Ionic Equilibria | Bronsted Lowry Acid Base Theory | Chemistry Class 12 | By Mrs.Shubhada Walawalkar
1 like215 views
This video discuss about bronsted lowry concept of acid and base. Conjugate acid base pairs, relative strength of acid base, Advantages & Limitations bronsted lowry concept of acid and base and Examples of Acid base reactions.
1 of 18
Download to read offline









Recommended
Acidandbase chm141 thursday[1]goodday![Acidandbase chm141 thursday[1]goodday](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/acidandbasechm141-thursday1goodday-121121141355-phpapp02-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Acidandbase chm141 thursday[1]goodday](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/acidandbasechm141-thursday1goodday-121121141355-phpapp02-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Acidandbase chm141 thursday[1]goodday](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/acidandbasechm141-thursday1goodday-121121141355-phpapp02-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Acidandbase chm141 thursday[1]goodday](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/acidandbasechm141-thursday1goodday-121121141355-phpapp02-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
Acidandbase chm141 thursday[1]gooddayDr Robert Craig PhD
╠²
This document discusses Lewis acids and bases, strong acids and bases, pH and pOH scales, autoionization of water, and buffer solutions. It provides definitions and examples of Arrhenius acids and bases, Bronsted-Lowry acids and bases, and Lewis acids and bases. It also discusses properties of strong acids and bases, calculating pH and pOH, and how buffer solutions resist changes in pH through acid-base equilibriums.Chemistry zimsec chapter 22 ionic equilibria



Chemistry zimsec chapter 22 ionic equilibriaalproelearning
╠²
This document provides an overview of Chapter 22 from a chemistry textbook, which covers topics related to ionic equilibria including:
- pH, Ka, pKa and Kw values and their use in calculations involving strong and weak acids and bases.
- Acid-base titration curves and how they differ for strong-strong, strong-weak, weak-strong, and weak-weak acid-base titrations.
- How acid-base indicators work and their use in determining the endpoint of a titration.
It also lists learning outcomes for understanding these concepts and performing related calculations.Lewis acid and base



Lewis acid and baseKamal Metwalli
╠²
This document contains 3 questions about classifying reactants as Lewis acids or bases in chemical reactions. The first question identifies methanol (CH3OH) as the Lewis base and boron trifluoride (BF3) as the Lewis acid in their reaction. The second question classifies aluminum ions (Al3+) as the Lewis acid and water (H2O) as the Lewis base in the given reaction. The third question asks to classify additional reactants as either Lewis acids or bases.New chm 152 unit 3 power points sp13



New chm 152 unit 3 power points sp13caneman1
╠²
This document provides information on acids and bases, including:
- The Arrhenius, Br├Ėnsted-Lowry, and Lewis theories of acids and bases.
- Classification of acids and bases as strong or weak based on degree of ionization.
- Conjugate acid-base pairs and how they are involved in acid-base reactions.
- The pH scale and relationships between [H+], [OH-], pH, pOH, and pKw.
- Key acid-base concepts such as autoionization of water, amphoteric nature of water, and using Ka/pKa values to determine acid strength.Acids andbases cheat sheet



Acids andbases cheat sheetTimothy Welsh
╠²
This document provides an overview of key concepts related to acids and bases in chemistry. It defines different types of acids and bases according to several theories. It also discusses properties of acids and bases such as tastes and colors of litmus paper. Strong and weak acids and bases are compared. Buffers are described as mixtures of weak acids and bases that resist pH change. The pH scale is introduced and methods for solving pH problems are outlined, including using Ka, Kb, and Kw values and ICE charts. Acid-base properties of salts and the principles of titrations are also summarized.acids _bases



acids _basesAyush karn
╠²
This document provides an overview of acid-base theories and chemistry. It defines acids and bases according to three main theories:
1) Arrhenius theory defines acids as substances that donate H+ ions in water and bases as those that donate OH- ions.
2) Bronsted-Lowry theory defines acids as proton donors and bases as proton acceptors, providing a better explanation of substances like ammonia.
3) Lewis theory defines acids as electron pair acceptors and bases as electron pair donors, explaining both traditional acids/bases and coordination compounds.
The document then discusses acid/base reactions and equilibrium expressions, relative acid/base strengths, and the differences between strong vs. weak acids and5-2 Balancing Reactions



5-2 Balancing Reactionsrkelch
╠²
This document discusses balancing chemical equations by manipulating coefficients to ensure conservation of mass. It provides examples of balancing a variety of chemical equations, including N2H4 + O2 ŌåÆ N2 + H2O, 2Na + 2H2O ŌåÆ 2NaOH + H2, and K2CrO4 + Pb(NO3)2 ŌåÆ PbCrO4 + 2KNO3. The key steps are to count atoms on each side, change coefficients until balanced, and show that mass is conserved.Co ordination chemistry



Co ordination chemistryMukeshPareek14
╠²
This document provides information about coordination compounds and coordination chemistry. It defines key terms such as coordination compounds, coordination entities, central atoms/ions, ligands, and discusses the classification of ligands. It also covers topics like oxidation number, coordination number, coordination polyhedra, classification of complexes, and Werner's theory of coordination compounds. IUPAC nomenclature for naming coordination compounds is also presented.Bronsted lowry acid and base



Bronsted lowry acid and baseKamal Metwalli
╠²
This document discusses the Br├Ėnsted-Lowry theory of acids and bases. It defines acids as proton donors and bases as proton acceptors. An acid-base pair consists of a conjugate acid and conjugate base, where the acid donates a proton to form the conjugate base, or the base accepts a proton to form the conjugate acid. Water is described as amphiprotic because it can act as both an acid and a base. Examples of acid-base reactions and identification of conjugate species are provided.Chapter 15.2 Acid-Base Theories



