ipv6 presentation by Rahul uit BU
Download as pptx, pdf1 like342 views
Internet Protocol (IP) delivers packets between hosts using IP addresses. IP version 4 and 6 are the main versions, with IPv6 addressing increasing the address space to 128 bits. IPv6 addresses are classified as unicast for a single interface, anycast for a group of interfaces, or multicast for multiple hosts. IPv6 supports routing protocols and provides benefits over IPv4 like larger addressing, simpler headers, and improved security. Major organizations like Cisco and the U.S. Census Bureau are transitioning networks to IPv6 as IPv4 addresses become depleted.
1 of 14
Download to read offline











Ad
Recommended
Ipv4 and Ipv6
Ipv4 and Ipv6Kinza Razzaq
╠²
IPv4 uses 32-bit addresses which limits the total number of available addresses to around 4 billion, whereas IPv6 was developed to support the continued growth of the internet using 128-bit addresses providing trillions of addresses to meet future demand. IPv4 routes most current internet traffic and assigns each device a unique numerical IP address, while IPv6 offers improvements and was created by IETF to address the looming problem of IPv4 address exhaustion.IPv4 and IPv6
IPv4 and IPv6saurav kumar mourya
╠²
IPv4 and IPv6 are different versions of the Internet Protocol. IPv4 uses 32-bit addresses which limits the available number of unique addresses, while IPv6 expanded the address space to 128 bits to accommodate many more devices. IPv6 was developed to replace IPv4 and resolve issues like its diminishing available address space as more devices connect to the internet. Some key differences are that IPv6 addresses are much longer at 128 bits compared to 32 bits for IPv4, IPv6 has a larger address space to allow for more connections, and security features like IPSec are mandatory in IPv6.Internet protocol v6
Internet protocol v6Pramith P
╠²
IPv6 was developed to address the impending exhaustion of IPv4 addresses. It uses 128-bit addresses compared to IPv4's 32-bit addresses, providing vastly more unique addresses. IPv6 simplifies address assignment, network renumbering, and router announcements. It also implements additional features like improved security via IPsec. While the transition to IPv6 presents challenges, it is necessary to support future internet growth given IPv4's limited address space.Ipv4 and Ipv6
Ipv4 and Ipv6Rishav Bhurtel
╠²
This document provides information about IPv4 and IPv6 by comparing their key aspects. IPv4 uses 32-bit addresses while IPv6 uses 128-bit addresses, allowing for more available addresses. IPv4 addresses are represented in dotted decimal notation while IPv6 uses colon-separated hexadecimal. IPv6 was developed to address limitations in IPv4 such as address space exhaustion and lack of security features. The document outlines differences between the two protocols in areas like packet fragmentation, checksums, and address types.IPv4 and IPv6
IPv4 and IPv6Muhammad Ibrar
╠²
This document discusses IPV4 and IPV6. It begins by defining what an IP address is and how they are distributed. It then explains the uses of IP addresses and the two main types: IPv4 and IPv6. IPv4 uses 32-bit addresses represented in decimal form, while IPv6 uses 128-bit addresses in hexadecimal form. The document outlines the classes, types, and terminologies associated with IPv4, and how IPv6 aims to address the exhaustion of IPv4 addresses by supporting a vastly larger number of unique addresses. It concludes by discussing challenges around the deployment of IPv6.IPv4 VS IPv6
IPv4 VS IPv6Humayra Khanum
╠²
This presentation compares IPv4 and IPv6. It begins with introductions of the group members and defines IP as an Internet Protocol address assigned to devices connected to a network. It then discusses the evolution of IP versions from IPv1 to the current IPv6. Key details provided include that IPv4 uses 32-bit addresses limiting its capacity while IPv6 uses 128-bit addresses allowing for vast expansion. The presentation outlines advantages and limitations of IPv4 and reasons for the development of IPv6, including the growing shortage of IPv4 addresses. It clarifies that IPv4 and IPv6 are not compatible but can co-exist on networks using dual stack technology.Ipv4 and Ipv6
Ipv4 and Ipv6rahul kundu
╠²
The document discusses IP addresses and the differences between IPv4 and IPv6. It defines what an IP address is and explains the classes of IPv4 addresses including Class A, B, C, D and E. It also defines IPv6, noting it uses 128-bit addresses represented by 8 groups of hexadecimal digits separated by colons. The key differences between IPv4 and IPv6 are that IPv4 uses 32-bit addresses in dot-decimal notation while IPv6 uses 128-bit addresses in hexadecimal colon-separated notation and has a much larger address space.Future protocol IP v6
Future protocol IP v6Manesh Sharma
╠²
The document discusses the development and features of Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6). It describes how IPv4 addresses are running out due to the exponential growth of the Internet. IPv6 was developed to address this by providing a huge number of IP addresses through the use of 128-bit addresses. IPv6 also aims to improve security and support new technologies such as mobile devices and the Internet of Things. The document outlines several key features of IPv6 such as improved address space, auto-configuration, built-in security, and support for mobility.ipv6 ppt
ipv6 pptShiva Kumar
╠²
This document provides an overview of IPv6, including:
- The need for IPv6 due to the depletion of IPv4 addresses and limitations of IPv4's classful addressing.
