Investigation 3 3 air as particles
Download as ppt, pdf0 likes404 views
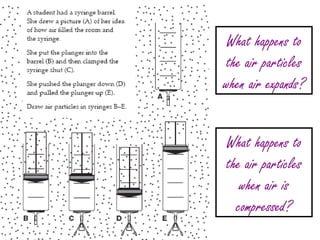
The document discusses what happens to air particles when air expands and is compressed, and instructs the reader to read a section of their resource book on the three phases of matter and complete a reading activity that is due on Friday.
1 of 3
Download to read offline


Ad
Recommended
Evaporation
EvaporationSahaj Rastogi
╠²
The document discusses factors that influence the rate of evaporation in nature, including temperature, concentration of the evaporating substance in the air, surface area, density, pressure, and intermolecular forces. Higher temperatures, lower concentrations in the air, larger surface areas, lower densities, lower pressures, and weaker intermolecular forces all cause evaporation to occur faster. Transpiration, the evaporation of water from plants, is also mentioned.Basicfluidflow
BasicfluidflowChinmay Mandal
╠²
This document provides an introduction to basic fluid mechanics and thermodynamics concepts. It discusses the properties of fluids including liquids and gases, fluid pressure, and fluids in motion. Key points covered include:
- The definition of a fluid and differences between liquids and gases in terms of molecular behavior and properties.
- Causes of fluid pressure from molecular bombardment on surfaces and definitions of pressure, pressure head, atmospheric pressure, and gauge pressure.
- Measurement of air pressure using barometers and differential pressure instruments.
- Fluid flow concepts including Bernoulli's equation, viscosity, laminar and turbulent flow, and frictional losses.Investigation 4.1 and 4.3 gas and solid expansion
Investigation 4.1 and 4.3 gas and solid expansionmrslarmour
╠²
The document discusses kinetic energy and the expansion and contraction of solids and gases when heated and cooled. It provides materials to demonstrate how the volume of air changes when heated or cooled, with rules that nothing is placed inside the bottle and its integrity is maintained.Mid summative 8 answers 2010
Mid summative 8 answers 2010mrslarmour
╠²
The document discusses various structural and behavioral adaptations of different organisms that help them survive in their environments. It notes that some butterflies migrate farther than others, squirrels store nuts for winter, clams have hard shells to burrow in sand, and giraffes have longer necks. Variation in traits like coloration help organisms like beetles and walkingsticks camouflage and live in different habitats.Mid Summative 6 Answers
Mid Summative 6 Answersmrslarmour
╠²
The document discusses several factors that can limit wildlife populations including reproductive potential, age of reproduction, number of offspring, frequency of reproduction, lifespan, offspring survival rates, disease, predation, temperature, drought, flooding, fire, loss of habitat, and food availability. It also notes some benefits and problems with removing mountain lions from an area, such as decreasing human and deer injuries/deaths but also increasing deer disease and accidents from higher deer populations without a natural predator to control numbers.Mid Summative 3 4 Answers
Mid Summative 3 4 Answersmrslarmour
╠²
This document discusses an ecosystem and the organisms within a community, including raccoons, herons, fish, frogs, dragonflies, snails, algae, bacteria, and how they interact through food webs and are influenced by abiotic factors such as water, air, heat, and the sky.Mid Summative 5 7 Answers
Mid Summative 5 7 Answersmrslarmour
╠²
The document discusses various topics related to energy transfer and phase changes, including:
1) Energy always flows from hot to cold, so when cold milk is mixed with hot cocoa, energy flows from the hot chocolate to the milk, raising its temperature.
2) Kinetic energy is the energy of moving particles - the faster particles move, the more kinetic energy they have. When particles collide, energy transfers between them.
3) During different phase changes like melting, freezing, evaporation, and condensation, kinetic energy and the distance between particles either increases or decreases.