Chapter 15.2 Acid-Base TheoriesChris Foltz
╠²
The document discusses acid-base theories including Bronsted-Lowry acids and bases, Lewis acids and bases, and monoprotic and polyprotic acids. Under the Bronsted-Lowry definition, an acid is a proton donor and a base is a proton acceptor in a proton transfer reaction. A Lewis acid is an electron pair acceptor that forms a covalent bond, while a Lewis base is an electron pair donor. Monoprotic acids donate one proton, while polyprotic acids like sulfuric acid can donate multiple protons in successive reactions.New chm-152-unit-3-power-points-sp13-140227172047-phpapp01



New chm-152-unit-3-power-points-sp13-140227172047-phpapp01Cleophas Rwemera
╠²
This document provides information about acids and bases including:
- Svante Arrhenius' theory that acids produce H+ ions and bases produce OH- ions in aqueous solutions.
- The difference between strong acids that completely ionize and weak acids that only partially ionize.
- Common strong acids like HCl and HNO3 and common weak acids like HF and carboxylic acids.
- The Br├Ėnsted-Lowry and Lewis definitions of acids and bases as proton donors/acceptors and electron pair donors/acceptors respectively.
- Key aspects of acid-base chemistry including conjugate acid-base pairs, the pH scale, acid and base strength, and acid-base reactions.Diploma_I_Applied science(chemistry)U-III Acid & bases 



Diploma_I_Applied science(chemistry)U-III Acid & bases Rai University
╠²
1) Acids cause substances like lemons and food to be sour and can damage materials like teeth and sculptures. Acids have positively charged hydrogen ions and turn litmus red.
2) Bases have negatively charged hydroxide ions, feel slippery, and turn litmus blue. Common bases include hand soaps and drain cleaners.
3) The Br├Ėnsted-Lowry concept defines acids as proton donors and bases as proton acceptors in reversible acid-base reactions. Both acids and bases can act as conjugates of each other by gaining or losing protons.ACID BASE THEORY 



ACID BASE THEORY Nitin Bansod
╠²
This document discusses different definitions of acids and bases that were proposed over time:
1. Lavoisier defined acids as containing oxygen. Liebig later defined acids as containing hydrogen that can be replaced by a metal.
2. Arrhenius defined acids as substances that produce hydrogen ions (H+) in aqueous solution and bases as substances that produce hydroxide (OH-) ions.
3. Br├Ėnsted and Lowry defined acids as proton donors and bases as proton acceptors in acid-base reactions, forming conjugate acid-base pairs.
4. Lewis expanded the definition to include electron pair donors and acceptors in both aqueous and non-aqueous reactions.
It also discussesChap 12 Acids and Bases (3) defintions s



Chap 12 Acids and Bases (3) defintions sfuat8
╠²
This document discusses several key concepts in acid-base chemistry including: the Arrhenius, Bronsted-Lowry, and Lewis definitions of acids and bases. It explains that according to the Arrhenius definition, acids increase the concentration of H+ ions in water while bases increase OH- ions. The Bronsted-Lowry definition states that acids donate protons while bases accept protons. Lewis acids and bases involve the sharing of electron pairs between reactants. Equilibrium constants like Ka and Kb can be used to describe and relate acid and base dissociation strengths. Water autoionizes into H+ and OH- ions according to the ion product constant Kw.Bronsted Lowry Acid and Base.pptx



Bronsted Lowry Acid and Base.pptxCaileRykerMico
╠²
1. The document discusses acid-base concepts including the Br├Ėnsted-Lowry theory of acids and bases. It defines Arrhenius, Br├Ėnsted-Lowry acids and bases, and conjugate acid-base pairs.
2. Factors that influence acid strength are examined, including bond polarity, bond strength, and structural features of oxoacids and carboxylic acids.
3. The autoionization of water is discussed, including the ion product constant Kw and its implications for solutions being acidic, basic, or neutral.bronsted lowry.pptx



bronsted lowry.pptxzenhernandez1
╠²
1. The document discusses different definitions of acids and bases including Arrhenius, Br├Ėnsted-Lowry, and Lewis models.
2. Under the Br├Ėnsted-Lowry definition, acids donate protons and bases accept protons to form conjugate acid-base pairs.
3. The Br├Ėnsted-Lowry model is more inclusive than the Arrhenius model because it classifies ammonia as a base since it can accept protons, even though it does not produce OH-.Ab Lec1



Ab Lec1teacher.mimi
╠²
Acids and bases can be defined operationally based on experimental observations or conceptually based on theories. Operationally, acids are sour electrolytes that turn litmus red and react with metals, while bases are bitter electrolytes that turn litmus blue. Conceptually, acids are proton donors according to Arrhenius and Bronsted-Lowry, or electron pair acceptors according to Lewis. Conjugate acid-base pairs involve the transfer of a proton between an acid and its conjugate base. The strength of an acid or base depends on its tendency to donate or accept protons.B sc_I_General chemistry U-II Ionic equilibria in aqueous solution 



B sc_I_General chemistry U-II Ionic equilibria in aqueous solution Rai University
╠²
This document provides an overview of acids, bases, and pH. It defines acids and bases according to Arrhenius, Br├Ėnsted-Lowry, and Lewis theories. Acids are substances that produce H+ ions in water or donate protons in reactions, while bases produce OH- ions or accept protons. The document also discusses acid and base strength, pH, self-ionization of water, and using pH to calculate hydrogen or hydroxide ion concentrations. Common examples like acids in orange juice and blood pH are provided.B sc i chemistry i u ii ionic equilibria in aqueous solution a



B sc i chemistry i u ii ionic equilibria in aqueous solution aRai University
╠²
This document provides an overview of acids, bases, and pH. It defines acids and bases according to Arrhenius, Br├Ėnsted-Lowry, and Lewis theories. Acids are substances that produce H+ ions in water or donate protons in reactions, while bases produce OH- ions or accept protons. The document also discusses acid and base strength, pH, self-ionization of water, and examples of calculating pH from H+ concentration and vice versa. Common acids, bases, and pH indicators are listed.Acid base concept