- Techniques used to extend IPv4 like subnetting, CIDR, and NAT.
- Key features of IPv6 like its larger 128-bit address space, stateless autoconfiguration, and security improvements.
- Differences between IPv4 and IPv6 headers and IPv6's use of extension headers.
- The presentation concludes that IPv6 builds upon IPv4's foundations but addresses its limitations.Comparison between ipv4 and ipv6
Comparison between ipv4 and ipv6Dharmesh Patel
╠²
IPv4 uses 32-bit addresses and has a limited address space, while IPv6 uses 128-bit addresses and has a much larger address space to support more devices. IPv6 integrates network security directly into its design using IPSec and uses extension headers to encode optional information. It also features stateless address autoconfiguration to simplify configuration, and allows communication with IPv4 nodes through mapping and tunneling.Ipv4 & ipv6
Ipv4 & ipv6Amit Kundu
╠²
The document discusses IP addresses and the differences between IPv4 and IPv6. It defines what an IP address is, its uses, and the classes and addressing in IPv4. It describes problems with IPv4 like limited address space. It then defines IPv6 addressing which uses 128-bit addresses written in hexadecimal, and types of IPv6 addresses. It lists advantages of IPv6 like larger address space and built-in security. Tables compare features of IPv4 and IPv6 like address space, header fields, and representation.IPv6 Fundamentals
IPv6 FundamentalsMatt Bynum
╠²
This document provides an overview of IPv6 fundamentals, including:
- Key differences between IPv4 and IPv6 such as larger addressing space and elimination of NAT.
- Details of the IPv6 header format and use of extension headers for additional functions.
- The IPv6 addressing architecture including the various address types and formats.
- Protocols for autoconfiguration, neighbor discovery, and multicast in IPv6 networks.IPv6 next generation protocol
IPv6 next generation protocolRupshanker Mishra
╠²
IPv6 is the most recent version of the Internet Protocol. It features a 128-bit address space, compared to 32 bits in IPv4, allowing for many more IP addresses. IPv6 also includes features like stateless autoconfiguration of hosts, plug and play capability, built-in IP security, and mobility. Transition mechanisms like dual stacking, tunneling, and translation are needed for IPv6 hosts to communicate with IPv4 networks during the transition period. Most modern operating systems and applications now support IPv6.IPV4 vs IPV6
IPV4 vs IPV6Devang Doshi
╠²
This document compares and contrasts IPv4 and IPv6. It begins by defining Internet Protocol (IP) and its purpose of identifying hosts and enabling location addressing. It then describes IPv4, including its 32-bit address structure, address notation, and class-based allocation that resulted in address exhaustion issues. The document also covers IPv6's 128-bit addresses that provide vastly more capacity to address this problem. Key differences between IPv4 and IPv6 are outlined, such as IPv6's elimination of NAT. The concepts of subnetting, supernetting, and private address ranges are also introduced to optimize IPv4 network design.IPv4 vs IPv6
IPv4 vs IPv6NetProtocol Xpert
╠²
IPv4 uses 32-bit addresses represented in decimals, while IPv6 uses 128-bit addresses represented in hexadecials. IPv6 has built-in IPSec support, packet flow identification, and address auto-configuration, whereas IPv4 has optional IPSec, no packet identification, and requires manual or dynamic configuration. Other differences include IPv6 eliminating broadcast messages, checksum fields, and options fields, while IPv4 supports fragmentation by routers and uses ARP and IGMP which are replaced by NDP and MLD in IPv6.Ipv4 & ipv6
Ipv4 & ipv6urooj ehsan
╠²
IPv4 is a widely used, connectionless internet protocol employing 32-bit addresses organized into five classes. It is increasingly limited by address scarcity, leading to the development of IPv6, which utilizes 128-bit addresses to potentially accommodate a vastly larger number of devices. IPv6 is not backward compatible with IPv4 but shares similar fundamentals and is designed to meet the expanding needs of internet connectivity.Internet Protocol version 6
Internet Protocol version 6Rekha Yadav
╠²
The document discusses Internet Protocol Version 6 (IPv6) and compares it to IPv4, addressing issues like IP address depletion and classful addressing inefficiencies. It highlights IPv6 features such as a larger address space, improved header efficiency, and mandatory security measures, along with techniques like subnetting, Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR), and Network Address Translation (NAT) to optimize IP address usage. The conclusion emphasizes that IPv6 builds on the foundations of IPv4 while introducing enhanced capabilities and configurations.Internet Protocol Version 6
Internet Protocol Version 6sandeepjain
╠²
IPv6 is the next generation Internet protocol that replaces IPv4. It features a vastly larger 128-bit address space to avoid future address exhaustion. IPv6 addresses are written as eight groups of four hexadecimal digits separated by colons and supports stateless autoconfiguration of hosts and other improvements over IPv4.Internet Protocol Version 6 By Suvo 2002
Internet Protocol Version 6 By Suvo 2002suvobgd
╠²
IPv6 is the next-generation Internet protocol that replaces IPv4. It features a 128-bit address size allowing for many more IP addresses compared to IPv4's 32-bit addresses. IPv6 also includes improvements in routing, network autoconfiguration, security, quality of service, and extensibility. A transition from IPv4 to IPv6 is underway using mechanisms like dual stacking that allow both protocols to coexist on networks. While not yet widely deployed, IPv6 is expected to fully replace IPv4 in the coming years.I pv4 vs ipv6
I pv4 vs ipv6liiramlkprov
╠²