4) Systems reach equilibrium when the energy transfer between colliding particles is equal across hot and cold regions.Mid Summative Exam 4 Answers
Mid Summative Exam 4 Answersmrslarmour
╠²
When air is heated, the kinetic energy of the particles increases causing them to move faster. This results in more space between particles, increasing the volume in a process called expansion. Cooling a material decreases kinetic energy, causing particles to move slower and occupy less space, making the object contract. While liquids can expand when heated, they cannot be compressed because the particles are already tightly packed with little space between them. Solids are characterized by particles with low kinetic energy that are tightly bonded and close together.Mixing water lab
Mixing water labmrslarmour
╠²
The document provides instructions for a lab experiment mixing hot and cold water. Students are asked to record their initial hypothesis about the resulting temperature and then take measurements after mixing equal amounts of 10┬░C and 50┬░C water in a third cup. They are finally asked to reflect on what happens to water particles during the mixing process.Capture the gas lab1
Capture the gas lab1mrslarmour
╠²
Slylock Fox investigated trash that was dumped on Rachel Rabbit's lawn by one of two suspects. By observing bones in the trash, Slylock was able to identify the suspect as the raccoon, since raccoons are omnivores that eat both plants and animals unlike the herbivorous bull.Mid summative 3 answers 2011
Mid summative 3 answers 2011mrslarmour
╠²
Mr. and Mrs. Clatter have 5 children, half of which are boys. The document also contains riddles about how this is possible, what is something that is heavy forward but not backward, and what did you eat if you threw away the outside and cooked the inside of something and then ate the outside and threw away the inside. The document also contains brief explanations of solids, liquids, gases, matter, elements, chemical reactions, substances, using the periodic table, and gas expansion and contraction.Mid summative 1-2 answers 2011
Mid summative 1-2 answers 2011mrslarmour
╠²
The document contains a word scramble activity using element symbols. It provides the scrambled element combinations and clues to figure out 4 words. The answers are:
1. RETINA (Sodium + Titanium + Rhenium)
2. PERSON (Sulfur + Nitrogen + Phosphorous + Oxygen + Erbium)
3. CABIN (Calcium + Indium + Boron)
4. POKER (Erbium + Polonium + Potassium)Investigation 3 2 air is matter 2010
Investigation 3 2 air is matter 2010mrslarmour
╠²
The document discusses several safety concerns that should be identified in an image showing a laboratory setting. It then asks what elements and gas would be produced from the reaction of sodium bicarbonate and citric acid. Finally, it asks questions about the properties of air and gases, such as whether air takes up space and is considered matter.Capture the gas lab1
Capture the gas lab1mrslarmour
╠²
Slylock Fox investigated trash that was dumped on Rachel Rabbit's lawn by one of two suspects. By observing bones in the trash, Slylock was able to identify the suspect as the raccoon, since raccoons are omnivores that eat both plants and animals unlike the herbivorous bull.Mid summative 1-2 answers 2011
Mid summative 1-2 answers 2011mrslarmour
╠²
The document contains a word scramble activity using element symbols. It provides the scrambled element combinations and clues to figure out 4 words. The answers are:
1. RETINA (Sodium + Titanium + Rhenium)
2. PERSON (Sulfur + Nitrogen + Phosphorous + Oxygen + Erbium)
3. CABIN (Calcium + Indium + Boron)
4. POKER (Erbium + Polonium + Potassium)Investigation 2 2 vocab
Investigation 2 2 vocabmrslarmour
╠²
The document defines key chemistry terms and their relationships:
Elements are fundamental substances that cannot be broken down further. All matter is made up of combinations of elements, which can change and form new substances through chemical reactions. Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space, and a substance is a unique form of matter that is different from other forms.Investigation 3 2 air is matter 2010
Investigation 3 2 air is matter 2010mrslarmour
╠²
The document discusses several safety concerns that should be identified in an image showing a laboratory setting. It then asks what elements and gas would be produced from the reaction of sodium bicarbonate and citric acid. Finally, it asks questions about the properties of air and gases, such as whether air takes up space and is considered matter.The periodic table_of_elements
The periodic table_of_elementsmrslarmour
╠²
The document provides information about the periodic table of elements including:
- It defines elements and their symbols for oxygen, lithium, beryllium, nitrogen, argon, chlorine, phosphorus, aluminum, boron, and nickel.
- It discusses Dmitri Mendeleev's creation of the periodic table in the 1860s and how he arranged elements based on their atomic masses and properties.
- It describes the three main classes of elements - metals, non-metals, and metalloids - and where they are located on the periodic table.
