Ir spectroscopy
8 likes596 views
IR spectroscopy involves the interaction of infrared radiation with matter. Molecules absorb characteristic frequencies of IR radiation depending on their natural vibrational frequencies. This allows IR spectroscopy to be used to determine a molecule's structure by identifying its functional groups. An IR spectrometer consists of a light source, sample holder, monochromator, and detector. It measures the infrared light absorbed by a sample to produce an IR spectrum that can be used for applications like compositional analysis, detection of impurities and functional groups, and structural elucidation of organic compounds.
1 of 7
Downloaded 17 times






Ad
Recommended
X ray diffraction
X ray diffractionArvind Singh Heer
╠²
X-ray diffraction is a technique used to analyze the crystal structure of materials. When X-rays strike a crystalline material, they cause the atoms to diffract in predictable patterns. By analyzing these diffraction patterns, properties of the crystal such as its d-spacing and unit cell parameters can be determined. Powder XRD is commonly used, where a sample is finely powdered and exposed to monochromatic X-rays, producing a characteristic diffraction pattern that can identify unknown crystalline materials.I R spectroscopy & its application
I R spectroscopy & its application Amit Agnihotri
╠²
IR spectroscopy analyzes the vibrational frequencies of bonds in molecules to determine their structure. It works by measuring the absorption of IR radiation by molecular bonds. Different functional groups absorb at characteristic frequencies, producing a molecular "fingerprint". IR spectroscopy is useful for identification of unknown compounds, analyzing purity, and monitoring chemical reactions through changes in bond absorption. It is a nondestructive technique applied in various fields such as pharmaceutical analysis, biomedical research, forensic science, and atmospheric studies.Infra Red Spectroscopy and Its Applications
Infra Red Spectroscopy and Its ApplicationsVikram Choudhary
╠²
The document discusses infrared spectroscopy, including its principles, instrumentation, and applications in various fields like pharmaceuticals and industrial quality control. It explains the interaction of infrared light with molecules, types of vibrations, and the components of an infrared spectrometer. Additionally, it highlights FT-IR spectroscopy and its role in identifying substances, studying reactions, and detecting impurities.FOURIER TRANSFORM - INFRARED SPECTROSCOPY
FOURIER TRANSFORM - INFRARED SPECTROSCOPYSalmanLatif14
╠²
Infrared spectroscopy is a technique that uses infrared light to determine the functional groups present in molecules based on the vibrations of atoms. It works by passing infrared radiation through a sample and measuring the absorption of specific wavelengths, which correspond to vibrations between bonds of different atoms. The peaks in an infrared spectrum can identify functional groups and chemical bonds based on the wavelength of absorption. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy is now commonly used as it allows simultaneous detection of all infrared wavelengths for faster analysis.Infrared Spectroscopy
Infrared SpectroscopyJACOB THON BIOR
╠²
This document provides an overview of infrared (IR) spectroscopy. It discusses the principle behind IR spectroscopy, the different modes of molecular vibration, instrumentation including sources, detectors and monochromators. It also covers sample handling techniques, factors that affect vibrational frequencies and applications of IR spectroscopy such as structure elucidation.Derivative spectrophotometry
Derivative spectrophotometryRahul Krishnan
╠²
Derivative spectroscopy involves converting a normal UV-Vis absorption spectrum into its first or second derivative spectrum. This allows removal of spectral interferences and increases selectivity for analytical determinations. Derivative spectra are generated mathematically or by using a dual-beam spectrophotometer with a small wavelength interval between the beams. This provides better resolution of overlapping bands and permits more accurate determination of components in multi-component mixtures compared to conventional absorption spectroscopy. Derivative spectroscopy finds applications in pharmaceutical analysis and other areas requiring determination of individual components in the presence of interferants.Principle of UV visible Spectroscopy
Principle of UV visible SpectroscopyDr. Mahendra GS
╠²
This document provides an overview of the principles of UV-visible spectroscopy. It discusses how UV-visible spectroscopy involves exciting electrons from lower to higher orbital energies using electromagnetic radiation between 200-800nm. The absorption of radiation is dependent on the structure of the compound and type of electron transition. The main types of electron transitions are Žā->Žā*, n->ŽĆ*, ŽĆ->ŽĆ*, and n->Žā*. Selection rules determine which transitions are allowed. UV-visible spectroscopy is used in pharmaceutical analysis for qualitative, quantitative, and structural analysis of compounds in solution.FT-IR spectroscopy Instrumentation and Application, By- Anubhav singh, M.pharm
FT-IR spectroscopy Instrumentation and Application, By- Anubhav singh, M.pharmAnubhav Singh
╠²
This document discusses instrumentation and applications of Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy. It begins by explaining the basic principles of FTIR spectroscopy, how it works, and its advantages over dispersive infrared spectroscopy. It then describes various applications of FTIR spectroscopy like polymer processing, plasma etching, identification of materials, and analysis of formulations. Specific examples discussed include drying and curing polymers, monitoring plasma etching, identifying contamination, and distinguishing different functional groups in molecules. The document concludes by noting the advantages, limitations, and comparison of FTIR spectroscopy to dispersive infrared spectroscopy.Raman spectroscopy
Raman spectroscopyajamilan12
╠²
Raman spectroscopy is a spectroscopic technique that uses laser light to study vibrational, rotational, and other low-frequency modes in a system. It relies on inelastic scattering, or Raman scattering, of monochromatic light, usually from a laser in the visible, near infrared, or near ultraviolet range. The laser light interacts with molecular vibrations, phonons or other excitations in the system, resulting in the energy of the laser photons being shifted up or down. The shift in energy gives information about the vibrational modes in the system. Raman spectroscopy is commonly used in chemistry to provide a fingerprint by which molecules can be identified. It has applications in fields such as physics, materials science, biology, medicine andCapillary electrophoresis- Mass spectrometry
