Introduction To Ethical Hacking
- 1. Introduction to Ethical Hacking BY: TEAM CEH
- 2. O verview 1.Introduction 2.Types of Hackers 3.Purpose Of Hacking 4.Hacking Methodology 5.Hacking Techniques 6.How to get rid of? 7.References
- 3. What is Hacking ? ? Hacking is the art of finding solutions to real life problems. ? The word ˇ° Hack ˇ° is not directly related to computers.
- 4. Hacking and Computers ? The concept of hacking entered the computer culture at the MIT University in the 1960s. ? There are two kinds of students 1. Tools 2. Hackers
- 5. 1. Tools ? A ``tool'' is someone who attends class in the college regularly ? is always to be found in the library when no class is meeting, ? Always Try to get Excellent grades in the examination. ? Sole Aim: get placed in high paying Company
- 6. 2. Hacker ? A ``hacker'' is the opposite: someone who never goes to class, ? who in fact sleeps all day, ? and who spends the night pursuing recreational activities rather than studying text books. What does this have to do with computers? Originally, nothing.
- 7. Hackers vs Tools ? There are standards for success as a hacker, just as grades form a standard for success as a tool. ? Overall Hackers are more successful in life and they emerge as a leader in their field.
- 9. 1.White Hat Hacker 2.Grey Hat Hacker 3.Black Hat Hacker
- 10. White Hat Hackers - They use their knowledge and skill set for good, constructive intents. They find out new security loopholes and their solutions. A white hat that does VAPT is also known as Pentester.
- 11. Black Hat Hacker- They use their knowledge and skill set for illegal activities, destructive intents, without authorization. Black hat hackers are also referred to as the "crackers" within the security industry and by modern programmers. Crackers keep the awareness of the vulnerabilities to themselves and do not notify the general public or the manufacturer for patches to be applied.
- 12. Grey Hat Hacker- They exhibits traits from both white hats & black hats. Like a white hat, he'll inform the administrator of the website of the vulnerabilities, he found after hacking through the site. Like a black hat, heˇŻll hack any site freely and without any authorization from owners whatsoever. He'll even offer to repair the vulnerable site, that he exposed .
- 13. Purpose Of Hacking #To make security stronger ( Ethical Hacking ) #Just for fun #Show off #Hack other systems secretly & Steal important information
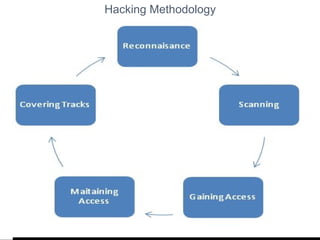
- 15. Reconnaissance Also called as Information Gathering. To gain vital information about target. Where an attacker seeks to gather as much information as possible about a target. Whatever methods (Art of Googling, Social Engineering) are used to perform reconnaissance, hackers will usually collect a large amount of information which may be useful during their attacks.
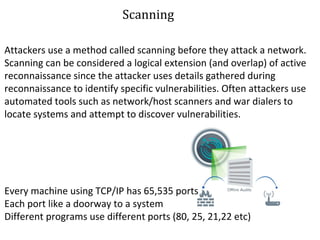
- 16. S Scanning Attackers use a method called scanning before they attack a network. Scanning can be considered a logical extension (and overlap) of active reconnaissance since the attacker uses details gathered during reconnaissance to identify specific vulnerabilities. Often attackers use automated tools such as network/host scanners and war dialers to locate systems and attempt to discover vulnerabilities. Every machine using TCP/IP has 65,535 ports Each port like a doorway to a system Different programs use different ports (80, 25, 21,22 etc)
- 17. Gaining Access Vulnerabilities exposed during the reconnaissance and scanning phase are now exploited to gain access. The hacker can gain access at operating system level, application level or network level. The hacker has control and can use that system as they wish.
- 18. Maintaining Access In this procedure the Hacker Gains more access. He break into more sensitive administrator root accounts. Install Trojan horse program or backdoors to maintain his access and to gather additional information.
- 19. Covering Tracks This is the last & final stage where a hacker deletes all logs showing his malicious behavior. So, They donˇŻt get caught. 1.Clearing the event log 2.Evidence Elimination 3.Hiding
- 20. Hacking Techniques Low Tech Methods High Tech Methods
- 21. Low Tech Methods Social Engineering ?Hacker takes advantage of trusting human being to get information from them ?eg a ploy to install new security update on your system Shoulder Surfing Guessing ?weak password like death of birth, pet name, nick name etc..
- 22. High Tech Methods Phishing Brute Force Attacks Sniffing LFI(Local File Inclusion) Metasploit Dos Attack SQL Injection
- 23. Hacking Tools Password Cracking : AirCrack, Cain and Able , THC Hydra Network Scanning : Nmap, AngryIPScanner , Wireshark System Hacking : Lost Door, Olllydgb , Keylogger Exploitation : Metasploit , Sqlmap , Social Engineering Toolkit
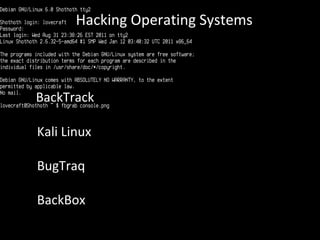
- 24. Hacking Operating Systems BackTrack Kali Linux BugTraq BackBox
- 25. How to get rid of? ? Keep system softwares up to date ? Avoid Downloading/Installing unknown programs ? Use Internet Security ? Keep firewall ON ? Use strong passwords(uppercase , lowercase letters with numbers & special symbols) ?Avoid storing important data in system like bank account information, any important documents etc..
- 26. Reference www.google.com/ http://sectools.org/ Wikipedia http://thehackernews.com/
- 27. ANY QUESTIONS?
- 28. THANK YOU !