Introduction to phasor measurements units (pm us)
- 1. Introduction to Phasor Measurements Units (PMUs) By Supriya Senapati Under gidance of Dr.K.D.B & Dr.J.K.Das
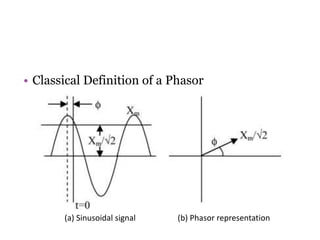
- 2. Introduction ŌĆó Classical Definition of a Phasor ŌĆō A pure sinusoidal waveform can be represented by a unique complex number known as a ŌĆśphasorŌĆÖ. ŌĆó A sinusoidal signal ŌĆó The phasor representation of this sinusoid is given by
- 3. ŌĆó Classical Definition of a Phasor ŌĆō The RMS cosine-reference voltage and current phasors are. i j v j IeII VeVV i v ’ü▒ ’ü▒ ’ü▒ ’ü▒ ’āÉ’ĆĮ’ĆĮ ’āÉ’ĆĮ’ĆĮ |||| ||||
- 4. ŌĆó Classical Definition of a Phasor (a) Sinusoidal signal (b) Phasor representation