IPv4 and IPv6 are different versions of the Internet Protocol. IPv4 uses 32-bit addresses which limits the available number of addresses to around 4 billion, while IPv6 uses 128-bit addresses allowing for a vast number of available addresses. Some techniques were used to extend IPv4 such as subnetting and NAT, but IPv6 was developed to provide a long-term solution and overcome IPv4's scaling limitations. IPv6 improves upon IPv4 in areas such as efficiency, security, auto-configuration, and header structure. Widespread adoption of IPv6 has been slowed due to compatibility issues and costs of upgrading systems.Ip4 vs ip6
Ip4 vs ip6Mani Singh
╠²
IPv4 was first developed in 1978 and has been deployed globally but will soon run out of addresses as it only provides 4 billion addresses. IPv6 was developed in 1993 to replace IPv4 and provides an immense 340 undecillion addresses to accommodate continued growth of the internet. IPv6 improves on IPv4 with a larger 128-bit address size, built-in security features, and auto-configuration to simplify network management. While IPv6 has been available since 1999, many networks and devices still rely on IPv4, but further IPv6 adoption will be necessary to sustain long term growth of internet connectivity.Basic of IPv6
Basic of IPv6Jubin Aghara
╠²
This document provides an overview of IPv6 basics including:
- The need for IPv6 due to the depletion of IPv4 addresses with the rise of Internet of Things devices.
- IPv6 uses a 128-bit address format composed of 8 groups of 4 hexadecimal digits separated by colons.
- IPv6 addresses are categorized into different types including link-local, unique local, and global unicast addresses.
- IPv6 uses prefix lengths like CIDR notation to represent prefixes and subnets are based on dividing the 64-bit prefix.
- IPv6 addresses can be auto-configured using EUI-64 or randomly generated interface IDs, and DHCPv6 can assign addresses and options.IPv6: Internet Protocol version 6
IPv6: Internet Protocol version 6Ankita Mahajan
╠²
IPv6 addresses are 128-bit identifiers for interfaces compared to 32-bit in IPv4. The presentation discusses the various address formats and types in IPv6 including unicast, anycast, and multicast. It also covers the changes in IPv6 packet header format versus IPv4 as well as new features like flow labeling and extension headers. Key advantages of IPv6 are larger address space, simplified header format, improved support for extensions, and better mobility and security features.IPV6 Addressing
IPV6 Addressing Heba_a
╠²
This document provides an overview of IPv6 addressing and address types. It discusses the 128-bit IPv6 address space and address notation. The main types of IPv6 addresses covered are unicast addresses, including global unicast, link-local, and unique local addresses, as well as multicast addresses and their uses for neighbor discovery. Solicited-node addresses are described as a method for IPv6 nodes to resolve link-layer addresses without broadcasting.IPV6 Introduction
IPV6 Introduction Heba_a
╠²
This document provides an introduction to IPv6, including an overview of its key features and differences from IPv4. It discusses how IPv6 was developed to address the exhaustion of IPv4 address space and larger routing tables. The core features covered are the new IPv6 header format, its large 128-bit address space, stateless and stateful address configuration, built-in security via IPsec, and improved support for areas like quality of service and network interactions through protocols like Neighbor Discovery.Ipv4
Ipv4asimnawaz54
╠²
Internet Protocol (IP) is used to carry data from source to destination hosts across the Internet by providing addressing, fragmentation and reassembly, packet timeouts, and prioritization of traffic. IP uses 32-bit addresses to identify sending and receiving hosts and allows packets to be split into smaller fragments if needed to travel across networks. Routers use the IP Time to Live field to discard packets that have been traveling too long to prevent flooding of networks.IPv6 - The Next next generation protocol
IPv6 - The Next next generation protocolMohit Sharma
╠²
The document discusses IPv6, the successor to IPv4, highlighting its features such as a larger address space of 128 bits, enhanced security, and improved network management. It compares IPv4 and IPv6 in terms of packet structure, address allocation, and routing efficiency while also detailing the benefits and challenges of transitioning from IPv4 to IPv6. Additionally, it mentions the initiatives taken in India for IPv6 deployment and education.MAC & IP addresses
MAC & IP addressesNetProtocol Xpert
╠²
A MAC address is a 48-bit hardware address that uniquely identifies network interfaces for communication in an Ethernet network. It is stored in the network card's firmware and is usually written as 12 hexadecimal digits separated by hyphens. An IP address is a 32-bit logical address that identifies a device on an IP network and can be configured manually or automatically via DHCP. Private IP address ranges like 10.0.0.0/8 and 192.168.0.0/16 are non-routable and used for local area networks.IP Address
IP AddressRahul P
╠²
The document provides a comprehensive overview of IP addresses, explaining their purpose, different types (private, public, static, dynamic), and classifications (classes A to E). It discusses the structure of IPv4 and IPv6 addresses, highlighting their differences, including address length and representation. Additionally, it covers the organization of the IP address space and the assignment of addresses, emphasizing the transition from IPv4 to IPv6 due to address exhaustion.Introduction to IPv6
Introduction to IPv6Sara Q. Abedulridha
╠²
The document provides a comprehensive overview of IPv6, detailing its features, advantages over IPv4, address types, header structure, and address modes. It highlights IPv6's larger address space, simplified routing, enhanced security features, and various address configurations, including unicast, multicast, and anycast. Additionally, it covers IPv6 address abbreviation rules, the importance of auto-configuration, and the transition from IPv4 to IPv6.More Related Content
What's hot (20)
ipv6 ppt
ipv6 pptShiva Kumar
╠²
This document provides an overview of IPv6, including:
- The need for IPv6 due to the depletion of IPv4 addresses and limitations of IPv4's classful addressing.
