Introduction to Life Science - ELS .pptx
- 2. Introduction to Life Science Maricriz S. Bioco
- 3. Biology ? a science that deals with all forms of life, including their classification, physiology, chemistry, and interactions. The term was introduced in Germany in 1800 and popularized by the French naturalist Jean-Baptiste de Lamarck as a means of encompassing the growing number of disciplines involved with the study of living forms.
- 4. Where did life begin?
- 5. Theory of SPECIAL CREATION ? in accordance with the Book of Genesis, that every species was individually created by God in the form in which it exists today and is not capable of undergoing any change.
- 6. Cosmozoic Theory (Panspermia Theory) ? the idea proposed by Richter in 1865 and supported by Arrhenius (1908). According to this theory, life has reached the planet Earth from other heavenly bodies such as meteorites, in the form of highly resistant spores of some microorganisms. The spores of some microorganisms are called cosmozoa or panspermia because they are preserved inside meteorites coming to the earth from the outer space. These meteorites struck the barren earth to release the cosmozoa and they developed into different creatures on the earth.
- 7. Theory of Spontaneous Generation also known as Abiogenesis ?the idea that life arose from nonlife more than 3.5 billion years ago on Earth. Abiogenesis proposes that the first life-forms generated were very simple and through a gradual process became increasingly complex.
- 8. Biogenesis Theory ?life is derived from the reproduction of other life, was presumably preceded by abiogenesis, which became impossible once Earth¡¯s atmosphere assumed its present composition.
- 9. Primordial Soup Theory ?According to primordial soup theory proposed by Alexander Oparin and John Haldane, life started in a primordial soup of organic molecules. ?Some form of energy from lightning combined with the chemicals in the atmosphere to make the building blocks of protein known as the amino acids.
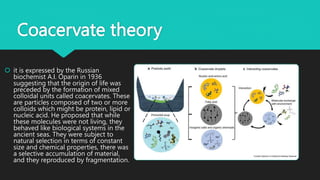
- 10. Coacervate theory ? it is expressed by the Russian biochemist A.I. Oparin in 1936 suggesting that the origin of life was preceded by the formation of mixed colloidal units called coacervates. These are particles composed of two or more colloids which might be protein, lipid or nucleic acid. He proposed that while these molecules were not living, they behaved like biological systems in the ancient seas. They were subject to natural selection in terms of constant size and chemical properties, there was a selective accumulation of material, and they reproduced by fragmentation.
- 12. FOSSIL EVIDENCE ? Fossil evidence indicates that life on Earth appeared about 3.5 billion years ago in the oceans ? Provided protection from Ultraviolet (UV) rays ? Allowed multidirectional movement ? Served as a medium for essential chemical reactions. ? Anaerobic prokaryotes
- 13. Early forms of life ? The first forms of life are believed to have appeared some 3.5 billion years ago. ? Photosynthetic organisms are organisms who make their own food by utilizing the energy from the sun and the carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. The process of photosynthesis produced more oxygen that changed the Earth¡¯s early atmosphere, allowed oxygen- breathing organisms to exist. ? Cyanobacteria (blue-green algae) are the first photosynthetic organisms to form.
- 14. The Early Life ?The formation of planets did not use up all the materials orbiting the sun, so the early Earth received shower of meteorites and was struck by many asteroids. These extraterrestrial materials and the recurring volcanic eruptions paved the way for the formation of Earth¡¯s land, seas, and atmosphere.
- 15. The Early Life ? It is still a matter of discussion, but geological evidence suggests that the early Earth began with little or no free Oxygen (O2)¡ªhad O2 been present iron oxidation (rust formation) in most ancient rocks would have been observed, but no such sign of oxidation was found. Had O2 been present, small organic compounds would have broken apart as quickly as they formed due oxidation reactions.
- 16. The Early Life ?We know that water is essential to life because molecules that are parts of life-sustaining processes would have to be dissolved in water. The Earth¡¯s lithosphere did not exist then, but it was covered by molted rock, hence water was in the form of vapor. But as evidence from ancient rocks suggests, Earth had cooled down 4.3 billion years ago causing pools of water to arise
- 17. The Early Life ? Chemists thought that organic molecules were only made by living organisms and it possessed a special vital force. But in the early 1900, a chemist was able to make urea the organic molecule found in urine. Then another was able to synthesized and amino acid called alanine. The synthesis of these molecules showed the possibility that organic molecules can be formed synthetically.
- 18. The Early Life ?In the present, there are three (3) main hypotheses that explain the mechanism on how the organic monomers came about in early Earth. These mechanisms are not mutually exclusive and might have set off simultaneously contributing to the formation of the simple organic compounds in Earth¡¯s early seas¡ªwhere early life could have started.
- 19. Extraterrestrial Materials ?At present, meteorites that fall to Earth are often analyzed and was found out that some contains amino acids, sugars, and nucleotide bases. These compounds (or their precursors) have been found in gas clouds that surrounds nearby star. Thus, the third hypothesis¡ªthat early life may have been brought about by the extraterrestrial materials that fell on the early Earth received¡ªwas created. This hypothesis suggests that materials from space carried with them organic monomers that were formed from outer space.
- 20. Extraterrestrial Materials ?At present, meteorites that fall to Earth are often analyzed and was found out that some contains amino acids, sugars, and nucleotide bases. These compounds (or their precursors) have been found in gas clouds that surrounds nearby star. Thus, the third hypothesis¡ªthat early life may have been brought about by the extraterrestrial materials that fell on the early Earth received¡ªwas created. This hypothesis suggests that materials from space carried with them organic monomers that were formed from outer space.