Introduction to HRM
- 2. Content to be Covered under Unit No -I •Human Resource Management – Concept, Functions •Role, Status and Competencies of HR Manager •HR Policies •Evolution of HRM •Emerging challenges of HRM
- 3. Introduction to HRM  HRM = HR +M  HR= Manpower, Personnel, Labour.  HR= Labour – Imp. Factor of Production.  HRM =View changed – from – liability to asset.
- 4. Definition of HRM  Edwin Flippo:- “HRM is the planning, organizing, directing and controlling of the procurement, development, compensation, integration, maintenance and separation of human resource to the end that individual, organizational and social objectives are accomplished”.
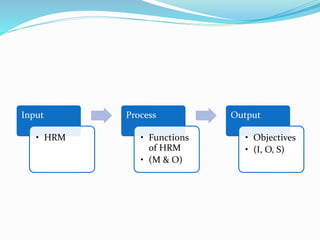
- 5. Input • HRM Process • Functions of HRM • (M & O) Output • Objectives • (I, O, S)
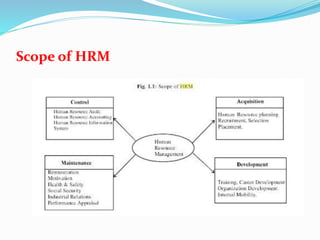
- 7. Scope of HRM
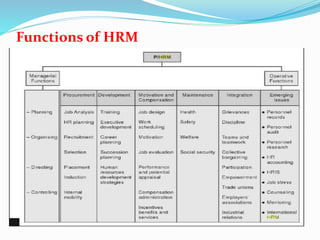
- 9. Role, Status and Competencies of HR Manager ď‚— HR managers plays a vital role in an organization and helps in fulfilling the goals and objectives of the organization. ď‚— HRM processes are carried out by the HR managers to fulfill the goals and objectives of the organization. They perform two sets of functions, namely managerial functions and operative functions. All managers, irrespective of their departments, perform management functions. The operative functions, on the other hand, are specialized activities performed exclusively by the HR managers, usually for all the departments.
- 10. HR Manager – Roles  The manager has to get things done through and with people.  This involves allotting major activities to individual employees, guiding them in day to day working, motivating them to improve performance and controlling employees through performance appraisal system.  Therefore he requires special assistance and HR manager is a specialist who provides expert advice to the managers on matters connected with human resources
- 11.  He plays different roles such as –  Counselor  Trainer  Problem solver  Mediator  Legal expert  HR advisor etc.
- 12.  Competencies of HR Manager – 1) Human Relations Skills 2) Decision-Making Skills 3) Leadership Skills 4) Technical Skills 5) Communication Skills 6) Motivational Skills 7) Analytical Skills
- 13. HR Policies ď‚— Human resource policies are continuing guidelines on the approach of which an organization intends to adopt in managing its people. ď‚— They represent specific guidelines to HR managers on various matters concerning employment and state the intent of the organization on different aspects of Human Resource management such as recruitment, promotion, compensation, training and selection etc. ď‚— They therefore serve as a reference point when human resources management practices are being developed or when decisions are being made about an organization's workforce.
- 14. ď‚— A good HR policy provides generalized guidance on the approach adopted by the organization, and therefore its employees, concerning various aspects of employment. A procedure spells out precisely what action should be taken in line with the policies. ď‚—
- 15. ď‚— In actuality, policies and procedures serve a number of purposes: - 1. They provide clear communication between the organization and their employees regarding their condition of employment. 2. They form a basis for treating all employees fairly and equally. 3. They are a set of guidelines for supervisors and managers. 4. They create a basis for developing the employee handbook. 5. They establish a basis for regularly reviewing possible changes affecting employees. 6. They form a context for supervisor training programs and employee orientation programs.
- 16. ď‚— Human resource management consists of deliberate organizational activities designed to improve employee productivity and administration through such means as recruitment, compensation, performance, evaluation, training, record keeping and compliance. ď‚— HR policies should be developed for key HR management functions covering eight commonly accepted responsibilities: ď‚— Compensation and benefits ď‚— Labor management relations ď‚— Employment practices and placement ď‚— Workplace diversity ď‚— Health, safety and security ď‚— Human resources information systems ď‚— Human resource research ď‚— Training and development
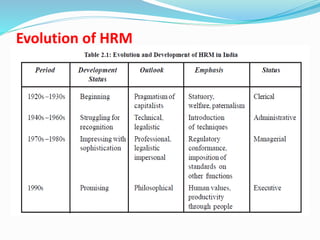
- 17. Evolution of HRM
- 18. Emerging Challenges of HRM 1) Workforce Diversity 2) Empowerment 3) Downsizing 4) VRS 5) HRIS
- 19. Reference Books ď‚— HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT by S. S. Khanka (S. Chand Publication) ď‚— Human Resource Management by V. S. P. Rao (Excel Books)