ŌĆō 1954) ’éä Second Generation (1955 ŌĆō 1964) ’éä Third Generation (1965 ŌĆō 1974) ’éä Fourth Generation (1975 - ) ’éä Fifth Generation ’éä PicŌĆÖs 3
- 4. TYPES OF COMPUTERS On the basis of Computing Power & Size: ’éä Laptop / Palmtop ’éä Micro Computer / Desktop ’éä Mini Computer / Mainframe ’éä Super Computer 4
- 5. DEVICES THAT COMPRISE A COMPUTER SYSTEM 5 Printer (output) Monitor (output) Speaker (output) Scanner (input) Mouse (input) Keyboard (input) System unit (processor, memoryŌĆ”) Storage devices (CD-RW, Floppy, Hard disk, zip,ŌĆ”)
- 6. WHAT DOES A COMPUTER DO? Computers can perform four general operations, which comprise the information processing cycle. ’ü« Input ’ü« Process ’ü« Output ’ü« Storage 6
- 7. DATA AND INFORMATION ’éä All computer processing requires data, which is a collection of raw facts, figures and symbols, such as numbers, words, images, video and sound, given to the computer during the input phase. ’éä Computers manipulate data to create information. Information is data that is organized, meaningful, and useful. ’éä During the output Phase, the information that has been created is put into some form, such as a printed report. ’éä The information can also be put in computer storage for future use. 7
- 8. WHY IS A COMPUTER SO POWERFUL? ’éäThe ability to perform the information processing cycle with amazing speed. ’éäReliability (low failure rate). ’éäAccuracy. ’éäAbility to store huge amounts of data and information. ’éäAbility to communicate with other computers. 8
- 9. HOW DOES A COMPUTER KNOW WHAT TO DO? ’éä It must be given a detailed list of instructions, called a compute program or software, that tells it exactly what to do. ’éä Before processing a specific job, the computer program corresponding to that job must be stored in memory. ’éä Once the program is stored in memory the compute can start the operation by executing the program instructions one after the other. 9
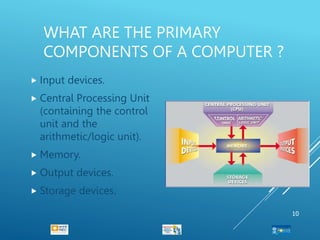
- 10. WHAT ARE THE PRIMARY COMPONENTS OF A COMPUTER ? ’éä Input devices. ’éä Central Processing Unit (containing the control unit and the arithmetic/logic unit). ’éä Memory. ’éä Output devices. ’éä Storage devices. 10
- 12. THE KEYBOARD The most commonly used input device is the keyboard on which data is entered by manually keying in or typing certain keys. A keyboard typically has 101 or 105 keys. 12
- 13. THE MOUSE Is a pointing device which is used to control the movement of a mouse pointer on the screen to make selections from the screen. A mouse has one to five buttons. The bottom of the mouse is flat and contains a mechanism that detects movement of the mouse. 13
- 14. THE CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT The central processing unit (CPU) contains electronic circuits that cause processing to occur. The CPU interprets instructions to the computer, performs the logical and arithmetic processing operations, and causes the input and output operations to occur. It is considered the ŌĆ£brainŌĆØ of the computer. 14
- 15. MEMORY Memory also called Random Access Memory or RAM (temporary memory) is the main memory of the computer. It consists of electronic components that store data including numbers, letters of the alphabet, graphics and sound. Any information stored in RAM is lost when the computer is turned off. Read Only Memory or ROM is memory that is etched on a chip that has start-up directions for your computer. It is permanent memory. 15
- 16. OUTPUT DEVICES Output devices make the information resulting from the processing available for use. The two output devices more commonly used are the printer and the computer screen. The printer produces a hard copy of your output, and the computer screen produces a soft copy of your output. 17
- 17. STORAGE DEVICES Auxiliary storage devices are used to store data when they are not being used in memory. The most common types of auxiliary storage used on personal computers are floppy disks, hard disks and CD-ROM drives. 18
- 18. FLOPPY DISKS A floppy disk is a portable, inexpensive storage medium that consists of a thin, circular, flexible plastic disk with a magnetic coating enclosed in a square-shaped plastic shell. 19
- 19. ’éä The diskŌĆÖs storage locations are divided into pie- shaped sections called sectors. ’éä A sectors is capable of holding 512 bytes of data. ’éä A typical floppy stores data on both sides and has 80 tracks on each side with 18 sectors per track. 21