Capillary electrophoresis- Mass spectrometryVasanthaTS
╠²
This document summarizes a presentation on Capillary Electrophoresis - Mass Spectrometry (CE-MS). It discusses the principles and instrumentation of both CE and MS and how they are coupled. CE separates ions based on electrophoretic mobility, while MS further separates ions based on their mass-to-charge ratio. The document describes various interfaces for coupling CE to MS, including sheath flow, sheathless, and liquid junction interfaces. Applications of CE-MS discussed include drug analysis, analysis of intact proteins and peptides, analysis of amino acids, and food analysis.UV visible spectroscopy principles and instrumentation
UV visible spectroscopy principles and instrumentationSajjad Ullah
╠²
The document provides an overview of various instrumental methods of analysis, focusing on spectroscopic techniques, particularly UV-visible spectroscopy. It details the principles of electromagnetic radiation (EMR), the relationship between wavelength and energy, different types of spectroscopic instruments, and the importance of components such as light sources, wavelength selectors, and detectors. Additionally, it discusses selection rules for electronic transitions and the basics of quantitative analysis in absorption spectroscopy.NMR Spectroscopy
NMR Spectroscopytabirsir
╠²
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy uses the NMR phenomenon to study the physical, chemical, and biological properties of matter. NMR occurs when atomic nuclei are placed in a magnetic field and exposed to a second oscillating field. Only certain atomic nuclei experience NMR, depending on whether they have a quantum property called spin. NMR spectroscopy is valuable in chemistry for determining molecular structure. It is commonly used to map the carbon-hydrogen framework of organic molecules. More advanced NMR techniques also study protein structure and dynamics in biological chemistry.Mass spectrometry
Mass spectrometryHari Sharan Makaju
╠²
Mass spectrometry is an analytical technique that ionizes molecules and separates the resulting ions based on their mass-to-charge ratio. It is a powerful qualitative and quantitative technique used to measure a wide range of clinically relevant analytes. Various ionization sources are used depending on the type of sample, including electron ionization, chemical ionization, electrospray ionization, and matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization. Ions are accelerated into a mass analyzer such as a quadrupole, magnetic sector, or time-of-flight analyzer which separates the ions based on m/z. The detected ions produce a mass spectrum that provides information about molecular structure.Basics of Infrared Spectroscopy : Theory, principles and applications
Basics of Infrared Spectroscopy : Theory, principles and applicationsHemant Khandoliya
╠²
1. Spectroscopy involves using electromagnetic radiation to obtain information about atoms and molecules. Infrared (IR) spectroscopy specifically analyzes molecular vibrations that occur when IR radiation is absorbed.
2. IR spectroscopy is useful for structure elucidation and identification of organic compounds by determining their functional groups based on characteristic absorption bands. It can also be used to study reaction progress and detect impurities.
3. Factors like hydrogen bonding, coupling effects, and electronic effects can influence vibrational frequencies observed in IR spectra. Advanced applications include quantitative analysis, studying isomerism, and determining unknown contaminants.FT NMR
FT NMRRahul B S
╠²
The document discusses Fourier-transform nuclear magnetic resonance (FT-NMR) spectroscopy. It provides an introduction to Fourier transforms and their use in converting time domain NMR spectra to frequency domain spectra. It describes the components of an FT-NMR instrument, including an RF transmitter coil, magnet, receiver coil, and computer. Key advantages of FT-NMR are its dramatic increase in sensitivity over continuous wave NMR, allowing detection of samples under 5 mg, and its ability to rapidly provide high signal-to-noise ratio spectra.FT- NMR
FT- NMRaishuanju
╠²
FT-NMR uses Fourier transforms to convert time domain signals from nuclear magnetic resonance into frequency domain spectra. The sample is placed in a strong magnet and exposed to pulses of radio frequency radiation, producing a free induction decay signal that is recorded over time. This time domain signal is then digitized and analyzed using a Fourier transform program on a computer to produce the frequency domain NMR spectrum. FT-NMR provides higher sensitivity than continuous wave NMR, allowing analysis of smaller sample sizes.Sana 13 nmr
Sana 13 nmrsanjay patil
╠²
13C NMR gives distinct signals for each non-equivalent carbon atom based on its chemical environment. It has a wider chemical shift range than 1H NMR, allowing for easier separation of signals. However, 13C NMR spectra are complicated by weak signals due to the low natural abundance of 13C. Modern Fourier transform NMR techniques have helped overcome this issue. Proton-decoupled 13C NMR provides simple spectra with one peak per carbon, while proton-coupled spectra show splitting patterns indicating directly bonded protons. 13C NMR finds numerous applications inApplications of infrared spectroscopy
Applications of infrared spectroscopy Shruthi Krishnaswamy
╠²
This document discusses applications of infrared spectroscopy. It begins by explaining how infrared radiation corresponds to vibrational modes in molecules and can be used to identify functional groups and determine molecular structure. It then discusses specific applications such as identifying exchangeable hydrogens, determining substances, tracking organic nanoparticles in space, quantifying proteins, and various applications in food analysis, forensics, homeland security, medicine, and more. Infrared spectroscopy is a powerful analytical technique due to its non-destructive nature and ability to identify functional groups and analyze molecular structure and composition.FOURIER -TRANSFORM INFRARED SPECTROMETER [FTIR]
FOURIER -TRANSFORM INFRARED SPECTROMETER [FTIR] Sagar K Savale
╠²
The document discusses Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), highlighting its advantages, disadvantages, and instrumentation compared to traditional dispersive IR spectroscopy. FTIR provides rapid scans with higher sensitivity and simultaneous detection of all frequencies, making it a powerful tool for chemical analysis. Additionally, important concepts such as sample preparation, infrared wave properties, and the role of the Michelson interferometer in creating an interferogram are covered.Ft ir instrumentation