Acid base conceptShisam Neupane
╠²
An acid is any substance that in water solution tastes sour, changes blue litmus paper to red, reacts with some metals to liberate hydrogen, reacts with bases to form salts, and promotes chemical reactions (acid catalysis).
A base is a substance that can neutralize the acid by reacting with hydrogen ions. Most bases are minerals that react with acids to form water and salts.
Salt is a chemical compound consisting of an ionic assembly of cations and anions. Bronsted Lowary Acid Base concept



Bronsted Lowary Acid Base conceptrabbiasaeed
╠²
Bronsted and Lowery proposed an acid-base theory in 1923 to overcome limitations of Arrhenius' theory. According to Bronsted-Lowery theory, an acid is a proton donor and a base is a proton acceptor. Examples of acids given are CH3COOH and H2SO4, which donate protons. NH3 acts as a base by accepting protons. Water can also act as both an acid and base, making it an amphoteric species.Reset Help By the Brnsted-Lowry definition- acids are proton donors an.docx



Reset Help By the Brnsted-Lowry definition- acids are proton donors an.docxacarolyn
╠²
Reset Help By the Br├ā┬Ėnsted-Lowry definition, acids are proton donors and bases are proton acceptors. By the Lewis definition, acids are electron-pair acceptors and bases are electron-pair donors. For bases, the two definitions are equivalent such that all Lewis bases are Br├ā┬Ėnsted-Lowry bases and vice versa However, it is possible to have a Lewis acid that is not a Br├ā┬Ėnsted-Lowry acid. This is because Lewis acids include molecules and cations that have a vacant valence orbital, regardless of whether they have a proton to donate Common examples of Lewis acids (that are not Br├ā┬Ėnsted-Lowry acids) are metal ions, such as Al+and Cu2+. The following is an example ofa Lewis acid-base reaction Lewis acids Lewis bases NH3 donates the electron pair to Cu2+. Therefore NH3 is a Lewis base, and Cu2 is a Lewis acid SubmitPrev Previous Answer
Solution
1. Lewis acids: Lewis acids are the species which accepts electrons.
SO 3 since S has only three electron domains. Hence it accepts electrons.
Fe 2+ is electron deficient. Hence it accepts electrons too.
CO 2 where C accepts electrons since it is bound to two highly electronegative oxygen atoms.
Lewis bases are species that donates electrons.
I - , CO, H - , CH 3 NH 2
2. The order of decreasing pH is:
Ba(OH) 2 > NaOH > N 2 H 4 > HOCl > HCl
Ba(OH) 2 decomposes to give 2 OH - ions. This is why it has higher pH than NaOH which decomposes to give only 1 OH - ion.
Hydrazine N 2 H 4 is basic however lesser than NaOH and Ba(OH) 2
HOCl is a weak acid that partially dissociates to give H + and ClO -
HCl is the strongest acid that completely dissociates into H + and Cl - and hence has the lowest pH.
More the H + ions in solution, lesser the pH.
More the OH - ions in solution, higher the pH.
3. Given,
[ OH - ] = 2.3 x 10 -2 M
We know that at 25 0 C,
[H + ] [OH - ] = Kw = Ionic product of water = 10 -14
Putting the value of [OH - ] in the above equation, we have,
[H + ] x 2.3 x 10 -2 = 10 -14
[H + ] = 10 -14 / (2.3 x 10 -2 )
[H + ] = 0.44 x 10 -12 M
.Final acid and bases rev.



Final acid and bases rev.North Coast medical Training College
╠²
Simplified understandable Acid and bases For nutrition and dietetics students at North Coast Medical Training.Acids & Bases



Acids & Baseszehnerm2
╠²
This document discusses acids and bases. It introduces some of their key properties including turning litmus red or blue and reacting with metals. It then discusses several theories of acids and bases:
1. Arrhenius theory which defined acids as producing H+ ions and bases as producing OH- ions in aqueous solutions.
2. Bronsted-Lowry theory which defined acids as proton donors and bases as proton acceptors. This new definition accounted for exceptions to Arrhenius theory.
3. Acids and bases are described further as conjugate acid-base pairs, amphoteric substances that can be acids or bases, and polyprotic acids that donate more than one H+.Theories of╠²Acids and Bases (Arrhenius, Bronsted and Lewis)



Theories of╠²Acids and Bases (Arrhenius, Bronsted and Lewis)Neetika Naudiyal
╠²
This ppt contains information for all the main theories of acids and bases.Acids & Bases slides



Acids & Bases slidesTimothy Welsh
╠²
This document provides an overview of acids and bases for a high school chemistry rapid learning series. It defines acids and bases based on Arrhenius, Br├Ėnsted-Lowry, and Lewis theories. It discusses strong versus weak acids and bases, and how concentrated or dilute solutions affect strength. Conjugate acids and bases are defined. Common strong acids and bases are listed. Properties of acids and bases like taste and effect on litmus are covered. The pH scale is introduced and calculating pH of strong acids and bases is demonstrated. How salts can have acidic, basic, or neutral properties is explained. Finally, buffers and how they resist pH change are described.Solutions | Osmotic Pressure | 12th Chemistry | By. Mrs. Shubhada Walawalkar



Solutions | Osmotic Pressure | 12th Chemistry | By. Mrs. Shubhada Walawalkarshubhada walawalkar
╠²
It discusses about semipermeable membrane, osmosis, osmotic pressure,relation between osmotic pressure and concentration and molar mass of solute, Isotonic ,hypertonic,hypotonic solutions,Reverse osmosis.
Solutions | Freezing Point Depression | Chemistry Class 12 | By. Mrs Shubhada...