- Techniques used to extend IPv4 like subnetting, CIDR, and NAT.
- Key features of IPv6 like its larger 128-bit address space, stateless autoconfiguration, and security improvements.
- Differences between IPv4 and IPv6 headers and IPv6's use of extension headers.
- The presentation concludes that IPv6 builds upon IPv4's foundations but addresses its limitations.Comparison between ipv4 and ipv6
Comparison between ipv4 and ipv6Dharmesh Patel
╠²
IPv4 uses 32-bit addresses and has a limited address space, while IPv6 uses 128-bit addresses and has a much larger address space to support more devices. IPv6 integrates network security directly into its design using IPSec and uses extension headers to encode optional information. It also features stateless address autoconfiguration to simplify configuration, and allows communication with IPv4 nodes through mapping and tunneling.Ipv4 & ipv6
Ipv4 & ipv6Amit Kundu
╠²
The document discusses IP addresses and the differences between IPv4 and IPv6. It defines what an IP address is, its uses, and the classes and addressing in IPv4. It describes problems with IPv4 like limited address space. It then defines IPv6 addressing which uses 128-bit addresses written in hexadecimal, and types of IPv6 addresses. It lists advantages of IPv6 like larger address space and built-in security. Tables compare features of IPv4 and IPv6 like address space, header fields, and representation.IPv6 Fundamentals
IPv6 FundamentalsMatt Bynum
╠²
This document provides an overview of IPv6 fundamentals, including:
- Key differences between IPv4 and IPv6 such as larger addressing space and elimination of NAT.
- Details of the IPv6 header format and use of extension headers for additional functions.
- The IPv6 addressing architecture including the various address types and formats.
- Protocols for autoconfiguration, neighbor discovery, and multicast in IPv6 networks.IPv6 next generation protocol
IPv6 next generation protocolRupshanker Mishra
╠²
IPv6 is the most recent version of the Internet Protocol. It features a 128-bit address space, compared to 32 bits in IPv4, allowing for many more IP addresses. IPv6 also includes features like stateless autoconfiguration of hosts, plug and play capability, built-in IP security, and mobility. Transition mechanisms like dual stacking, tunneling, and translation are needed for IPv6 hosts to communicate with IPv4 networks during the transition period. Most modern operating systems and applications now support IPv6.IPV4 vs IPV6
IPV4 vs IPV6Devang Doshi
╠²
This document compares and contrasts IPv4 and IPv6. It begins by defining Internet Protocol (IP) and its purpose of identifying hosts and enabling location addressing. It then describes IPv4, including its 32-bit address structure, address notation, and class-based allocation that resulted in address exhaustion issues. The document also covers IPv6's 128-bit addresses that provide vastly more capacity to address this problem. Key differences between IPv4 and IPv6 are outlined, such as IPv6's elimination of NAT. The concepts of subnetting, supernetting, and private address ranges are also introduced to optimize IPv4 network design.IPv4 vs IPv6
IPv4 vs IPv6NetProtocol Xpert
╠²
IPv4 uses 32-bit addresses represented in decimals, while IPv6 uses 128-bit addresses represented in hexadecials. IPv6 has built-in IPSec support, packet flow identification, and address auto-configuration, whereas IPv4 has optional IPSec, no packet identification, and requires manual or dynamic configuration. Other differences include IPv6 eliminating broadcast messages, checksum fields, and options fields, while IPv4 supports fragmentation by routers and uses ARP and IGMP which are replaced by NDP and MLD in IPv6.Ipv4 & ipv6
Ipv4 & ipv6urooj ehsan
╠²
IPv4 is a widely used, connectionless internet protocol employing 32-bit addresses organized into five classes. It is increasingly limited by address scarcity, leading to the development of IPv6, which utilizes 128-bit addresses to potentially accommodate a vastly larger number of devices. IPv6 is not backward compatible with IPv4 but shares similar fundamentals and is designed to meet the expanding needs of internet connectivity.Internet Protocol version 6
Internet Protocol version 6Rekha Yadav
╠²
The document discusses Internet Protocol Version 6 (IPv6) and compares it to IPv4, addressing issues like IP address depletion and classful addressing inefficiencies. It highlights IPv6 features such as a larger address space, improved header efficiency, and mandatory security measures, along with techniques like subnetting, Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR), and Network Address Translation (NAT) to optimize IP address usage. The conclusion emphasizes that IPv6 builds on the foundations of IPv4 while introducing enhanced capabilities and configurations.Internet Protocol Version 6