- It explains two important features of the periodic table: periods/rows which elements with the same number of orbitals/levelsInvestigation 2 2 vocab
Investigation 2 2 vocabmrslarmour
╠²
The document defines key chemistry terms and their relationships:
Elements are fundamental substances that cannot be broken down further. All matter is made up of combinations of elements, which can change and form new substances through chemical reactions. Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space, and a substance is a unique form of matter that is distinct from other forms.Investation 1.2 mystery mixture summary
Investation 1.2 mystery mixture summarymrslarmour
╠²
A night shift report tested combinations of white substances to identify a mystery mixture, ruling out those that did not fizz with water. When water was added to the mystery mixture, bubbles were produced, indicating a chemical reaction occurred where a new substance was formed from the components. The interrogation will test only listed suspects by combining substances with water and recording detailed observations.Investigation 1.2 white substance infor
Investigation 1.2 white substance informrslarmour
╠²
The document provides instructions for a team to interrogate suspects to identify the components of a mystery mixture. The team is told to record descriptions of each suspect, research their uses from a reference book, and look for patterns in their chemical names and formulas to deduce the identity of the mystery mixture. The team will then report their findings and reflect on whether they believe they could identify the true composition based on their interrogations.Mystery mixture
Mystery mixturemrslarmour
╠²
The document provides instructions for students to analyze a mystery mixture through a series of observations and tests. Students are told to wear goggles and not taste anything for safety. They obtain materials and record initial observations of the mixture. Then they add water pipette by pipette, observing any reactions and recording results. Finally, students summarize their observations and predict the makeup of the mystery mixture based on the results of the tests.Zork genetics
Zork geneticsmrslarmour
╠²
The document discusses genetics and inheritance in Zorks, fictional creatures. It provides examples of crossing different Zorks and using Punnett squares to determine possible genotypes and phenotypes of offspring. For example, crossing a heterozygous green-haired Zork with another results in 25% GG (green hair), 50% Gg (green hair), and 25% gg (yellow hair) offspring.Mid summative 9 answers 2010
Mid summative 9 answers 2010mrslarmour
╠²
The document discusses reproductive traits of organisms, limiting factors in populations, adaptations, phenotypes and genotypes. It provides examples of traits such as wing color variation, life span, growth rate, height, eye color and wool color that are determined by an organism's genotype. Dominant and recessive genotypes are shown determining phenotypes in populations.Punnett squares 9 4
Punnett squares 9 4mrslarmour
╠²
SpongeJunior Squarepants has a heterozygous genotype but displays the dominant phenotype like his homozygous dominant father. If SpongeJunior married another heterozygous sponge, a Punnett square could predict their offspring would have a 25% chance of being homozygous recessive, 50% chance of being heterozygous, and 25% chance of being homozygous dominant for body type traits.Invesitagtion 9.3
Invesitagtion 9.3mrslarmour
╠²
The document discusses genetics and inheritance. It explains that genetic information is contained in chromosomes located in the cell nucleus. Chromosomes contain DNA and genes which determine an organism's traits. Genes exist in variants called alleles which can be dominant or recessive and determine whether traits are expressed. The document uses examples like eye color and body shape to illustrate genetic inheritance patterns from parents to offspring.Investigation 9 2 2008
Investigation 9 2 2008mrslarmour
╠²
1. Genetic information is passed from parents to offspring through DNA, which is stored in chromosomes located in the cell nucleus.
2. Gregor Mendel studied trait inheritance in pea plants and discovered that offspring inherit discrete factors from each parent that determine traits like flower color.