Solutions | Freezing Point Depression | Chemistry Class 12 | By. Mrs Shubhada...shubhada walawalkar
╠²
It discusses briefly about Freezing Point Depression,Relation between Freezing Point Depression and Molarity and Molar Mass of Solute and Numerical on Freezing Point Depression.More Related Content
Similar to Ionic Equilibria | Bronsted Lowry Acid Base Theory | Chemistry Class 12 | By Mrs.Shubhada Walawalkar (20)
Bronsted lowry acid and base



Bronsted lowry acid and baseKamal Metwalli
╠²
This document discusses the Br├Ėnsted-Lowry theory of acids and bases. It defines acids as proton donors and bases as proton acceptors. An acid-base pair consists of a conjugate acid and conjugate base, where the acid donates a proton to form the conjugate base, or the base accepts a proton to form the conjugate acid. Water is described as amphiprotic because it can act as both an acid and a base. Examples of acid-base reactions and identification of conjugate species are provided.Chapter 15.2 Acid-Base Theories



Chapter 15.2 Acid-Base TheoriesChris Foltz
╠²
The document discusses acid-base theories including Bronsted-Lowry acids and bases, Lewis acids and bases, and monoprotic and polyprotic acids. Under the Bronsted-Lowry definition, an acid is a proton donor and a base is a proton acceptor in a proton transfer reaction. A Lewis acid is an electron pair acceptor that forms a covalent bond, while a Lewis base is an electron pair donor. Monoprotic acids donate one proton, while polyprotic acids like sulfuric acid can donate multiple protons in successive reactions.New chm-152-unit-3-power-points-sp13-140227172047-phpapp01



New chm-152-unit-3-power-points-sp13-140227172047-phpapp01Cleophas Rwemera
╠²
This document provides information about acids and bases including:
- Svante Arrhenius' theory that acids produce H+ ions and bases produce OH- ions in aqueous solutions.
- The difference between strong acids that completely ionize and weak acids that only partially ionize.
- Common strong acids like HCl and HNO3 and common weak acids like HF and carboxylic acids.
- The Br├Ėnsted-Lowry and Lewis definitions of acids and bases as proton donors/acceptors and electron pair donors/acceptors respectively.
- Key aspects of acid-base chemistry including conjugate acid-base pairs, the pH scale, acid and base strength, and acid-base reactions.Diploma_I_Applied science(chemistry)U-III Acid & bases 



Diploma_I_Applied science(chemistry)U-III Acid & bases Rai University
╠²
1) Acids cause substances like lemons and food to be sour and can damage materials like teeth and sculptures. Acids have positively charged hydrogen ions and turn litmus red.
2) Bases have negatively charged hydroxide ions, feel slippery, and turn litmus blue. Common bases include hand soaps and drain cleaners.
3) The Br├Ėnsted-Lowry concept defines acids as proton donors and bases as proton acceptors in reversible acid-base reactions. Both acids and bases can act as conjugates of each other by gaining or losing protons.ACID BASE THEORY 



ACID BASE THEORY Nitin Bansod
╠²
This document discusses different definitions of acids and bases that were proposed over time:
1. Lavoisier defined acids as containing oxygen. Liebig later defined acids as containing hydrogen that can be replaced by a metal.
2. Arrhenius defined acids as substances that produce hydrogen ions (H+) in aqueous solution and bases as substances that produce hydroxide (OH-) ions.
3. Br├Ėnsted and Lowry defined acids as proton donors and bases as proton acceptors in acid-base reactions, forming conjugate acid-base pairs.
4. Lewis expanded the definition to include electron pair donors and acceptors in both aqueous and non-aqueous reactions.
It also discussesChap 12 Acids and Bases (3) defintions s



Chap 12 Acids and Bases (3) defintions sfuat8
╠²
This document discusses several key concepts in acid-base chemistry including: the Arrhenius, Bronsted-Lowry, and Lewis definitions of acids and bases. It explains that according to the Arrhenius definition, acids increase the concentration of H+ ions in water while bases increase OH- ions. The Bronsted-Lowry definition states that acids donate protons while bases accept protons. Lewis acids and bases involve the sharing of electron pairs between reactants. Equilibrium constants like Ka and Kb can be used to describe and relate acid and base dissociation strengths. Water autoionizes into H+ and OH- ions according to the ion product constant Kw.Bronsted Lowry Acid and Base.pptx



Bronsted Lowry Acid and Base.pptxCaileRykerMico
╠²
1. The document discusses acid-base concepts including the Br├Ėnsted-Lowry theory of acids and bases. It defines Arrhenius, Br├Ėnsted-Lowry acids and bases, and conjugate acid-base pairs.
2. Factors that influence acid strength are examined, including bond polarity, bond strength, and structural features of oxoacids and carboxylic acids.
3. The autoionization of water is discussed, including the ion product constant Kw and its implications for solutions being acidic, basic, or neutral.bronsted lowry.pptx



bronsted lowry.pptxzenhernandez1
╠²
1. The document discusses different definitions of acids and bases including Arrhenius, Br├Ėnsted-Lowry, and Lewis models.
2. Under the Br├Ėnsted-Lowry definition, acids donate protons and bases accept protons to form conjugate acid-base pairs.
3. The Br├Ėnsted-Lowry model is more inclusive than the Arrhenius model because it classifies ammonia as a base since it can accept protons, even though it does not produce OH-.Ab Lec1



Ab Lec1teacher.mimi
╠²
Acids and bases can be defined operationally based on experimental observations or conceptually based on theories. Operationally, acids are sour electrolytes that turn litmus red and react with metals, while bases are bitter electrolytes that turn litmus blue. Conceptually, acids are proton donors according to Arrhenius and Bronsted-Lowry, or electron pair acceptors according to Lewis. Conjugate acid-base pairs involve the transfer of a proton between an acid and its conjugate base. The strength of an acid or base depends on its tendency to donate or accept protons.B sc_I_General chemistry U-II Ionic equilibria in aqueous solution 



B sc_I_General chemistry U-II Ionic equilibria in aqueous solution Rai University
╠²
This document provides an overview of acids, bases, and pH. It defines acids and bases according to Arrhenius, Br├Ėnsted-Lowry, and Lewis theories. Acids are substances that produce H+ ions in water or donate protons in reactions, while bases produce OH- ions or accept protons. The document also discusses acid and base strength, pH, self-ionization of water, and using pH to calculate hydrogen or hydroxide ion concentrations. Common examples like acids in orange juice and blood pH are provided.B sc i chemistry i u ii ionic equilibria in aqueous solution a