Ft ir instrumentationachyuth kumar gurram
╠²
FT-IR spectroscopy uses a Michelson interferometer to measure the absorption of infrared light by molecules. The key components are a source, beam splitter, two mirrors, sample, detector, and computer. Infrared light from the source is split at the beam splitter, reflected by the mirrors, and recombined to generate an interferogram, which is Fourier transformed by the computer into an infrared absorption spectrum. FT-IR spectroscopy can be used to determine molecular structure in gases, explore interstellar composition, perform quantitative analysis, and identify functional groups and bonds based on their characteristic vibrational frequencies.Spectroscopy 5201
Spectroscopy 5201Nur Fatihah
╠²
This document discusses various analytical techniques used in spectroscopy. It describes spectroscopy as the study of interaction between electromagnetic radiation and matter. There are different types of spectroscopy including absorption, emission, and scattering spectroscopy. Specific techniques are used to identify unknown substances, predict behavior of new materials, and qualitatively or quantitatively analyze chemical composition. The document provides examples of spectroscopy techniques and their applications in areas like determining organic structures and quantifying metal ions.Mass Analyser
Mass AnalyserVarun Girme
╠²
Mass analyzers separate ionized molecules based on their mass-to-charge ratios. The main types are quadrupole, time-of-flight, magnetic sector, quadrupole ion trap, and ion cyclotron resonance. A quadrupole uses oscillating electric fields to selectively transmit ions through four rods. Time-of-flight separates ions by their time of flight through a field-free region, with lighter ions arriving first. Magnetic sector analyzers use magnetic and electric fields to curve ion trajectories based on m/z.Dispersive & FTIR
Dispersive & FTIRbhavanavedantam
╠²
This document discusses the theory, instrumentation, and applications of dispersive and Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy. It begins with an introduction to IR spectroscopy and the IR region. It then covers dispersive IR instrumentation, which uses prism or grating monochromators to separate wavelengths, and has limitations like slow scan speeds and limited resolution. The document introduces FTIR instrumentation, which uses an interferometer to simultaneously measure all wavelengths and overcomes the limitations of dispersive IR. It concludes that FTIR provides faster, more accurate and sensitive analysis compared to dispersive IR.RAMAN SPECTROSCOPY AND ITS APPLICATIONS
RAMAN SPECTROSCOPY AND ITS APPLICATIONSVarinderKhepar
╠²
Raman spectroscopy involves the scattering of light by molecules, contrasting with absorption techniques. It differentiates between Rayleigh scattering, Stokes lines, and anti-Stokes lines and has applications across various fields including inorganic, organic, physical, pharmaceutical, forensic, and biological sciences. Despite its advantages, such as the ability to analyze gases, liquids, and solids, it faces limitations like high instrumentation costs and sensitivity to sample quality.Instrumentation of IR spectroscopy
Instrumentation of IR spectroscopyTalha Liaqat
╠²
1) IR spectroscopy uses infrared radiation to identify chemical substances by their absorption patterns.
2) The main components of an IR spectrometer are a radiation source, monochromator, sample cells, detectors, and recorder.
3) Common radiation sources are Nernst glowers, globar sources, and incandescent wires, which emit IR radiation that is focused through the sample.Nmr spectroscopy
Nmr spectroscopyMukesh Patil
╠²
1. 1H NMR spectroscopy is a technique used to analyze compounds by detecting hydrogen nuclei in a magnetic field. It provides information about functional groups, number of nuclei, and structure of compounds.
2. The principle involves hydrogen nuclei absorbing radio frequencies matching their Larmor frequency in an applied magnetic field. This absorption is measured to produce an NMR spectrum.
3. Factors like electronegativity, magnetic anisotropy, and spin-spin coupling influence the chemical shifts observed on the NMR spectrum, allowing identification of functional groups and structure elucidation.nmr spectroscopy
nmr spectroscopyShweta Singh
╠²
1) Early NMR spectrometers used permanent magnets or electromagnets with field strengths of 60-100 MHz for proton resonance, while modern instruments use superconducting magnets cooled by liquid helium to achieve fields over 100 MHz.
2) Key requirements of NMR spectrometers include high and stable magnetic field, field homogeneity, and a computer interface.
3) Pulsed Fourier transform (FT) NMR uses a radiofrequency pulse to simultaneously excite all nuclei, and the free induction decay signal is Fourier transformed to obtain the frequency domain spectrum.Application of ir
Application of irjoan vijetha
╠²
The document discusses the applications of infrared (IR) spectroscopy for qualitative and quantitative analysis. IR spectroscopy can be used to identify functional groups and determine molecular structures. It allows study of hydrogen bonding, geometrical isomers, and reaction progress. Near IR is applied to agriculture and pharmaceutical analysis while mid IR identifies organic and biological species. Far IR is used in medical treatments and astronomy. In summary, IR spectroscopy enables structural analysis and has various applications across chemistry, biology, medicine, and astronomy.Infrared spectroscopy
Infrared spectroscopy Dr NEETHU ASOKAN
╠²
Molecular vibrations cause characteristic absorption bands in the infrared region of the electromagnetic spectrum. [FTIR] spectroscopy involves passing infrared radiation through a sample and measuring the wavelengths absorbed. This creates a molecular "fingerprint" that can be used to identify unknown chemicals and study molecular structure. FTIR has numerous applications including analysis of organic materials, biological samples, and industrial contaminants. It provides a simple, rapid and sensitive technique for analytical chemistry.IR SPECTROSCOPY / biophysics/biophysical techniques
IR SPECTROSCOPY / biophysics/biophysical techniquesAryasurendran11
╠²
IR SPECTROSCOPY / biophysics/biophysical techniquesMore Related Content
What's hot (20)
Raman spectroscopy
Raman spectroscopyajamilan12
╠²