3. Genes, located on chromosomes, contain alleles that control traits. The combination of alleles makes up an organism's genotype, while the observable physical traits are known as the phenotype.Investigation 8 2b
Investigation 8 2bmrslarmour
╠²
Factors like reproductive potential and limiting factors like predation can determine population growth over time for organisms like walkingsticks and birds in a bush environment. Limiting factors for the walkingstick population besides bird predation could include biotic factors like food availability or abiotic factors like weather. Organisms described as having wings, webbed feet, ability to swim upstream, long legs or nocturnal hunting could include birds and other flying or aquatic animals adapted to their environments.More Related Content
More from mrslarmour (20)
Mixing water lab
Mixing water labmrslarmour
╠²
The document provides instructions for a lab experiment mixing hot and cold water. Students are asked to record their initial hypothesis about the resulting temperature and then take measurements after mixing equal amounts of 10┬░C and 50┬░C water in a third cup. They are finally asked to reflect on what happens to water particles during the mixing process.Capture the gas lab1
Capture the gas lab1mrslarmour
╠²
Slylock Fox investigated trash that was dumped on Rachel Rabbit's lawn by one of two suspects. By observing bones in the trash, Slylock was able to identify the suspect as the raccoon, since raccoons are omnivores that eat both plants and animals unlike the herbivorous bull.Mid summative 3 answers 2011
Mid summative 3 answers 2011mrslarmour
╠²
Mr. and Mrs. Clatter have 5 children, half of which are boys. The document also contains riddles about how this is possible, what is something that is heavy forward but not backward, and what did you eat if you threw away the outside and cooked the inside of something and then ate the outside and threw away the inside. The document also contains brief explanations of solids, liquids, gases, matter, elements, chemical reactions, substances, using the periodic table, and gas expansion and contraction.Mid summative 1-2 answers 2011
Mid summative 1-2 answers 2011mrslarmour
╠²
The document contains a word scramble activity using element symbols. It provides the scrambled element combinations and clues to figure out 4 words. The answers are:
1. RETINA (Sodium + Titanium + Rhenium)
2. PERSON (Sulfur + Nitrogen + Phosphorous + Oxygen + Erbium)
3. CABIN (Calcium + Indium + Boron)
4. POKER (Erbium + Polonium + Potassium)Investigation 3 2 air is matter 2010
Investigation 3 2 air is matter 2010mrslarmour
╠²
The document discusses several safety concerns that should be identified in an image showing a laboratory setting. It then asks what elements and gas would be produced from the reaction of sodium bicarbonate and citric acid. Finally, it asks questions about the properties of air and gases, such as whether air takes up space and is considered matter.Capture the gas lab1
Capture the gas lab1mrslarmour
╠²
Slylock Fox investigated trash that was dumped on Rachel Rabbit's lawn by one of two suspects. By observing bones in the trash, Slylock was able to identify the suspect as the raccoon, since raccoons are omnivores that eat both plants and animals unlike the herbivorous bull.Mid summative 1-2 answers 2011
Mid summative 1-2 answers 2011mrslarmour
╠²
The document contains a word scramble activity using element symbols. It provides the scrambled element combinations and clues to figure out 4 words. The answers are:
1. RETINA (Sodium + Titanium + Rhenium)
2. PERSON (Sulfur + Nitrogen + Phosphorous + Oxygen + Erbium)
3. CABIN (Calcium + Indium + Boron)
4. POKER (Erbium + Polonium + Potassium)Investigation 2 2 vocab
Investigation 2 2 vocabmrslarmour
╠²
The document defines key chemistry terms and their relationships:
Elements are fundamental substances that cannot be broken down further. All matter is made up of combinations of elements, which can change and form new substances through chemical reactions. Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space, and a substance is a unique form of matter that is different from other forms.Investigation 3 2 air is matter 2010
Investigation 3 2 air is matter 2010mrslarmour
╠²
The document discusses several safety concerns that should be identified in an image showing a laboratory setting. It then asks what elements and gas would be produced from the reaction of sodium bicarbonate and citric acid. Finally, it asks questions about the properties of air and gases, such as whether air takes up space and is considered matter.The periodic table_of_elements
The periodic table_of_elementsmrslarmour
╠²
The document provides information about the periodic table of elements including:
- It defines elements and their symbols for oxygen, lithium, beryllium, nitrogen, argon, chlorine, phosphorus, aluminum, boron, and nickel.
- It discusses Dmitri Mendeleev's creation of the periodic table in the 1860s and how he arranged elements based on their atomic masses and properties.
- It describes the three main classes of elements - metals, non-metals, and metalloids - and where they are located on the periodic table.