B sc i chemistry i u ii ionic equilibria in aqueous solution aRai University
╠²
This document provides an overview of acids, bases, and pH. It defines acids and bases according to Arrhenius, Br├Ėnsted-Lowry, and Lewis theories. Acids are substances that produce H+ ions in water or donate protons in reactions, while bases produce OH- ions or accept protons. The document also discusses acid and base strength, pH, self-ionization of water, and examples of calculating pH from H+ concentration and vice versa. Common acids, bases, and pH indicators are listed.Acid base concept



Acid base conceptShisam Neupane
╠²
An acid is any substance that in water solution tastes sour, changes blue litmus paper to red, reacts with some metals to liberate hydrogen, reacts with bases to form salts, and promotes chemical reactions (acid catalysis).
A base is a substance that can neutralize the acid by reacting with hydrogen ions. Most bases are minerals that react with acids to form water and salts.
Salt is a chemical compound consisting of an ionic assembly of cations and anions. Bronsted Lowary Acid Base concept



Bronsted Lowary Acid Base conceptrabbiasaeed
╠²
Bronsted and Lowery proposed an acid-base theory in 1923 to overcome limitations of Arrhenius' theory. According to Bronsted-Lowery theory, an acid is a proton donor and a base is a proton acceptor. Examples of acids given are CH3COOH and H2SO4, which donate protons. NH3 acts as a base by accepting protons. Water can also act as both an acid and base, making it an amphoteric species.Reset Help By the Brnsted-Lowry definition- acids are proton donors an.docx



Reset Help By the Brnsted-Lowry definition- acids are proton donors an.docxacarolyn
╠²
Reset Help By the Br├ā┬Ėnsted-Lowry definition, acids are proton donors and bases are proton acceptors. By the Lewis definition, acids are electron-pair acceptors and bases are electron-pair donors. For bases, the two definitions are equivalent such that all Lewis bases are Br├ā┬Ėnsted-Lowry bases and vice versa However, it is possible to have a Lewis acid that is not a Br├ā┬Ėnsted-Lowry acid. This is because Lewis acids include molecules and cations that have a vacant valence orbital, regardless of whether they have a proton to donate Common examples of Lewis acids (that are not Br├ā┬Ėnsted-Lowry acids) are metal ions, such as Al+and Cu2+. The following is an example ofa Lewis acid-base reaction Lewis acids Lewis bases NH3 donates the electron pair to Cu2+. Therefore NH3 is a Lewis base, and Cu2 is a Lewis acid SubmitPrev Previous Answer
Solution
1. Lewis acids: Lewis acids are the species which accepts electrons.
SO 3 since S has only three electron domains. Hence it accepts electrons.
Fe 2+ is electron deficient. Hence it accepts electrons too.
CO 2 where C accepts electrons since it is bound to two highly electronegative oxygen atoms.
Lewis bases are species that donates electrons.
I - , CO, H - , CH 3 NH 2
2. The order of decreasing pH is:
Ba(OH) 2 > NaOH > N 2 H 4 > HOCl > HCl
Ba(OH) 2 decomposes to give 2 OH - ions. This is why it has higher pH than NaOH which decomposes to give only 1 OH - ion.
Hydrazine N 2 H 4 is basic however lesser than NaOH and Ba(OH) 2
HOCl is a weak acid that partially dissociates to give H + and ClO -
HCl is the strongest acid that completely dissociates into H + and Cl - and hence has the lowest pH.
More the H + ions in solution, lesser the pH.
More the OH - ions in solution, higher the pH.
3. Given,
[ OH - ] = 2.3 x 10 -2 M
We know that at 25 0 C,
[H + ] [OH - ] = Kw = Ionic product of water = 10 -14
Putting the value of [OH - ] in the above equation, we have,
[H + ] x 2.3 x 10 -2 = 10 -14
[H + ] = 10 -14 / (2.3 x 10 -2 )
[H + ] = 0.44 x 10 -12 M
.Final acid and bases rev.



Final acid and bases rev.North Coast medical Training College
╠²
Simplified understandable Acid and bases For nutrition and dietetics students at North Coast Medical Training.Acids & Bases



Acids & Baseszehnerm2
╠²
This document discusses acids and bases. It introduces some of their key properties including turning litmus red or blue and reacting with metals. It then discusses several theories of acids and bases:
1. Arrhenius theory which defined acids as producing H+ ions and bases as producing OH- ions in aqueous solutions.
2. Bronsted-Lowry theory which defined acids as proton donors and bases as proton acceptors. This new definition accounted for exceptions to Arrhenius theory.
3. Acids and bases are described further as conjugate acid-base pairs, amphoteric substances that can be acids or bases, and polyprotic acids that donate more than one H+.Theories of╠²Acids and Bases (Arrhenius, Bronsted and Lewis)



Theories of╠²Acids and Bases (Arrhenius, Bronsted and Lewis)Neetika Naudiyal
╠²
This ppt contains information for all the main theories of acids and bases.Acids & Bases slides



Acids & Bases slidesTimothy Welsh
╠²
This document provides an overview of acids and bases for a high school chemistry rapid learning series. It defines acids and bases based on Arrhenius, Br├Ėnsted-Lowry, and Lewis theories. It discusses strong versus weak acids and bases, and how concentrated or dilute solutions affect strength. Conjugate acids and bases are defined. Common strong acids and bases are listed. Properties of acids and bases like taste and effect on litmus are covered. The pH scale is introduced and calculating pH of strong acids and bases is demonstrated. How salts can have acidic, basic, or neutral properties is explained. Finally, buffers and how they resist pH change are described.More from shubhada walawalkar (9)
Solutions | Osmotic Pressure | 12th Chemistry | By. Mrs. Shubhada Walawalkar



Solutions | Osmotic Pressure | 12th Chemistry | By. Mrs. Shubhada Walawalkarshubhada walawalkar
╠²
It discusses about semipermeable membrane, osmosis, osmotic pressure,relation between osmotic pressure and concentration and molar mass of solute, Isotonic ,hypertonic,hypotonic solutions,Reverse osmosis.
Solutions | Freezing Point Depression | Chemistry Class 12 | By. Mrs Shubhada...