Internet Protocol Version 6sandeepjain
╠²
IPv6 is the next generation Internet protocol that replaces IPv4. It features a vastly larger 128-bit address space to avoid future address exhaustion. IPv6 addresses are written as eight groups of four hexadecimal digits separated by colons and supports stateless autoconfiguration of hosts and other improvements over IPv4.Internet Protocol Version 6 By Suvo 2002
Internet Protocol Version 6 By Suvo 2002suvobgd
╠²
IPv6 is the next-generation Internet protocol that replaces IPv4. It features a 128-bit address size allowing for many more IP addresses compared to IPv4's 32-bit addresses. IPv6 also includes improvements in routing, network autoconfiguration, security, quality of service, and extensibility. A transition from IPv4 to IPv6 is underway using mechanisms like dual stacking that allow both protocols to coexist on networks. While not yet widely deployed, IPv6 is expected to fully replace IPv4 in the coming years.I pv4 vs ipv6
I pv4 vs ipv6liiramlkprov
╠²
IPv4 and IPv6 are different versions of the Internet Protocol. IPv4 uses 32-bit addresses which limits the available number of addresses to around 4 billion, while IPv6 uses 128-bit addresses allowing for a vast number of available addresses. Some techniques were used to extend IPv4 such as subnetting and NAT, but IPv6 was developed to provide a long-term solution and overcome IPv4's scaling limitations. IPv6 improves upon IPv4 in areas such as efficiency, security, auto-configuration, and header structure. Widespread adoption of IPv6 has been slowed due to compatibility issues and costs of upgrading systems.Ip4 vs ip6
Ip4 vs ip6Mani Singh
╠²
IPv4 was first developed in 1978 and has been deployed globally but will soon run out of addresses as it only provides 4 billion addresses. IPv6 was developed in 1993 to replace IPv4 and provides an immense 340 undecillion addresses to accommodate continued growth of the internet. IPv6 improves on IPv4 with a larger 128-bit address size, built-in security features, and auto-configuration to simplify network management. While IPv6 has been available since 1999, many networks and devices still rely on IPv4, but further IPv6 adoption will be necessary to sustain long term growth of internet connectivity.Basic of IPv6
Basic of IPv6Jubin Aghara
╠²
This document provides an overview of IPv6 basics including:
- The need for IPv6 due to the depletion of IPv4 addresses with the rise of Internet of Things devices.
- IPv6 uses a 128-bit address format composed of 8 groups of 4 hexadecimal digits separated by colons.
- IPv6 addresses are categorized into different types including link-local, unique local, and global unicast addresses.
- IPv6 uses prefix lengths like CIDR notation to represent prefixes and subnets are based on dividing the 64-bit prefix.
- IPv6 addresses can be auto-configured using EUI-64 or randomly generated interface IDs, and DHCPv6 can assign addresses and options.IPv6: Internet Protocol version 6
IPv6: Internet Protocol version 6Ankita Mahajan
╠²
IPv6 addresses are 128-bit identifiers for interfaces compared to 32-bit in IPv4. The presentation discusses the various address formats and types in IPv6 including unicast, anycast, and multicast. It also covers the changes in IPv6 packet header format versus IPv4 as well as new features like flow labeling and extension headers. Key advantages of IPv6 are larger address space, simplified header format, improved support for extensions, and better mobility and security features.IPV6 Addressing
IPV6 Addressing Heba_a
╠²
This document provides an overview of IPv6 addressing and address types. It discusses the 128-bit IPv6 address space and address notation. The main types of IPv6 addresses covered are unicast addresses, including global unicast, link-local, and unique local addresses, as well as multicast addresses and their uses for neighbor discovery. Solicited-node addresses are described as a method for IPv6 nodes to resolve link-layer addresses without broadcasting.IPV6 Introduction
IPV6 Introduction Heba_a
╠²
This document provides an introduction to IPv6, including an overview of its key features and differences from IPv4. It discusses how IPv6 was developed to address the exhaustion of IPv4 address space and larger routing tables. The core features covered are the new IPv6 header format, its large 128-bit address space, stateless and stateful address configuration, built-in security via IPsec, and improved support for areas like quality of service and network interactions through protocols like Neighbor Discovery.Ipv4
Ipv4asimnawaz54
╠²
Internet Protocol (IP) is used to carry data from source to destination hosts across the Internet by providing addressing, fragmentation and reassembly, packet timeouts, and prioritization of traffic. IP uses 32-bit addresses to identify sending and receiving hosts and allows packets to be split into smaller fragments if needed to travel across networks. Routers use the IP Time to Live field to discard packets that have been traveling too long to prevent flooding of networks.IPv6 - The Next next generation protocol
