Introduction to IT.pptx
- 1. Unit of Competence: Operate Personal Computer (OPC) LO 1: Start the computer
- 2. Introduction to IT What is information technology (IT)? ï Computer based system that input processing and outputting information. ï IT includes hardware and software. Components of IT Information technology is divided into three primary components. These are âĒï Computers: Accept data in some arranged form as an input âĒï Communications networks: to send and receive data and information over a communication network ï Know-how: to solve problems and to take advantages of the opportunities it creates. ï Therefore IT requires or implies know-how, knowing how to do something well.
- 3. Data Vs information Data: data is row fact. It is also row material for data processing. Information: data is processed into information. Data processing/information Inputï Sorting (Arranging) ï Processingï Filling (storing information) ï outputï Control (according to goal) Form of data: data is found in many formats for example inform of text, graphics, image, video and etc. Mode of information dissemination Information can be transmitted in many devises like Telephone, radio, E-mail, TV, Mobil and etc.
- 4. What is Computer? ï It is an electronic device that accepts data and process into information. Characteristics of computer âĒSpeed: The most important characteristic of a computer is its speed. Computer works only one step at a time. âĒAccuracy: computers are hundred percent accuracy. âĒReliability: Once the circuit and design of a computer have been perfected and tested, it becomes very reliable. âĒstoring : A computer is characterized for its greater capacity to hold larger amount of information âĒVersatility: Computer can be programmed and applied for different purposes.
- 5. Generation of computer 1st Generation (1940-1959) -Large size in computer. -Completed at Pennsylvania University. -Vacuum tubes. -Storing data. 2nd Generation (1959-1965) -It uses transistors in place of vacuum tubs. -Much small, faster, reliable, processing capacity. 3rd Generation (1965-1970) -Solid static circuitry -Improved secondary storage. -New input and output devices. 4th Generation (1970) -Introducing of microprocessors (CPU) -Mach small, faster, reliable and processing capacity. 5th Generation (since) -It is programmable and arterial intelligence.
- 6. Type of computer 1. In terms of size, cost, power and prosing speed. ïšMicro Computer: Is called personal computer (PC) is small but important and frequently used computer. ï Laptop computer: smaller version of micro computer. Limitation of laptop: - doesnât expand easily. ï Palmtop computer: pocket size micro computer. Limitation of palm top: - doesnât perform large application. ï Desktop: mostly used micro computer type. Limitation of desk top: - is not portable. ïšMini computer: it is middle-range computer it is powerful than micro-computer. ïšMainframes computer: larger, powerful computer than micro and mini computer. ïšSuper computer: It is extremely powerful computer.
- 7. 2. In terms of by purpose âĒSpecial purpose computer: Special purpose computer performs one specific job âĒGeneral-purpose computers: A general-purpose computer is able to store different programs of instructions and performs a variety of operation Application of computer: Information technology can be applied in varied spheres of economic and social activities of human beings âĒAt Home: âĒAt office : âĒAt factory : âĒTransport and communication: âĒEducation and training and etc
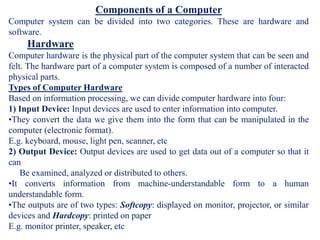
- 8. Components of a Computer Computer system can be divided into two categories. These are hardware and software. Hardware Computer hardware is the physical part of the computer system that can be seen and felt. The hardware part of a computer system is composed of a number of interacted physical parts. Types of Computer Hardware Based on information processing, we can divide computer hardware into four: 1) Input Device: Input devices are used to enter information into computer. âĒThey convert the data we give them into the form that can be manipulated in the computer (electronic format). E.g. keyboard, mouse, light pen, scanner, etc 2) Output Device: Output devices are used to get data out of a computer so that it can Be examined, analyzed or distributed to others. âĒIt converts information from machine-understandable form to a human understandable form. âĒThe outputs are of two types: Softcopy: displayed on monitor, projector, or similar devices and Hardcopy: printed on paper E.g. monitor printer, speaker, etc
- 9. 3) Storage device: It used to store data in the computer. Computer Memory measured in Bit, Byte, KB, MB and etc. Two types of storage devices: âĒPrimary storage device: is that stores data firstly. âĒRAM (Random access memory): is working area. Its also volatile memory. Temporary storage device. âĒROM (Read only Memory): is non volatile. It store basic information of computer. Permanent storage. âĒSecondary storage device: stores data permanently âĒMagnetic storage device: Magnetic disk is the most widely used storage medium on all computers. E.g. Hard disk, floppy Disk, flash disk, magnetic tape âĒOptical storage: Optical disks use laser light to read or write data from optical disk. Laser - Light Amplified Stimulated Emission of Rays. E.g. CD(Compact disk),DVD(digital video disk)
- 10. 4) Central Processing Unit (CPU): It is bran of computer. Speed of CPU is measured in Hz, MHz, KHz, GHz and etc. CPU has three sub-components: âĒControl Unit (CU): control over all activity. âĒArithmetic Logic Unit (ALU): processing the activity of pc. âĒRegister: small storage available on CPU. It stores before and after processing. The system Unit: The system unit control and executes all pc operation. Front of system: Power on/off Rest button Light Floppy disk drive and CD ROM drive Sound port
- 11. Back of the system unit: ï§ Power in and out sockets ï§ Expansion cards ï§ Video /monitor port ï§ Parallel port (for printer) ï§ PS2 ï§ Fan housing ï§ USB ï§Serial port e.t.c Inside your system unit: Mother board CPU Random access memory (RAM) RAM chipset Floppy disk drives and CD ROM drives Hard disk drive Power supply box Expansion slot ROM chips e.t.c
- 12. The peripherals ï A peripheral is any device connected to the system unit. These are keyboards, monitors, mice, printers, scanners, microphones, speakers, cameras, to list just the most familiar ones. Software ï A âsoftwareâ is a series of instructions given to a computer to solve any particular problem. These instructions should be understandable to the computer. Types of computer software Computer software can be classified in to two broad categories: âĒApplication Software: is specific function software. E.g. Word processor, spread sheet, database.etc âĒSystem Software: system software divided in two.