Solutions | Freezing Point Depression | Chemistry Class 12 | By. Mrs Shubhada...shubhada walawalkar
╠²
It discusses briefly about Freezing Point Depression,Relation between Freezing Point Depression and Molarity and Molar Mass of Solute and Numerical on Freezing Point Depression.Solutions | Boiling point elevation | Chemistry Class 12 | By. Mrs. Shubhada ...



Solutions | Boiling point elevation | Chemistry Class 12 | By. Mrs. Shubhada ...shubhada walawalkar
╠²
The document discusses boiling point elevation, which is when dissolving a nonvolatile solute into a solvent raises the boiling point of the solution above that of the pure solvent. It defines key terms like boiling point, vapor pressure, and explains how intermolecular forces affect boiling point. It describes how the vapor pressure-temperature curve of a solution lies below that of the pure solvent, resulting in a higher boiling point. The boiling point elevation (ΔTb) is directly proportional to molality (m) of the solution and a proportionality constant (Kb). The document gives an example problem calculating the molality of a solution from its boiling point elevation.Ionic Equilibria | Arrhenius Theory | Chemistry Class 12 | Mrs. Shubhada Wala...



Ionic Equilibria | Arrhenius Theory | Chemistry Class 12 | Mrs. Shubhada Wala...shubhada walawalkar
╠²
This video discusses about arrhenius theory of acid and base, strong acids, weak acids, neutralisation according to arrhenius theory, limitations of arrhenius theory.Ionic equilibria | chemical equilibria |Types of electrolyte |Degree of disso...



Ionic equilibria | chemical equilibria |Types of electrolyte |Degree of disso...shubhada walawalkar
╠²
It discusses about equilibrium,chemical equilibrium,ionic equilibrium,electrolytes,types of electrolyte,s degree of dissociation,percent dissociation.Solid state part 3 | Chemistry Class 12 | By Mrs. Shubhada Walawalkar



Solid state part 3 | Chemistry Class 12 | By Mrs. Shubhada Walawalkarshubhada walawalkar
╠²
This document discusses the crystal structure of solids. It defines a crystal as having both a lattice and a basis. The lattice is a regular arrangement of points in space, while the basis is a set of atoms associated with each lattice point. The unit cell is the smallest repeating unit that makes up the crystal structure when stacked together. There are four main types of unit cells: primitive, body-centered, face-centered, and base-centered. Crystals are categorized into seven crystal systems based on their lattice structures.Solid state part 2 | Chemistry Class 12 | By Mrs. Shubhada Walawalkar



Solid state part 2 | Chemistry Class 12 | By Mrs. Shubhada Walawalkarshubhada walawalkar
╠²
The document discusses the classification of crystalline solids. There are four main types of crystalline solids: 1) ionic solids which are formed from positively and negatively charged ions held together by electrostatic forces, 2) covalent network solids where atoms are linked by covalent bonds forming a rigid three-dimensional structure (examples given are different forms of carbon), 3) molecular solids where forces between molecules are weaker, and 4) metallic solids where delocalized valence electrons bind metallic atoms into a crystalline structure allowing metals to conduct electricity and heat. Each class has distinct properties depending on the type of bonds present in its crystalline structure.Solid state part 1 | Chemistry Class 12 | By Mrs. Shubhada Walawalkar



Solid state part 1 | Chemistry Class 12 | By Mrs. Shubhada Walawalkarshubhada walawalkar
╠²
The document discusses the different states of matter and types of solids. It defines the three common states of matter as solids, liquids, and gases, describing their key properties. It then describes the two main types of solids as crystalline and amorphous. Crystalline solids have a definite repeating arrangement of particles while amorphous solids lack long-range order. The document also discusses isomorphous solids that have the same structure and polymorphous solids that exist in different structures of the same substance.Solutions | Chemistry class 12 | By Mrs. Shubhada Walawalkar



Solutions | Chemistry class 12 | By Mrs. Shubhada Walawalkarshubhada walawalkar
╠²
The document discusses colligative properties of nonelectrolyte solutions, specifically vapor pressure lowering. It defines colligative properties as those that depend on the number of solute particles but not their identity. The four colligative properties are listed as vapor pressure lowering, boiling point elevation, freezing point depression, and osmotic pressure. Vapour pressure lowering occurs when a nonvolatile solute is dissolved, reducing the number of solvent molecules available at the surface for vaporization compared to pure solvent. This leads to a lower vapor pressure. The extent of lowering depends on the mole fraction of solute and is thus a colligative property. Raoult's law and calculations using mole fractions and molar masses are alsoSolutions | Freezing Point Depression | Chemistry Class 12 | By. Mrs Shubhada...



Solutions | Freezing Point Depression | Chemistry Class 12 | By. Mrs Shubhada...shubhada walawalkar
╠²
Solutions | Boiling point elevation | Chemistry Class 12 | By. Mrs. Shubhada ...



Solutions | Boiling point elevation | Chemistry Class 12 | By. Mrs. Shubhada ...shubhada walawalkar
╠²
Ionic Equilibria | Arrhenius Theory | Chemistry Class 12 | Mrs. Shubhada Wala...



Ionic Equilibria | Arrhenius Theory | Chemistry Class 12 | Mrs. Shubhada Wala...shubhada walawalkar
╠²
Ionic equilibria | chemical equilibria |Types of electrolyte |Degree of disso...