IPv6 - The Next next generation protocolMohit Sharma
╠²
The document discusses IPv6, the successor to IPv4, highlighting its features such as a larger address space of 128 bits, enhanced security, and improved network management. It compares IPv4 and IPv6 in terms of packet structure, address allocation, and routing efficiency while also detailing the benefits and challenges of transitioning from IPv4 to IPv6. Additionally, it mentions the initiatives taken in India for IPv6 deployment and education.MAC & IP addresses
MAC & IP addressesNetProtocol Xpert
╠²
A MAC address is a 48-bit hardware address that uniquely identifies network interfaces for communication in an Ethernet network. It is stored in the network card's firmware and is usually written as 12 hexadecimal digits separated by hyphens. An IP address is a 32-bit logical address that identifies a device on an IP network and can be configured manually or automatically via DHCP. Private IP address ranges like 10.0.0.0/8 and 192.168.0.0/16 are non-routable and used for local area networks.Similar to ipv6 presentation by Rahul uit BU (20)
IP Address
IP AddressRahul P
╠²
The document provides a comprehensive overview of IP addresses, explaining their purpose, different types (private, public, static, dynamic), and classifications (classes A to E). It discusses the structure of IPv4 and IPv6 addresses, highlighting their differences, including address length and representation. Additionally, it covers the organization of the IP address space and the assignment of addresses, emphasizing the transition from IPv4 to IPv6 due to address exhaustion.Introduction to IPv6
Introduction to IPv6Sara Q. Abedulridha
╠²
The document provides a comprehensive overview of IPv6, detailing its features, advantages over IPv4, address types, header structure, and address modes. It highlights IPv6's larger address space, simplified routing, enhanced security features, and various address configurations, including unicast, multicast, and anycast. Additionally, it covers IPv6 address abbreviation rules, the importance of auto-configuration, and the transition from IPv4 to IPv6.IPv6.pptx
IPv6.pptxssuser436067
╠²
IPv6 was created as a replacement for IPv4 to address its shortcomings like limited address space. IPv6 uses 128-bit addresses compared to 32-bit in IPv4, allowing for a vastly larger number of available addresses. It was designed with features like auto-configuration, IPsec security, prioritization support, and mobility in mind. The IPv6 header was also simplified compared to IPv4 to enable faster routing while still providing necessary routing information.IPV6
IPV6 Arnold Derrick Kinney
╠²
The document discusses IPv6, the next generation internet protocol. It introduces IPv6, describing its benefits over IPv4 including vastly larger address space. It then covers key aspects of IPv6 such as address types, auto-configuration, routing protocols, and technology scope. IPv6 aims to meet growing internet demands through expanded addressing and more efficient headers.mohammad.ppt jahsjajajajajajwjjwjwjwjajajaja
mohammad.ppt jahsjajajajajajwjjwjwjwjajajajaavishkarborule1
╠²
The document provides an overview of the transition from IPv4 to IPv6, highlighting the limitations of the current IPv4 addressing scheme and introducing Network Address Translation (NAT) as a solution for address conservation. It discusses the structure and components of IPv4 addresses, the need for NAT in converting private addresses to public ones, and the features and specifications of IPv6, including its expanded addressing capabilities and simplified header format. Additionally, it covers various address types in IPv6 and the mechanisms for transitioning between IPv4 and IPv6 networks.Ip seminar
Ip seminarYonasMegersa1
╠²
An IP address is a numerical label assigned to each device connected to a computer network using the Internet Protocol. There are two main versions in use today - IPv4 uses 32-bit addresses while IPv6 uses 128-bit addresses due to the depletion of IPv4 addresses. IP addresses can be static or dynamically assigned using DHCP. Private IP address ranges are reserved for use within private networks and are not routed on the public internet.I pv4 and ipv6
I pv4 and ipv6manirajan12
╠²
The document outlines key concepts related to IPv4 and IPv6 including:
- IPv4 uses 32-bit addresses and IPv6 uses 128-bit addresses. IPv6 simplifies the header format and introduces extension headers.
- It describes IP address classes in IPv4 and differences between IPv4 and IPv6 addressing schemes, header formats, and features like built-in security.
