Introduction to hackers
- 1. Hackers, Crackers, and Network Intruders Sponser www.harshpchacks.blogspot.com By Harsh Sharma
- 2. Agenda ŌĆó Hackers and their vocabulary ŌĆó Threats and risks ŌĆó Types of hackers ŌĆó Gaining access ŌĆó Intrusion detection and prevention ŌĆó Legal and ethical issues
- 3. Hacker Terms ŌĆó Hacking - showing computer expertise ŌĆó Cracking - breaching security on software or systems ŌĆó Phreaking - cracking telecom networks ŌĆó Spoofing - faking the originating IP address in a datagram ŌĆó Denial of Service (DoS) - flooding a host with sufficient network traffic so that it canŌĆÖt respond anymore ŌĆó Port Scanning - searching for vulnerabilities
- 4. Hacking through the ages ŌĆó 1969 - Unix ŌĆśhackedŌĆÖ together ŌĆó 1971 - Cap ŌĆśn Crunch phone exploit discovered ŌĆó 1988 - Morris Internet worm crashes 6,000 servers ŌĆó 1994 - $10 million transferred from CitiBank accounts ŌĆó 1995 - Kevin Mitnick sentenced to 5 years in jail ŌĆó 2000 - Major websites succumb to DDoS ŌĆó 2000 - 15,700 credit and debit card numbers stolen from Western Union (hacked while web database was undergoing maintenance) ŌĆó 2001 Code Red ŌĆō exploited bug in MS IIS to penetrate & spread ŌĆō probes random IPs for systems running IIS ŌĆō had trigger time for denial-of-service attack ŌĆō 2nd wave infected 360000 servers in 14 hours ŌĆó Code Red 2 - had backdoor installed to allow remote control ŌĆó Nimda -used multiple infection mechanisms email, shares, web client, IIS ŌĆó 2002 ŌĆō Slammer Worm brings web to its knees by attacking MS SQL Server
- 5. The threats ŌĆó Denial of Service (Yahoo, eBay, CNN, MS) ŌĆó Defacing, Graffiti, Slander, Reputation ŌĆó Loss of data (destruction, theft) ŌĆó Divulging private information (AirMiles, corporate espionage, personal financial) ŌĆó Loss of financial assets (CitiBank)
- 6. Types of hackers ŌĆó Professional hackers ŌĆō Black Hats ŌĆō the Bad Guys ŌĆō White Hats ŌĆō Professional Security Experts ŌĆó Script kiddies ŌĆō Mostly kids/students ŌĆó User tools created by black hats, ŌĆō To get free stuff ŌĆō Impress their peers ŌĆō Not get caught ŌĆó Underemployed Adult Hackers ŌĆō Former Script Kiddies ŌĆó CanŌĆÖt get employment in the field ŌĆó Want recognition in hacker community ŌĆó Big in eastern european countries ŌĆó Ideological Hackers ŌĆō hack as a mechanism to promote some political or ideological purpose ŌĆō Usually coincide with political events
- 7. Types of Hackers ŌĆó Criminal Hackers ŌĆō Real criminals, are in it for whatever they can get no matter who it hurts ŌĆó Corporate Spies ŌĆō Are relatively rare ŌĆó Disgruntled Employees ŌĆō Most dangerous to an enterprise as they are ŌĆ£insidersŌĆØ ŌĆō Since many companies subcontract their network services a disgruntled vendor could be very dangerous to the host enterprise
- 8. Top intrusion justifications ŌĆó IŌĆÖm doing you a favor pointing out your vulnerabilities ŌĆó IŌĆÖm making a political statement ŌĆó Because I can ŌĆó Because IŌĆÖm paid to do it
- 9. Gaining access ŌĆó Front door ŌĆō Password guessing ŌĆō Password/key stealing ŌĆó Back doors ŌĆō Often left by original developers as debug and/or diagnostic tools ŌĆō Forgot to remove before release ŌĆó Trojan Horses ŌĆō Usually hidden inside of software that we download and install from the net (remember nothing is free) ŌĆō Many install backdoors ŌĆó Software vulnerability exploitation ŌĆō Often advertised on the OEMs web site along with security patches ŌĆō Fertile ground for script kiddies looking for something to do
- 10. Back doors & Trojans ŌĆó e.g. Whack-a-mole / NetBus ŌĆó Cable modems / DSL very vulnerable ŌĆó Protect with Virus Scanners, Port Scanners, Personal Firewalls
- 11. Software vulnerability exploitation ŌĆó Buffer overruns ŌĆó HTML / CGI scripts ŌĆó Poor design of web applications ŌĆō Javascript hacks ŌĆō PHP/ASP/ColdFusion URL hacks ŌĆó Other holes / bugs in software and services ŌĆó Tools and scripts used to scan ports for vulnerabilities
- 12. Password guessing ŌĆó Default or null passwords ŌĆó Password same as user name (use finger) ŌĆó Password files, trusted servers ŌĆó Brute force ŌĆō make sure login attempts audited!