Raman spectroscopy is a spectroscopic technique that uses laser light to study vibrational, rotational, and other low-frequency modes in a system. It relies on inelastic scattering, or Raman scattering, of monochromatic light, usually from a laser in the visible, near infrared, or near ultraviolet range. The laser light interacts with molecular vibrations, phonons or other excitations in the system, resulting in the energy of the laser photons being shifted up or down. The shift in energy gives information about the vibrational modes in the system. Raman spectroscopy is commonly used in chemistry to provide a fingerprint by which molecules can be identified. It has applications in fields such as physics, materials science, biology, medicine andCapillary electrophoresis- Mass spectrometry
Capillary electrophoresis- Mass spectrometryVasanthaTS
╠²
This document summarizes a presentation on Capillary Electrophoresis - Mass Spectrometry (CE-MS). It discusses the principles and instrumentation of both CE and MS and how they are coupled. CE separates ions based on electrophoretic mobility, while MS further separates ions based on their mass-to-charge ratio. The document describes various interfaces for coupling CE to MS, including sheath flow, sheathless, and liquid junction interfaces. Applications of CE-MS discussed include drug analysis, analysis of intact proteins and peptides, analysis of amino acids, and food analysis.UV visible spectroscopy principles and instrumentation
UV visible spectroscopy principles and instrumentationSajjad Ullah
╠²
The document provides an overview of various instrumental methods of analysis, focusing on spectroscopic techniques, particularly UV-visible spectroscopy. It details the principles of electromagnetic radiation (EMR), the relationship between wavelength and energy, different types of spectroscopic instruments, and the importance of components such as light sources, wavelength selectors, and detectors. Additionally, it discusses selection rules for electronic transitions and the basics of quantitative analysis in absorption spectroscopy.NMR Spectroscopy
NMR Spectroscopytabirsir
╠²
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy uses the NMR phenomenon to study the physical, chemical, and biological properties of matter. NMR occurs when atomic nuclei are placed in a magnetic field and exposed to a second oscillating field. Only certain atomic nuclei experience NMR, depending on whether they have a quantum property called spin. NMR spectroscopy is valuable in chemistry for determining molecular structure. It is commonly used to map the carbon-hydrogen framework of organic molecules. More advanced NMR techniques also study protein structure and dynamics in biological chemistry.Mass spectrometry
Mass spectrometryHari Sharan Makaju
╠²
Mass spectrometry is an analytical technique that ionizes molecules and separates the resulting ions based on their mass-to-charge ratio. It is a powerful qualitative and quantitative technique used to measure a wide range of clinically relevant analytes. Various ionization sources are used depending on the type of sample, including electron ionization, chemical ionization, electrospray ionization, and matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization. Ions are accelerated into a mass analyzer such as a quadrupole, magnetic sector, or time-of-flight analyzer which separates the ions based on m/z. The detected ions produce a mass spectrum that provides information about molecular structure.Basics of Infrared Spectroscopy : Theory, principles and applications
Basics of Infrared Spectroscopy : Theory, principles and applicationsHemant Khandoliya
╠²
1. Spectroscopy involves using electromagnetic radiation to obtain information about atoms and molecules. Infrared (IR) spectroscopy specifically analyzes molecular vibrations that occur when IR radiation is absorbed.
2. IR spectroscopy is useful for structure elucidation and identification of organic compounds by determining their functional groups based on characteristic absorption bands. It can also be used to study reaction progress and detect impurities.
3. Factors like hydrogen bonding, coupling effects, and electronic effects can influence vibrational frequencies observed in IR spectra. Advanced applications include quantitative analysis, studying isomerism, and determining unknown contaminants.FT NMR
FT NMRRahul B S
╠²
The document discusses Fourier-transform nuclear magnetic resonance (FT-NMR) spectroscopy. It provides an introduction to Fourier transforms and their use in converting time domain NMR spectra to frequency domain spectra. It describes the components of an FT-NMR instrument, including an RF transmitter coil, magnet, receiver coil, and computer. Key advantages of FT-NMR are its dramatic increase in sensitivity over continuous wave NMR, allowing detection of samples under 5 mg, and its ability to rapidly provide high signal-to-noise ratio spectra.FT- NMR
FT- NMRaishuanju
╠²
FT-NMR uses Fourier transforms to convert time domain signals from nuclear magnetic resonance into frequency domain spectra. The sample is placed in a strong magnet and exposed to pulses of radio frequency radiation, producing a free induction decay signal that is recorded over time. This time domain signal is then digitized and analyzed using a Fourier transform program on a computer to produce the frequency domain NMR spectrum. FT-NMR provides higher sensitivity than continuous wave NMR, allowing analysis of smaller sample sizes.Sana 13 nmr
Sana 13 nmrsanjay patil
╠²
13C NMR gives distinct signals for each non-equivalent carbon atom based on its chemical environment. It has a wider chemical shift range than 1H NMR, allowing for easier separation of signals. However, 13C NMR spectra are complicated by weak signals due to the low natural abundance of 13C. Modern Fourier transform NMR techniques have helped overcome this issue. Proton-decoupled 13C NMR provides simple spectra with one peak per carbon, while proton-coupled spectra show splitting patterns indicating directly bonded protons. 13C NMR finds numerous applications inApplications of infrared spectroscopy
Applications of infrared spectroscopy Shruthi Krishnaswamy
╠²
This document discusses applications of infrared spectroscopy. It begins by explaining how infrared radiation corresponds to vibrational modes in molecules and can be used to identify functional groups and determine molecular structure. It then discusses specific applications such as identifying exchangeable hydrogens, determining substances, tracking organic nanoparticles in space, quantifying proteins, and various applications in food analysis, forensics, homeland security, medicine, and more. Infrared spectroscopy is a powerful analytical technique due to its non-destructive nature and ability to identify functional groups and analyze molecular structure and composition.FOURIER -TRANSFORM INFRARED SPECTROMETER [FTIR]
FOURIER -TRANSFORM INFRARED SPECTROMETER [FTIR] Sagar K Savale
╠²