- Transitioning from IPv4 to IPv6 poses challenges around increased management complexity, interoperability problems, and security concerns due to shared communication resources between the protocols.Index
Indexkamalmishra1105
╠²
An IP address is a numerical label assigned to devices participating in a computer network using the Internet Protocol. There are two main versions: IPv4 uses 32-bit addresses while IPv6 uses 128-bit addresses due to anticipated growth. IP addresses have two main functions - identification and location addressing. Various address ranges are reserved for private networks or autoconfiguration to avoid address depletion.Index
Indexkamalmishra1105
╠²
An IP address is a numerical label assigned to devices participating in a computer network using the Internet Protocol. There are two main versions: IPv4 uses 32-bit addresses while IPv6 uses 128-bit addresses due to anticipated growth. IP addresses have two main functions - identification and location addressing. They are administered globally by IANA and regionally by RIRs.IPv6 Addressing Architecture
IPv6 Addressing ArchitectureShreehari Dhat
╠²
The document provides an overview of IPv6 including key terminology, differences from IPv4, IPv6 addressing architecture, packet format, and configuration on Windows and Linux. It describes the larger 128-bit address space of IPv6 compared to IPv4 and how IPv6 addresses different address types including unicast, multicast, and anycast. It also outlines how to generate link-local addresses from MAC addresses and configure IPv6 networking on different operating systems.Ccna1v3 Mod09
Ccna1v3 Mod09aqeelhaider74
╠²
The document provides an overview of TCP/IP protocol suite and IP addressing. It describes the layers of the TCP/IP model including application, transport, internet and network access layers. It also discusses obtaining IP addresses through static and dynamic methods like DHCP, RARP, BOOTP and ARP. IPv4 and IPv6 addressing are also summarized.Networking presentation 9 march 2009
Networking presentation 9 march 2009Kinshook Chaturvedi
╠²
The document provides an introduction to computer networks and covers several key topics:
- It describes common networking protocols like TCP/IP and compares IPv4 and IPv6 addressing schemes.
- It explains IP addressing formats including classes A, B, C, D and E and how routing is used to transmit packets across networks.
- Interior and exterior routing protocols are defined, including examples like RIP, OSPF, BGP, and IS-IS.
- The roles of the Domain Name System (DNS) in mapping names to network resources and its hierarchical namespace are outlined.Internet of things notes IPv4 VS IPv6.pdf
Internet of things notes IPv4 VS IPv6.pdfutkarshlodhi4
╠²
The document outlines the differences and advantages of IPv6 over IPv4, emphasizing the need for a larger address space due to the increasing number of internet-connected devices. It covers technical aspects such as address formats, packet headers, neighbor discovery, autoconfiguration, and security measures within IPv6. The document also discusses the challenges faced during the transition from IPv4 to IPv6 and provides answers to common questions regarding the protocols.Ipv6
Ipv6PrachiSharma304
╠²
IPv6 is the newest version of the Internet Protocol that provides a 128-bit addressing system to replace IPv4 and address the problem of looming address exhaustion, featuring a vastly expanded address space, simplified header format, and security improvements to meet future networking needs. It was developed by the IETF and became an internet standard in 2017 to support continued growth of devices connected to the internet by providing trillions of addresses for devices using hexadecimal notation groups separated by colons.Networking
NetworkingRashmi
╠²
The document provides information about Cisco Certified Network Associate certification and networking concepts like network types, topologies, devices, IP addressing, routing, and static route configuration. It includes definitions of LAN, WAN, bus, star, ring, mesh topologies and network devices like NIC, hub, switch, router. It also summarizes the OSI model layers, IP address classes, NAT, router components, modes, static and dynamic routing. The end includes a sample static routing configuration project.Why We Need IPv6
Why We Need IPv6Netwax Lab
╠²
IPv6 is the latest version of the Internet Protocol, developed to address the limitations of IPv4, particularly the issue of address exhaustion. It uses 128-bit addresses, allowing for a vastly larger number of unique IP addresses compared to the 32-bit system of IPv4. IPv6 also offers improvements such as enhanced routing efficiency, simplified packet handling, and the elimination of the need for Network Address Translation (NAT).subneting-cnnnnnnnnccccccccccccccccc.pdf
subneting-cnnnnnnnnccccccccccccccccc.pdfmohammedalhato12345
╠²
The document provides an overview of IPv6 addressing, detailing the structure, representation, and types of IPv6 addresses. It covers key rules for writing IPv6 addresses including omitting leading zeros and using double colons for zero segments, as well as describing unicast, multicast, and anycast address types. Additionally, it explains the components of a global unicast address, such as the global routing prefix, subnet ID, and interface ID.Describe the similarities and differences between IPv4 & IPv6.So.pdf