- 13. Password/key theft ŌĆó Dumpster diving ŌĆō Its amazing what people throw in the trash ŌĆó Personal information ŌĆó Passwords ŌĆó Good doughnuts ŌĆō Many enterprises now shred all white paper trash ŌĆó Inside jobs ŌĆō Disgruntled employees ŌĆō Terminated employees (about 50% of intrusions resulting in significant loss)
- 14. Once inside, the hacker can... ŌĆó Modify logs ŌĆō To cover their tracks ŌĆō To mess with you ŌĆó Steal files ŌĆō Sometimes destroy after stealing ŌĆō A pro would steal and cover their tracks so to be undetected ŌĆó Modify files ŌĆō To let you know they were there ŌĆō To cause mischief ŌĆó Install back doors ŌĆō So they can get in again ŌĆó Attack other systems
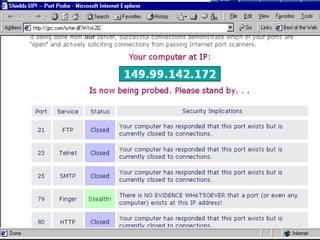
- 15. Intrusion detection systems (IDS) ŌĆó A lot of research going on at universities ŌĆō Doug Somerville- EE Dept, Viktor Skorman ŌĆō EE Dept ŌĆó Big money available due to 9/11 and Dept of Homeland Security ŌĆó Vulnerability scanners ŌĆō pro-actively identifies risks ŌĆō User use pattern matching ŌĆó When pattern deviates from norm should be investigated ŌĆó Network-based IDS ŌĆō examine packets for suspicious activity ŌĆō can integrate with firewall ŌĆō require one dedicated IDS server per segment
- 16. Intrusion detection systems (IDS) ŌĆó Host-based IDS ŌĆō monitors logs, events, files, and packets sent to the host ŌĆō installed on each host on network ŌĆó Honeypot ŌĆō decoy server ŌĆō collects evidence and alerts admin
- 17. Intrusion prevention ŌĆó Patches and upgrades (hardening) ŌĆó Disabling unnecessary software ŌĆó Firewalls and Intrusion Detection Systems ŌĆó ŌĆśHoneypotsŌĆÖ ŌĆó Recognizing and reacting to port scanning
- 18. Risk management Probability Impact Ignore (e.g. delude yourself) Prevent (e.g. firewalls, IDS, patches) Backup Plan (e.g. redundancies) Contain & Control (e.g. port scan)
- 19. Legal and ethical questions ŌĆó ŌĆśEthicalŌĆÖ hacking? ŌĆó How to react to mischief or nuisances? ŌĆó Is scanning for vulnerabilities legal? ŌĆō Some hackers are trying to use this as a business model ŌĆó Here are your vulnerabilities, let us help you ŌĆó Can private property laws be applied on the Internet?
- 21. Computer Crimes ŌĆó Financial Fraud ŌĆó Credit Card Theft ŌĆó Identity Theft ŌĆó Computer specific crimes ŌĆō Denial-of-service ŌĆō Denial of access to information ŌĆō Viruses Melissa virus cost New Jersey man 20 months in jail ŌĆó Melissa caused in excess of $80 Million ŌĆó Intellectual Property Offenses ŌĆō Information theft ŌĆō Trafficking in pirated information ŌĆō Storing pirated information ŌĆō Compromising information ŌĆō Destroying information ŌĆó Content related Offenses ŌĆō Hate crimes ŌĆō Harrassment ŌĆō Cyber-stalking ŌĆó Child privacy
- 22. Federal Statutes ŌĆó Computer Fraud and Abuse Act of 1984 ŌĆō Makes it a crime to knowingly access a federal computer ŌĆó Electronic Communications Privacy Act of 1986 ŌĆō Updated the Federal Wiretap Act act to include electronically stored data ŌĆó U.S. Communications Assistance for Law Enforcement Act of 1996 ŌĆō Ammended the Electronic Communications Act to require all communications carriers to make wiretaps possible ŌĆó Economic and Protection of Proprietary Information Act of 1996 ŌĆō Extends definition of privacy to include proprietary economic information , theft would constitute corporate or industrial espionage ŌĆó Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 ŌĆō Standards for the electronic transmission of healthcare information ŌĆó National Information Infrastructure Protection Act of 1996 ŌĆō Amends Computer Fraud and Abuse Act to provide more protection to computerized information and systems used in foreign and interstate commerce or communications ŌĆó The Graham-Lynch-Bliley Act of 1999 ŌĆō Limits instances of when financial institution can disclose nonpublic information of a customer to a third party