The document discusses Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), highlighting its advantages, disadvantages, and instrumentation compared to traditional dispersive IR spectroscopy. FTIR provides rapid scans with higher sensitivity and simultaneous detection of all frequencies, making it a powerful tool for chemical analysis. Additionally, important concepts such as sample preparation, infrared wave properties, and the role of the Michelson interferometer in creating an interferogram are covered.Ft ir instrumentation
Ft ir instrumentationachyuth kumar gurram
╠²
FT-IR spectroscopy uses a Michelson interferometer to measure the absorption of infrared light by molecules. The key components are a source, beam splitter, two mirrors, sample, detector, and computer. Infrared light from the source is split at the beam splitter, reflected by the mirrors, and recombined to generate an interferogram, which is Fourier transformed by the computer into an infrared absorption spectrum. FT-IR spectroscopy can be used to determine molecular structure in gases, explore interstellar composition, perform quantitative analysis, and identify functional groups and bonds based on their characteristic vibrational frequencies.Spectroscopy 5201
Spectroscopy 5201Nur Fatihah
╠²
This document discusses various analytical techniques used in spectroscopy. It describes spectroscopy as the study of interaction between electromagnetic radiation and matter. There are different types of spectroscopy including absorption, emission, and scattering spectroscopy. Specific techniques are used to identify unknown substances, predict behavior of new materials, and qualitatively or quantitatively analyze chemical composition. The document provides examples of spectroscopy techniques and their applications in areas like determining organic structures and quantifying metal ions.Mass Analyser
Mass AnalyserVarun Girme
╠²
Mass analyzers separate ionized molecules based on their mass-to-charge ratios. The main types are quadrupole, time-of-flight, magnetic sector, quadrupole ion trap, and ion cyclotron resonance. A quadrupole uses oscillating electric fields to selectively transmit ions through four rods. Time-of-flight separates ions by their time of flight through a field-free region, with lighter ions arriving first. Magnetic sector analyzers use magnetic and electric fields to curve ion trajectories based on m/z.Dispersive & FTIR
Dispersive & FTIRbhavanavedantam
╠²
This document discusses the theory, instrumentation, and applications of dispersive and Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy. It begins with an introduction to IR spectroscopy and the IR region. It then covers dispersive IR instrumentation, which uses prism or grating monochromators to separate wavelengths, and has limitations like slow scan speeds and limited resolution. The document introduces FTIR instrumentation, which uses an interferometer to simultaneously measure all wavelengths and overcomes the limitations of dispersive IR. It concludes that FTIR provides faster, more accurate and sensitive analysis compared to dispersive IR.RAMAN SPECTROSCOPY AND ITS APPLICATIONS
RAMAN SPECTROSCOPY AND ITS APPLICATIONSVarinderKhepar
╠²
Raman spectroscopy involves the scattering of light by molecules, contrasting with absorption techniques. It differentiates between Rayleigh scattering, Stokes lines, and anti-Stokes lines and has applications across various fields including inorganic, organic, physical, pharmaceutical, forensic, and biological sciences. Despite its advantages, such as the ability to analyze gases, liquids, and solids, it faces limitations like high instrumentation costs and sensitivity to sample quality.Instrumentation of IR spectroscopy
Instrumentation of IR spectroscopyTalha Liaqat
╠²
1) IR spectroscopy uses infrared radiation to identify chemical substances by their absorption patterns.
2) The main components of an IR spectrometer are a radiation source, monochromator, sample cells, detectors, and recorder.
3) Common radiation sources are Nernst glowers, globar sources, and incandescent wires, which emit IR radiation that is focused through the sample.Nmr spectroscopy
Nmr spectroscopyMukesh Patil
╠²
1. 1H NMR spectroscopy is a technique used to analyze compounds by detecting hydrogen nuclei in a magnetic field. It provides information about functional groups, number of nuclei, and structure of compounds.
2. The principle involves hydrogen nuclei absorbing radio frequencies matching their Larmor frequency in an applied magnetic field. This absorption is measured to produce an NMR spectrum.
3. Factors like electronegativity, magnetic anisotropy, and spin-spin coupling influence the chemical shifts observed on the NMR spectrum, allowing identification of functional groups and structure elucidation.nmr spectroscopy
nmr spectroscopyShweta Singh
╠²
1) Early NMR spectrometers used permanent magnets or electromagnets with field strengths of 60-100 MHz for proton resonance, while modern instruments use superconducting magnets cooled by liquid helium to achieve fields over 100 MHz.
2) Key requirements of NMR spectrometers include high and stable magnetic field, field homogeneity, and a computer interface.
3) Pulsed Fourier transform (FT) NMR uses a radiofrequency pulse to simultaneously excite all nuclei, and the free induction decay signal is Fourier transformed to obtain the frequency domain spectrum.Application of ir
Application of irjoan vijetha
╠²
The document discusses the applications of infrared (IR) spectroscopy for qualitative and quantitative analysis. IR spectroscopy can be used to identify functional groups and determine molecular structures. It allows study of hydrogen bonding, geometrical isomers, and reaction progress. Near IR is applied to agriculture and pharmaceutical analysis while mid IR identifies organic and biological species. Far IR is used in medical treatments and astronomy. In summary, IR spectroscopy enables structural analysis and has various applications across chemistry, biology, medicine, and astronomy.Similar to Ir spectroscopy (20)
Infrared spectroscopy
Infrared spectroscopy Dr NEETHU ASOKAN
╠²
Molecular vibrations cause characteristic absorption bands in the infrared region of the electromagnetic spectrum. [FTIR] spectroscopy involves passing infrared radiation through a sample and measuring the wavelengths absorbed. This creates a molecular "fingerprint" that can be used to identify unknown chemicals and study molecular structure. FTIR has numerous applications including analysis of organic materials, biological samples, and industrial contaminants. It provides a simple, rapid and sensitive technique for analytical chemistry.IR SPECTROSCOPY / biophysics/biophysical techniques
IR SPECTROSCOPY / biophysics/biophysical techniquesAryasurendran11
╠²
IR SPECTROSCOPY / biophysics/biophysical techniquesIntroduction to infrared spectroscopy: A literature
Introduction to infrared spectroscopy: A literatureAnkitaParmanik1