Ionic equilibria | chemical equilibria |Types of electrolyte |Degree of disso...shubhada walawalkar
╠²
Recently uploaded (20)
Inventory Reporting in Odoo 17 - Odoo 17 Inventory App



Inventory Reporting in Odoo 17 - Odoo 17 Inventory AppCeline George
╠²
This slide will helps us to efficiently create detailed reports of different records defined in its modules, both analytical and quantitative, with Odoo 17 ERP.BISNIS BERKAH BERANGKAT KE MEKKAH ISTIKMAL SYARIAH



BISNIS BERKAH BERANGKAT KE MEKKAH ISTIKMAL SYARIAHcoacharyasetiyaki
╠²
BISNIS BERKAH BERANGKAT KE MEKKAH ISTIKMAL SYARIAHASP.NET Web API Interview Questions By Scholarhat



ASP.NET Web API Interview Questions By ScholarhatScholarhat
╠²
ASP.NET Web API Interview Questions By ScholarhatAdministrative bodies( D and C Act, 1940



Administrative bodies( D and C Act, 1940P.N.DESHMUKH
╠²
These presentation include information about administrative bodies such as D.T.A.B
CDL AND DCC, etc.Helping Autistic Girls Shine Webinar ║▌║▌▀Żs



Helping Autistic Girls Shine Webinar ║▌║▌▀ŻsPooky Knightsmith
╠²
For more information about my speaking and training work, visit: https://www.pookyknightsmith.com/speaking/AI and Academic Writing, Short Term Course in Academic Writing and Publicatio...



AI and Academic Writing, Short Term Course in Academic Writing and Publicatio...Prof. (Dr.) Vinod Kumar Kanvaria
╠²
AI and Academic Writing, Short Term Course in Academic Writing and Publication, UGC-MMTTC, MANUU, 25/02/2025, Prof. (Dr.) Vinod Kumar Kanvaria, University of Delhi, vinodpr111@gmail.comAzure Administrator Interview Questions By ScholarHat



Azure Administrator Interview Questions By ScholarHatScholarhat
╠²
Azure Administrator Interview Questions By ScholarHatHow to Configure Proforma Invoice in Odoo 18 Sales



How to Configure Proforma Invoice in Odoo 18 SalesCeline George
╠²
In this slide, weŌĆÖll discuss on how to configure proforma invoice in Odoo 18 Sales module. A proforma invoice is a preliminary invoice that serves as a commercial document issued by a seller to a buyer.Interim Guidelines for PMES-DM-17-2025-PPT.pptx



Interim Guidelines for PMES-DM-17-2025-PPT.pptxsirjeromemanansala
╠²
This is the latest issuance on PMES as replacement of RPMS. Kindly message me to gain full access of the presentation. Bß╗ś TEST KIß╗éM TRA GIß╗«A K├ī 2 - TIß║ŠNG ANH 10,11,12 - CHUß║©N FORM 2025 - GLOBAL SU...



Bß╗ś TEST KIß╗éM TRA GIß╗«A K├ī 2 - TIß║ŠNG ANH 10,11,12 - CHUß║©N FORM 2025 - GLOBAL SU...Nguyen Thanh Tu Collection
╠²
https://app.box.com/s/ij1ty3vm7el9i4qfrr41o756xycbahmgOral exam Kenneth Bech - What is the meaning of strategic fit?



Oral exam Kenneth Bech - What is the meaning of strategic fit?MIPLM
╠²
Presentation of the CEIPI DU IPBA oral exam of Kenneth Bech - What is the meaning of strategic fit? Dot NET Core Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHat



Dot NET Core Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHatScholarhat
╠²
Dot NET Core Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHatAzure Data Engineer Interview Questions By ScholarHat



Azure Data Engineer Interview Questions By ScholarHatScholarhat
╠²
Azure Data Engineer Interview Questions By ScholarHatHow to Configure Deliver Content by Email in Odoo 18 Sales



How to Configure Deliver Content by Email in Odoo 18 SalesCeline George
╠²
In this slide, weŌĆÖll discuss on how to configure proforma invoice in Odoo 18 Sales module. A proforma invoice is a preliminary invoice that serves as a commercial document issued by a seller to a buyer.Blind spots in AI and Formulation Science, IFPAC 2025.pdf



Blind spots in AI and Formulation Science, IFPAC 2025.pdfAjaz Hussain
╠²
The intersection of AI and pharmaceutical formulation science highlights significant blind spotsŌĆösystemic gaps in pharmaceutical development, regulatory oversight, quality assurance, and the ethical use of AIŌĆöthat could jeopardize patient safety and undermine public trust. To move forward effectively, we must address these normalized blind spots, which may arise from outdated assumptions, errors, gaps in previous knowledge, and biases in language or regulatory inertia. This is essential to ensure that AI and formulation science are developed as tools for patient-centered and ethical healthcare.AI and Academic Writing, Short Term Course in Academic Writing and Publicatio...



AI and Academic Writing, Short Term Course in Academic Writing and Publicatio...Prof. (Dr.) Vinod Kumar Kanvaria
╠²
Bß╗ś TEST KIß╗éM TRA GIß╗«A K├ī 2 - TIß║ŠNG ANH 10,11,12 - CHUß║©N FORM 2025 - GLOBAL SU...