- 13. 1. Computer Programming Languages: human being is communicates with the computer-programming languages understandable to the computer. ï Programming languages for computers are divided in to two: âĒLow level programming language :Low level programming languages are further sub divided in to: A)Machine Languages. B)Assembly Languages. âĒMachine Languages: Machine language is the âMother Tongueâ of the computer. In this language only 0s and 1s are used while communicating with the computer âĒAssembly Languages: In assembly language instead of using 0s and 1s, each code is represented by a âmnemonicâ. A mnemonic is an aid to the human memory âĒHigh level programming language: High-level languages use complete words taken from the English language. They are therefore relatively easy to learn. It is relatively easy to understand and It is easy to modify 2. Operating system software: The operating system is the link between the hardware and the software. E.g. win xp, win2000, vista, UNIX
- 14. Functions of an Operating system -resource management, -data management, -job (task) management, and -standard means of communication between user and computer. Types of an of an operating system 1. Single User Operating System: A single user OS as the name suggests is designed for one user to effectively use a computer at a time. 2. Multi-Tasking Operating System: In this type of OS several applications maybe simultaneously loaded and used in the memory 3. Multi-User Operating System: This type of OS allows multiple users to simultaneously use the system
- 15. Virus ï Virus is a malicious (destructive) program/software that damages computer. It copies itself on to other programs and spreads through multiple computer system. Some of actions performed by virus include: âĒDuplicating themselves âĒDelete or modify your files(documents) âĒDamage your software âĒDamage your hardware, etc. Worm ï Worm is a malicious program like virus. But it does not need help to move from one computer to another which viruses canât do. Trojan horse ï Trojan horses are software that seems to perform useful activity but which has malicious programs in it. It may damage files, and perform other harmful actions on your computer
- 16. Unit two Data representation 1.Units of data representation âĒWhen data is stored, processed or communicated within the computer system, it is packed in units; âĒArranged from the smallest to the largest, the units are called bit, byte and word; âĒThese units are based on the binary number system; ïķ Bit âĒBit (derived from binary digit) is the basic unit of data storage âĒBits are the smallest units and can convey only two possible states 0 or 1; âĒIn the computer âONâ is represented by the existence of current and âOFFâ is represented by the non existence of current.
- 17. ïķByte âĒBits can be organized into large units to make them represent more and meaningful information; âĒThis large unit is called a byte and is the basic âunit of data representationâ in a computer system; âĒThe commonly used byte contains 8 bits; âĒSince each bit has two states and there are 8 bits in a byte, the total amount of data that can be represented is 28 or 256 possible combinations; âĒEach byte can represent a character(a character is either a letter, a number or a special symbol such as +,-,?,*, $, etc ïķWord âĒA word can contain one, two, three or four bytes based on the capacity of the computer; âĒWord length is usually given in bits âĒWe say that a computer is an 8-bits, a 16 bit, a 32 bit or a 64 bit computer to indicate that the amount of data it can process at a time;
- 18. ïķKilobyte 1 Kilobyte (1KB) is 210 or 1024 bytes âĒMegabyte 1 Megabyte (MB) is 220 bytes or 210 kilobytes âĒGiga byte 1 Gigabyte (GB) is 230 bytes or 220 kilobytes or 210 megabytes 1.The number system: A number system is a set of symbols used for counting. There are various number systems E.g. Decimal, binary, octal, hexadecimal etc. âĒDecimal Number System: The number system that we use in our day-to-day life is called decimal number system. Starting from (0-9) used in the system. âĒBinary Number System: The binary numeral system (base 2 numerals) represents numeric values using two symbols, typically 0 and 1.
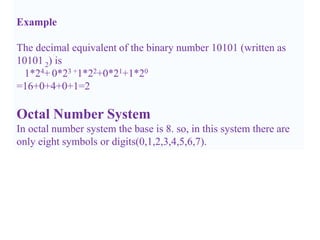
- 19. Example The decimal equivalent of the binary number 10101 (written as 10101 2) is 1*24+ 0*23 +1*22+0*21+1*20 =16+0+4+0+1=2 Octal Number System In octal number system the base is 8. so, in this system there are only eight symbols or digits(0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7).
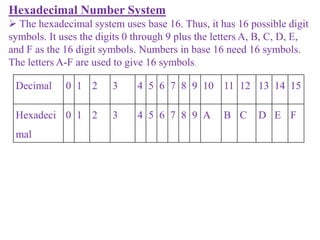
- 20. Hexadecimal Number System ï The hexadecimal system uses base 16. Thus, it has 16 possible digit symbols. It uses the digits 0 through 9 plus the letters A, B, C, D, E, and F as the 16 digit symbols. Numbers in base 16 need 16 symbols. The letters A-F are used to give 16 symbols. Decimal 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 Hexadeci mal 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F