╠²
Infrared spectroscopy studies the absorption of infrared radiation by chemical compounds, primarily to identify functional groups and elucidate molecular structure. The IR spectrum is divided into three regions: near IR, mid IR, and far IR, with mid IR being widely used in pharmaceutical applications. The technique is based on the absorption of specific frequencies of infrared radiation by molecular vibrations, making it a valuable tool for qualitative compound analysis.Theory of IR spectroscopy
Theory of IR spectroscopychiranjibi68
╠²
The document summarizes infrared (IR) spectroscopy, including its principle, instrumentation, applications, and interpretation of spectra. IR spectroscopy works by detecting the vibrational and rotational absorption frequencies of molecules when exposed to IR radiation. The spectrum produced provides information on molecular structure and bonding. Key regions of the IR spectrum correspond to common functional groups like C=O, N-H, and O-H. Analysis of peak positions and relative intensities allows identification of compounds and detection of impurities.IR Spectroscopy.pptx
IR Spectroscopy.pptxinshasaife1
╠²
Given:
A = Absorbance = 1
l = Path length = 2 cm
╬Ą = Molar absorptivity = 2x10^4 L/mol.cm
Using the Beer-Lambert's law:
A = ╬Ą x c x l
1 = 2x10^4 x c x 2
c = 1 / (2x10^4 x 2)
c = 2.5x10^-5 mol/L
So, the concentration of the substance is 2.5x10^-5 mol/L.Ir spectroscopy
Ir spectroscopyKhansaBajwa1
╠²
Infrared spectroscopy involves using infrared light to analyze chemical bonding and molecular structure. Infrared light is passed through a sample, and the wavelengths absorbed can be measured to identify chemical groups and determine structural features. The technique is widely used to analyze organic materials and identify unknown compounds based on their infrared absorption spectra. Limitations include an inability to determine molecular weight or relative positions of functional groups within a molecule from the infrared spectrum alone.Introduction and principle of ir spectrophotometry
Introduction and principle of ir spectrophotometryRajat Choudhary
╠²
This document provides an introduction to infrared (IR) spectrophotometry. It explains that IR spectroscopy analyzes molecular vibrations by measuring the absorption of IR radiation. When the radiation frequency matches a molecule's natural vibration frequency, absorption occurs. For absorption to take place, the radiation wavelength must match the vibration and cause a change in the molecule's dipole moment. IR spectroscopy is used to determine a substance's functional groups by their characteristic absorption peak values in the IR spectrum.Microwave and infrared spectroscopy of polyatomic molecules
Microwave and infrared spectroscopy of polyatomic moleculesAreebaWarraich1
╠²
Microwave and infrared spectroscopy can be used to study the rotational and vibrational states of polyatomic molecules. Microwave spectroscopy specifically probes the rotational transitions of molecules with a permanent dipole moment, in the microwave frequency range of 300MHz-300GHz. Infrared spectroscopy analyzes the vibrational transitions of molecules when exposed to infrared radiation, divided into stretching and bending vibrations. Both techniques provide information on molecular structure through analysis of absorption spectra.IR:Objectives: 1. The concept of the IR spectroscopy. 2. The application of ...
IR:Objectives: 1. The concept of the IR spectroscopy. 2. The application of ...Waleednaji1
╠²
Objectives:
1. The concept of the IR spectroscop
IR : Infrared Absorption Spectroscopy Objectives: 1. The concept of the IR s...
IR : Infrared Absorption Spectroscopy Objectives: 1. The concept of the IR s...Waleednaji1
╠²
Objectives:
1. The concept of the IR spectroscopy.
2. The application of the IR.Prabhakar singh ii sem-paper-ir spectroscopy & fluorimetry
Prabhakar singh ii sem-paper-ir spectroscopy & fluorimetryDepartment of Biochemistry, Veer Bahadur Singh Purvanchal Univarsity, Jaunpur
╠²
This document provides an overview of infrared spectroscopy, Raman spectroscopy, and fluorimetry techniques. It discusses the principles behind infrared and Raman spectroscopy, including how they provide information about molecular vibrations and differences in selection rules. Instrumentation for these techniques and applications in chemistry and biochemistry are also summarized. Principles of fluorescence, sources of excitation, instrumentation of fluorimeters, quenching effects, and applications of fluorimetry are described. Finally, the document briefly discusses luminescence and luminometry.null.pptx
null.pptxmineme2
╠²
The document discusses infrared spectroscopy. It begins with an overview of spectroscopy and defines key terms like spectrometer and spectrum. It then focuses on infrared spectroscopy, explaining that it identifies functional groups in molecules based on their interaction with infrared radiation. The document outlines the infrared region of the electromagnetic spectrum and discusses the principle and instrumentation of infrared spectroscopy. It describes different vibration modes observed in molecules and regions of infrared spectra, namely the functional group region and fingerprint region. Applications of infrared spectroscopy include identification of compounds and detection of impurities. In the end, it provides an example of using the fingerprint region to distinguish between structural isomers.IR SPECTROSCOPY working& application.ppt
IR SPECTROSCOPY working& application.pptmeghaskaravattu
╠²
Infrared (IR) spectroscopy is a technique that studies the interaction of infrared radiation with matter, particularly focusing on vibrational transitions in molecules. It is widely used across various fields, including chemistry and pharmaceuticals, for identifying functional groups and conducting qualitative and quantitative analyses. The technique relies on specific absorption frequencies that allow for the characterization of molecular structures and is employed in applications such as quality control, environmental analysis, and forensic science.IR SPECTROSCOPY
IR SPECTROSCOPY Priyanka Bharti
╠²
IR spectroscopy is the study of infrared spectra caused by vibrational transitions in molecules. It provides a valuable tool for probing molecular structure. IR spectroscopy works by detecting the frequencies at which molecules vibrate when absorbed infrared radiation. Different functional groups within molecules vibrate at characteristic frequencies, allowing IR spectroscopy to be used to determine a molecule's structure. It has various applications such as compositional analysis of organic compounds, detection of impurities, and analysis of aircraft exhausts and toxic gases.INTRODUCTION TO VARIOUS SPECTROSCOPY TECHNIQUES