Bß╗ś TEST KIß╗éM TRA GIß╗«A K├ī 2 - TIß║ŠNG ANH 10,11,12 - CHUß║©N FORM 2025 - GLOBAL SU...Nguyen Thanh Tu Collection
╠²
Ionic Equilibria | Bronsted Lowry Acid Base Theory | Chemistry Class 12 | By Mrs.Shubhada Walawalkar
- 1. Chemistry Class 12 3. IONIC EQUILIBRIA Part-3 Bronsted ŌĆōLowry Theory of Acids and Bases 03-08-2020 s.s.walawalkar. 1
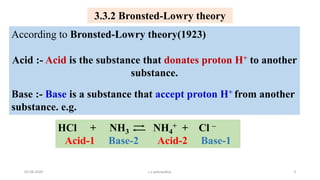
- 3. 3.3.2 Bronsted-Lowry theory According to Bronsted-Lowry theory(1923) Acid :- Acid is the substance that donates proton H+ to another substance. Base :- Base is a substance that accept proton H+ from another substance. e.g. HCl + NH3 NH4 + + Cl ŌĆō Acid-1 Base-2 Acid-2 Base-1 03-08-2020 s.s.walawalkar. 3
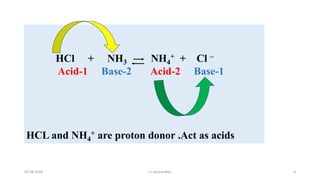
- 4. HCl + NH3 NH4 + + Cl ŌĆō Acid-1 Base-2 Acid-2 Base-1 HCL and NH4 + are proton donor .Act as acids 03-08-2020 s.s.walawalkar. 4
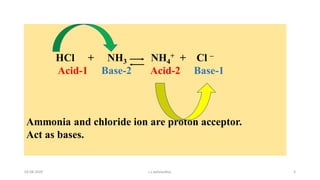
- 5. HCl + NH3 NH4 + + Cl ŌĆō Acid-1 Base-2 Acid-2 Base-1 Ammonia and chloride ion are proton acceptor. Act as bases. 03-08-2020 s.s.walawalkar. 5
- 6. Arrhenius acids are also Bronsted acids. But Arrhenius bases are not Bronsted bases. 1. HCL(aq)+ H2O(l) H3O+ + Cl- (aq) acid 1 base2 acid 2 base1 2. NH3 (aq) + H2O(l) NH4 +(aq) + OH-(aq) base2 acid 1 acid 2 base1 3. H2O(l) + CO3 2-(aq) HCO3 -(aq) + OH-(aq) acid 1 base2 acid 2 base1 4. NH4 +(aq) + H2O(l) H3O+(aq) + NH3(aq) acid 1 base2 acid 2 base1 03-08-2020 s.s.walawalkar. 6
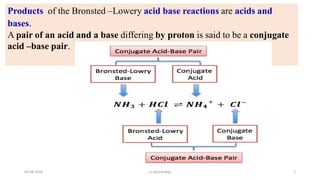
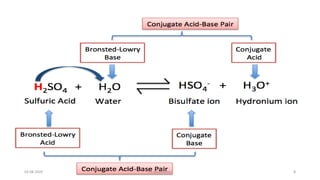
- 7. Products of the Bronsted ŌĆōLowery acid base reactions are acids and bases. A pair of an acid and a base differing by proton is said to be a conjugate acid ŌĆōbase pair. 03-08-2020 s.s.walawalkar. 7
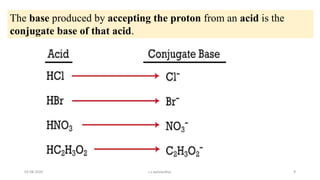
- 9. The base produced by accepting the proton from an acid is the conjugate base of that acid. 03-08-2020 s.s.walawalkar. 9
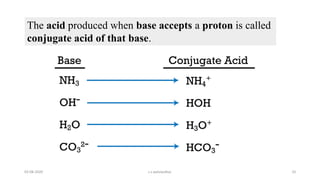
- 10. The acid produced when base accepts a proton is called conjugate acid of that base. 03-08-2020 s.s.walawalkar. 10
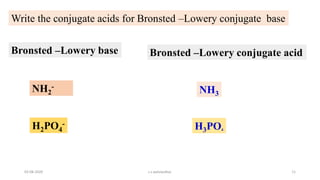
- 11. 03-08-2020 s.s.walawalkar. 11 Write the conjugate acids for Bronsted ŌĆōLowery conjugate base Bronsted ŌĆōLowery base Bronsted ŌĆōLowery conjugate acid NH2 - H2PO4 - NH3 H3PO4
- 12. 03-08-2020 s.s.walawalkar. 12 Write the conjugate acids for Bronsted ŌĆōLowery conjugate base Bronsted ŌĆōLowery acid Bronsted ŌĆōLowery conjugate base HCN H2O CN- OH-
- 13. 03-08-2020 s.s.walawalkar. 13 ŌØ¢ Points to be remember ŌØ¢ Acid= conjugate base + H+ ŌØ¢ Base + H+ = conjugate acid ŌØ¢ Each conjugate acid has one extra proton. ŌØ¢ Each conjugate base has one proton less.
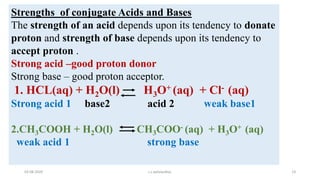
- 14. Strengths of conjugate Acids and Bases The strength of an acid depends upon its tendency to donate proton and strength of base depends upon its tendency to accept proton . Strong acid ŌĆōgood proton donor Strong base ŌĆō good proton acceptor. 1. HCL(aq) + H2O(l) H3O+ (aq) + Cl- (aq) Strong acid 1 base2 acid 2 weak base1 2.CH3COOH + H2O(l) CH3COO- (aq) + H3O+ (aq) weak acid 1 strong base 03-08-2020 s.s.walawalkar. 14
- 15. 03-08-2020 s.s.walawalkar. 15 ŌØ¢ Points to be remember Strong acid has weak conjugate base. Weak acid has strong conjugate base Strong base has weak conjugate acid. Weak base has strong conjugate acid.
- 16. Advantages of Bronsted ŌĆōLowery concept:- 1)This concept explain basic characters of substances like Na2CO3, NH3 . 2) This concept is not limited to molecules but explain acidic and basic characters of ionic species. 3) It can explain acid base reaction in the non aqueous medium. 03-08-2020 s.s.walawalkar. 16
- 17. Bronsted ŌĆōLowery concept fails to explain:- 1)Acidic substances which do not have proton e.g ALCl3 , BF3 2)Reaction between acidic oxides and basic oxides. CaO + SO3 ŌåÆ CaSO4 03-08-2020 s.s.walawalkar. 17