Describe the similarities and differences between IPv4 & IPv6.So.pdfmayorothenguyenhob69
╠²
IPv4 and IPv6 are both internet protocols enabling device communication, with IPv4 using 32-bit addresses and supporting approximately 4.29 billion unique IPs, while IPv6 uses 128-bit addresses to accommodate the growing number of devices. Key differences include IPv6's built-in IPSec support, absence of a checksum field, and features like packet flow identification and auto-configuration of addresses. IPv6 also replaces certain protocols and functions, including the transition from ARP to NDP and the use of multicast listener discovery instead of IGMP.Ipv4 over ipv6 by Jigar Tarsariya
Ipv4 over ipv6 by Jigar TarsariyaJigar Tarsariya
╠²
This document provides an overview of IPv4 and IPv6. It discusses that IPv4 uses 32-bit addresses and is running out of available addresses, while IPv6 uses 128-bit addresses providing vastly more address space. IPv6 was developed to replace IPv4 and improves on areas like security, quality of service, and mobility. The document compares features of IPv4 and IPv6 such as address syntax, header fields, and configuration methods.IPv4.pdf
IPv4.pdfSravanKosaraju1
╠²
This document provides information about the CS352 course on Internetworking Protocols. It discusses the topics that will be covered in Unit III, including IPv6 transition issues, IPsec, addressing, extension headers, routing, autoconfiguration, and more. It lists the course instructor and their details. It then provides background on problems with IPv4 and advantages of IPv6. Several sections define IPv6 headers and addressing, describing the fixed header, extension headers, address notation, and network/node addressing splits.Ad
ipv6 presentation by Rahul uit BU
- 2. Internet Protocol:- IP, as the primary protocol in the Internet layer of the Internet protocol suite, has the task of delivering packets from the source host to the destination host solely based on the IP addresses in the packet headers. IP Addressing:- An Internet Protocol address (IP address) is a numerical label assigned to each device (e.g., computer, printer) participating in a computer network that uses the Internet Protocol for communication. Introduction
- 3. IP Version:- Two versions of the Internet Protocol (IP) are in use: ’ü▒ IP Version 4
- 4. ’ü▒ IP Version 6
- 5. An Internet Protocol Version 6 address (IPv6 address) is a numerical label that is used to identify a network interface of a computer or other network node participating in an IPv6 computer network. IP v6
- 6. Unicast A unicast address identifies a single network interface Anycast An anycast address is assigned to a group of interfaces Multicast A multicast address is also used by multiple hosts IP v6 address classes
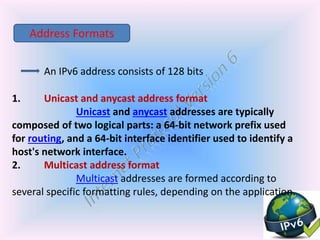
- 7. An IPv6 address consists of 128 bits 1. Unicast and anycast address format Unicast and anycast addresses are typically composed of two logical parts: a 64-bit network prefix used for routing, and a 64-bit interface identifier used to identify a host's network interface. 2. Multicast address format Multicast addresses are formed according to several specific formatting rules, depending on the application. Address Formats
- 8. Unicast and anycast address format:- Note:-Routing prefix size varies bits 48(or more) 16(or fewer) 64 field routing prefix Subnet id interface identifier
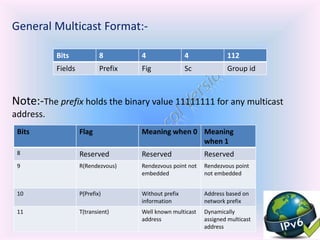
- 9. General Multicast Format:- Note:-The prefix holds the binary value 11111111 for any multicast address. Multicast address flags Bits 8 4 4 112 Fields Prefix Fig Sc Group id Bits Flag Meaning when 0 Meaning when 1 8 Reserved Reserved Reserved 9 R(Rendezvous) Rendezvous point not embedded Rendezvous point not embedded 10 P(Prefix) Without prefix information Address based on network prefix 11 T(transient) Well known multicast address Dynamically assigned multicast address
- 10. ’üČ IPv6 addresses use 128 bits to represent an address which includes bits to be used for subnetting. The second half of the address (least significant 64 bits) is always used for hosts only. Therefore, there is no compromise if we subnet the network. IP V6 Subnetting Routing Prefix Subnet id Interface id 48 bits 16 bits 64 bits
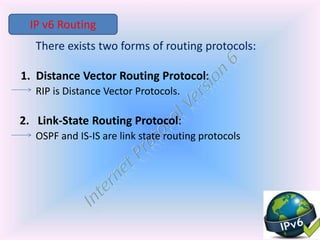
- 11. There exists two forms of routing protocols: 1. Distance Vector Routing Protocol: RIP is Distance Vector Protocols. 2. Link-State Routing Protocol: OSPF and IS-IS are link state routing protocols IP v6 Routing
- 12. ’üČ larger address space (128 bits rather than 32 bits) ’üČ simplified header format ’üČ automatic configuration ’üČ more efficient routing ’üČ improved quality of service and security ’üČ compliance with regulatory requirements ’üČ widespread use in global markets IPv6 includes these benefits over IPv4:
- 13. Future of IPv6:- ’üČ Cisco Systems initially began investigating IPv6 in 2002, but accelerated deploying IPv6 in 2010. They developed a two part strategy that split the project into deploying IPv6 for CiscoŌĆÖs web presence, and deploying IPv6 for CiscoŌĆÖs internal corporate network. ’üČ The United States Census Bureau is one of the leading implementors of IPv6 within the U.S. government. Charles Sun, IPv6 Transition Manager for the U.S. Census Bureau, provided us with information noting Case Study: IPv6 at Cisco Case Study: IPv6 At The U.S. Census Bureau
- 14. Thank You