INTRODUCTION TO VARIOUS SPECTROSCOPY TECHNIQUESISF COLLEGE OF PHARMACY MOGA
╠²
The document provides an overview of various spectroscopy techniques, including infrared, UV/Vis, and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, describing their principles and applications in analyzing compounds. It details the types of molecular vibrations in infrared spectroscopy as well as the Beer-Lambert law for UV/Vis spectroscopy. Additionally, it discusses the significance of NMR in organic structure determination and references important literature in the field.Infrared Spec.pptx
Infrared Spec.pptxSurendraBabu980252
╠²
Infrared spectroscopy analyzes the interaction of molecules with infrared light, detecting frequencies absorbed that are characteristic of molecular structures and functional groups, allowing identification of substances; an infrared spectrophotometer directs infrared light through a sample using various optical components, and a detector converts absorbed light into an electrical signal providing an infrared spectrum for analysis.Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) Likhith K
Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) Likhith KLIKHITHK1
╠²
This document provides an overview of Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy. It discusses the electromagnetic spectrum and how infrared radiation interacts with molecular bonds to produce vibrational modes. The basic principles of FTIR are explained, including how an interferogram is produced and transformed into an infrared absorption spectrum using Fourier transform. Common instrumentation components like detectors, radiation sources, and sample holders are also mentioned. The document serves as an introduction to FTIR spectroscopy and the molecular information it can provide through analysis of infrared absorption spectra.IR spectroscopy
IR spectroscopy Japheth Ofosu
╠²
This document discusses the use of infrared spectroscopy (IR) to determine the functional groups of compounds. It provides background on IR spectroscopy, including how IR radiation causes molecular vibrations and the types of vibrational modes that can be observed. It also describes the basic components of IR instruments, including sources that emit IR radiation, detectors, and the mechanisms of dispersive and Fourier transform IR spectrometers. The document serves to explain how IR spectroscopy can be used to identify functional groups present in compounds based on their vibrational absorption spectra.Infrared spectroscopy i
Infrared spectroscopy iDrBasavarajaiahSm
╠²
The document provides a comprehensive overview of infrared spectroscopy, including its principles, instrumentation, and applications. It discusses the absorption of infrared radiation, vibrational modes of molecules, and factors influencing absorption frequencies, while comparing infrared and Raman spectroscopy. Additionally, it outlines sampling techniques and the significance of group frequencies in analyzing different compounds.AYUSHI (IR SPECTROSCOPY)2221940018new.pptx
AYUSHI (IR SPECTROSCOPY)2221940018new.pptxkisnasaini7
╠²
The document is a comprehensive overview of infrared (IR) absorption spectroscopy, detailing its basic theory, principles, types of molecular vibrations, and applications in identifying functional groups and studying reactions. It explains the structural significance of absorption bands, particularly in characterizing compounds, as well as the factors influencing vibrational frequencies. The document also includes numerical problems to illustrate the application of IR spectroscopy in distinguishing between various chemical compounds.Prabhakar singh ii sem-paper-ir spectroscopy & fluorimetry
Prabhakar singh ii sem-paper-ir spectroscopy & fluorimetryDepartment of Biochemistry, Veer Bahadur Singh Purvanchal Univarsity, Jaunpur
╠²
Ad
Recently uploaded (20)
Impact of Network Topologies on Blockchain Performance
Impact of Network Topologies on Blockchain Performancevschiavoni
╠²
Best Student Paper Award at ACM DEBS 2025.
Paper here:
https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3701717.3730540
Since blockchains are increasingly adopted in real-world applications, it is of paramount importance to evaluate their performance across diverse scenarios. Although the network infrastructure plays a fundamental role, its impact on performance remains largely unexplored. Some studies evaluate blockchain in cloud environments, but this approach is costly and difficult to reproduce. We propose a cost-effective and reproducible environment that supports both cluster-based setups and emulation capabilities and allows the underlying network topology to be easily modified. We evaluate five industry-grade blockchains ŌĆō Algorand, Diem, Ethereum, Quorum, and Solana ŌĆō across five network topologies ŌĆō fat-tree, full mesh, hypercube, scale-free, and torus ŌĆō and different realistic workloads ŌĆō smart contract requests and transfer transactions. Our benchmark framework, Lilith, shows that full mesh, hypercube, and torus topologies improve blockchain performance under heavy workloads. Algorand and Diem perform consistently across the considered topologies, while Ethereum remains robust but slower.Chromatography ║▌║▌▀Żs for the course of Introduction to Biology and Chemistry...
Chromatography ║▌║▌▀Żs for the course of Introduction to Biology and Chemistry...Md. Arif Shahriar
╠²
This presentation was made as a coursework of "Introduction to Biology and Chemistry for Computation" Course under Fatema Tuj Johora ma'am at Daffodil International University.GBSN__Unit 2 - Control of Microorganisms
GBSN__Unit 2 - Control of MicroorganismsAreesha Ahmad
╠²
Microbiology for Nursing students - According to New PNC course curriculum - 2025
Science 8 Quarter 4 first quiz digestive system.docx
Science 8 Quarter 4 first quiz digestive system.docxjunefermunez
╠²
Quiz for the topic Digestive System. 4th QaurterGBSN_ Unit 1 - Introduction to Microbiology
GBSN_ Unit 1 - Introduction to MicrobiologyAreesha Ahmad
╠²
Microbiology for Nursing students - According to New PNC course curriculum - 2025Investigatory_project Topic:-effect of electrolysis in solar desalination .pdf
Investigatory_project Topic:-effect of electrolysis in solar desalination .pdfshubham997ku
╠²
Cbse class 12. chemistry investigatory project An Analysis Of The Pearl Short Story By John Steinbeck
An Analysis Of The Pearl Short Story By John SteinbeckBillyDarmawan3
╠²
John Steinbeck Popular Short Story
The Pearl adalah sebuah novella yang ditulis oleh John Steinbeck yang mengisahkan perjuangan seorang nelayan miskin bernama Kino dan istrinya, Juana, yang hidup sederhana di sebuah desa kecil Meksiko. Suatu hari, Kino menemukan sebuah mutiara raksasa ŌĆö "the Pearl of the World" ŌĆö yang diyakini akan mengubah nasib mereka.