- It explains two important features of the periodic table: periods/rows which elements with the same number of orbitals/levelsInvestigation 2 2 vocab
Investigation 2 2 vocabmrslarmour
╠²
The document defines key chemistry terms and their relationships:
Elements are fundamental substances that cannot be broken down further. All matter is made up of combinations of elements, which can change and form new substances through chemical reactions. Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space, and a substance is a unique form of matter that is distinct from other forms.Investation 1.2 mystery mixture summary
Investation 1.2 mystery mixture summarymrslarmour
╠²
A night shift report tested combinations of white substances to identify a mystery mixture, ruling out those that did not fizz with water. When water was added to the mystery mixture, bubbles were produced, indicating a chemical reaction occurred where a new substance was formed from the components. The interrogation will test only listed suspects by combining substances with water and recording detailed observations.Investigation 1.2 white substance infor
Investigation 1.2 white substance informrslarmour
╠²
The document provides instructions for a team to interrogate suspects to identify the components of a mystery mixture. The team is told to record descriptions of each suspect, research their uses from a reference book, and look for patterns in their chemical names and formulas to deduce the identity of the mystery mixture. The team will then report their findings and reflect on whether they believe they could identify the true composition based on their interrogations.Mystery mixture
Mystery mixturemrslarmour
╠²
The document provides instructions for students to analyze a mystery mixture through a series of observations and tests. Students are told to wear goggles and not taste anything for safety. They obtain materials and record initial observations of the mixture. Then they add water pipette by pipette, observing any reactions and recording results. Finally, students summarize their observations and predict the makeup of the mystery mixture based on the results of the tests.Zork genetics
Zork geneticsmrslarmour
╠²
The document discusses genetics and inheritance in Zorks, fictional creatures. It provides examples of crossing different Zorks and using Punnett squares to determine possible genotypes and phenotypes of offspring. For example, crossing a heterozygous green-haired Zork with another results in 25% GG (green hair), 50% Gg (green hair), and 25% gg (yellow hair) offspring.Mid summative 9 answers 2010
Mid summative 9 answers 2010mrslarmour
╠²
The document discusses reproductive traits of organisms, limiting factors in populations, adaptations, phenotypes and genotypes. It provides examples of traits such as wing color variation, life span, growth rate, height, eye color and wool color that are determined by an organism's genotype. Dominant and recessive genotypes are shown determining phenotypes in populations.Punnett squares 9 4
Punnett squares 9 4mrslarmour
╠²
SpongeJunior Squarepants has a heterozygous genotype but displays the dominant phenotype like his homozygous dominant father. If SpongeJunior married another heterozygous sponge, a Punnett square could predict their offspring would have a 25% chance of being homozygous recessive, 50% chance of being heterozygous, and 25% chance of being homozygous dominant for body type traits.Invesitagtion 9.3
Invesitagtion 9.3mrslarmour
╠²
The document discusses genetics and inheritance. It explains that genetic information is contained in chromosomes located in the cell nucleus. Chromosomes contain DNA and genes which determine an organism's traits. Genes exist in variants called alleles which can be dominant or recessive and determine whether traits are expressed. The document uses examples like eye color and body shape to illustrate genetic inheritance patterns from parents to offspring.Investigation 9 2 2008
Investigation 9 2 2008mrslarmour
╠²
1. Genetic information is passed from parents to offspring through DNA, which is stored in chromosomes located in the cell nucleus.
2. Gregor Mendel studied trait inheritance in pea plants and discovered that offspring inherit discrete factors from each parent that determine traits like flower color.
3. Genes, located on chromosomes, contain alleles that control traits. The combination of alleles makes up an organism's genotype, while the observable physical traits are known as the phenotype.Investigation 8 2b
Investigation 8 2bmrslarmour
╠²
Factors like reproductive potential and limiting factors like predation can determine population growth over time for organisms like walkingsticks and birds in a bush environment. Limiting factors for the walkingstick population besides bird predation could include biotic factors like food availability or abiotic factors like weather. Organisms described as having wings, webbed feet, ability to swim upstream, long legs or nocturnal hunting could include birds and other flying or aquatic animals adapted to their environments.Investigation 3 3 air as particles
- 1. ╠²
- 2. What happens to the air particles when air expands? What happens to the air particles when air is compressed?
- 3. Read ŌĆ£Three Phases of MatterŌĆØ Pages 16 ŌĆō 22 of resource book Complete one of the reading activities Due Friday