- 20. HARD DISKS ’éä Another form of auxiliary storage is a hard disk. A hard disk consists of one or more rigid metal plates coated with a metal oxide material that allows data to be magnetically recorded on the surface of the platters. ’éä The hard disk platters spin at a high rate of speed, typically 5400 to 7200 revolutions per minute (RPM). ’éä Storage capacites of hard disks for personal computers range from 10 GB to 120 GB (one billion bytes are called a gigabyte). 22
- 21. COMPACT DISCS ’éä A compact disk (CD), also called an optical disc, is a flat round, portable storage medium that is usually 4.75 inch in diameter. ’éä A CD-ROM (read only memory), is a compact disc that used the same laser technology as audio CDs for recording music. In addition it can contain other types of data such as text, graphics, and video. ’éä The capacity of a CD-ROM is 650 MB of data. 23
- 22. ADVANTAGES OF USING COMPUTERS ’éä Speed: Computers can carry out instructions in less than a millionth of a second. ’éä Accuracy : Computers can do the calculations without errors and very accurately. ’éä Diligence : Computers are capable of performing any task given to them repetitively. ’éä Storage Capacity : Computers can store large volume of data and information on magnetic media. 24
- 23. COMPUTER SOFTWARE Computer software is the key to productive use of computers. Software can be categorized into two types: ’ü« Operating system software ’ü« Application software. 25
- 24. OPERATING SYSTEM SOFTWARE Operating system software tells the computer how to perform the functions of loading, storing and executing an application and how to transfer data. Today, many computers use an operating system that has a graphical user interface (GUI) that provides visual clues such as icon symbols to help the user. Microsoft Windows 98 is a widely used graphical operating system. DOS (Disk Operating System) is an older but still widely used operating system that is text-based. 26
- 25. OPERATING SYSTEM FUNCTION ’ā╝ File Management ’ā╝ Memory Management ’ā╝ Process Management ’ā╝ Device Management 27
- 26. APPLICATION SOFTWARE Application Software consists of programs that tell a computer how to produce information. Some of the more commonly used packages are: ’ü« Word processing ’ü« Electronic spreadsheet ’ü« Database ’ü« Presentation graphics 28
- 27. WORD PROCESSING ’éä Word Processing software is used to create and print documents. A key advantage of word processing software is that users easily can make changes in documents. 29
- 28. ELECTRONIC SPREADSHEETS ’éä Electronic spreadsheet software allows the user to add, subtract, and perform user-defined calculations on rows and columns of numbers. These numbers can be changed and the spreadsheet quickly recalculates the new results. 30
- 29. DATABASE SOFTWARE ’éä Allows the user to enter, retrieve, and update data in an organized and efficient manner, with flexible inquiry and reporting capabilities. 31
- 30. PRESENTATION GRAPHICS ’éä Presentation graphic software allows the user to create documents called slides to be used in making the presentations. Using special projection devices, the slides display as they appear on the computer screen. 32
- 31. NETWORKING ’éä A Computer Network is interconnection of Computers to share resources. ’éä Resources can be : Information, Load, Devices etc. 33
- 32. TYPES OF NETWORKS On the basis of Size: ’éäLocal Area Network (LAN) Its a network of the computers locally i.e. in one room, one building. ’éäWide Area Network (WAN) Its a network of the computers spread widely geographically. 34
- 33. BENEFITS OF COMPUTER NETWORKS ’éä Information Sharing ’éä Device Sharing ’éä Load Sharing ’éä Mobility ’éä Fast Communication ’éä Anywhere Anytime Banking 35
- 34. A LOOK INSIDEŌĆ” ’éä Identify all the major components: ’éä Power Supply ’éä Motherboard ’éä Memory ’éä Card Slots ’éä Cards (sound, video, network) ’éä CPU, heatsink and fan ’éä Drives (floppy, hard and CD-ROM) 36
- 35. THE NEW TECHNOLOGY ’éä A.I. is the future? What is this? 37






































































![DT Presentation[1].pptxeffsffewfwefewfewefefeef](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/dtpresentation1-250404175210-289fff92-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)