Namun, alih-alih membawa kebahagiaan, mutiara itu justru menimbulkan keserakahan, kekerasan, dan penderitaan. Masyarakat di sekitarnya mulai menunjukkan niat jahat, dan bahkan keluarga Kino sendiri terjebak dalam konflik batin antara harapan dan kehancuran. Pada akhirnya, The Pearl menjadi simbol ironi: sesuatu yang tampak sebagai berkah berubah menjadi kutukan.
Melalui cerita ini, Steinbeck mengeksplorasi tema keserakahan, harapan, kemiskinan, dan ketimpangan sosial. Dengan gaya narasi yang lugas namun penuh makna simbolik, The Pearl menjadi refleksi tajam tentang sifat manusia dan dampak tragis dari keinginan yang tak terkendali.
GBSN_Unit 3 - Medical and surgical Asepsis
GBSN_Unit 3 - Medical and surgical AsepsisAreesha Ahmad
╠²
Microbiology for Nursing students - According to New PNC course curriculum - 2025
The scientific heritage No 162 (162) (2025)
The scientific heritage No 162 (162) (2025)The scientific heritage
╠²
The scientific heritage No 162 (162) (2025)EV REGENERATIVE ACCELERATION INNOVATION SUMMARY PITCH June 13, 2025.pdf
EV REGENERATIVE ACCELERATION INNOVATION SUMMARY PITCH June 13, 2025.pdfThane Heins NOBEL PRIZE WINNING ENERGY RESEARCHER
╠²
Summary: This document presents a breakthrough in electric vehicle (EV) innovationŌĆö the EV Regenerative Acceleration Innovation (EVRAI)ŌĆödeveloped and patented by Thane Heins Energy Inc. of Ottawa, Canada, Peer-reviewed, validated and independently replicated at the University of Ottawa following performance confirmations at MIT. EVRAI now provides all EVs and hybrid vehicles with the ability to completely recharge themselves as they drive, eliminating the need for external plug-in recharging and reducing battery size requirements by up to 80%. This document outlines the new physics principles, internationally confirmed, validated replications, individual and commercial implications of this paradigm-shifting innovation in the context of sustainable mobility.Overview of Stem Cells and Immune Modulation.ppsx
Overview of Stem Cells and Immune Modulation.ppsxAhmedAtwa29
╠²
This presentation, "Stem Cells & Immune Modulation: The Future of Regenerative Medicine?" by Dr. Ahmed Atwa, explores the groundbreaking potential of stem cells in regenerative medicine and immune regulation. It covers stem cell types (Embryonic, Adult, iPSCs), their unique properties (self-renewal, differentiation), and therapeutic applications in tissue repair, disease modeling, and immunomodulation. Special focus is given to mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) and their role in modulating immune responses through cytokines, extracellular vesicles (EVs), and preconditioning strategies. The slides also address clinical challenges, cancer stem cell evasion, and future directions in stem cell therapy.
Chromatography ║▌║▌▀Żs for the course of Introduction to Biology and Chemistry...
Chromatography ║▌║▌▀Żs for the course of Introduction to Biology and Chemistry...Md. Arif Shahriar
╠²
EV REGENERATIVE ACCELERATION INNOVATION SUMMARY PITCH June 13, 2025.pdf
EV REGENERATIVE ACCELERATION INNOVATION SUMMARY PITCH June 13, 2025.pdfThane Heins NOBEL PRIZE WINNING ENERGY RESEARCHER
╠²
Ad
Ir spectroscopy
- 1. IR SPECTROSCOPY Presentation by:- Dr. Willy J. Shah Asst. Professor Vartak College, Vasai Rd. This work is licensed under a creative common Attribution ŌĆō Noncommerical ŌĆō ShareAlike 4.0 International License 1
- 2. ’üČIR spectroscopy involves the interaction of infrared radiation with matter. ’üČIR spectroscopy is also called as vibrational spectroscopy. ’üČIt is mostly based on absorption spectroscopy. ’üČIR region ranges from 14000cm-1 to 10cm-1 ’üČIR portion of the electromagnetic spectrum is usually divided into three regions; near, mid and far. ’üČ Mid region ranging from 4000-400cm-1 is used in the analysis of chemical substances. 2 INTRODUCTION https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Infrared_spectroscopy
- 3. ’üČMolecules are made up of atoms and bonds, their movement is like spring and ball. This characteristic vibration are called natural frequency of vibration. ’üČWhen the applied infrared frequency matches with natural frequency of vibration then IR radiation are absorbed and a peak is observed. ’üČDifferent functional group absorb characteristic frequencies of IR radiation and hence give characteristic peak. ’üČOnly those molecules are IR active which have dipole moment 3 PRINCIPLE /razaram1/introduction-and-principle-of-ir- spectroscopy-25872192
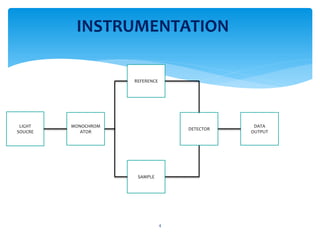
- 5. 1) Light Source - Emits light of different wavelength. Nerst glower lamp, CO2 Laser and Hg arc lamp are employed 2) Sample Holder ŌĆō Made up of alkali halides like NaCl or KBr. Solid, liquid and gases can be analysed. For solid press pellet technique is used. Whereas there are separate assemblies having KBr window to analyse liquid and gas 3) Monochromator - selects particular wavelength of light. Prisms or grating sheets are used. 4) Detector ŌĆō measures light transmitted from the sample. Photon detectors and thermal detectors are used. 5 /rakhirrajan1/infrared-spectroscopy-50410465
- 6. ’üČCompositional analysis of organic and inorganic compound. ’üČDetection of impurities. ’üČDetection of functional groups. ’üČStructural elucidation of organic compounds. ’üČQuantitative and qualitative analysis of pharmaceutical substances. 6 APPLICATIONS /rakhirrajan1/infrared-spectroscopy-50410465
