Iron Deficiency Anemia - FCM in brief.pptx
- 1. TREATMENT OF IRON DEFICIENCY ANEMIA WITH FERRIC CARBOXYMALTOSE Dr. Kunal Chhattani MBBS MD DrNB [Clinical Hematology] Hematologist and Hemato-Oncologist, Chhattani Hematology Clinic, Nagpur
- 2. ANAEMIA
- 3. ’éó WHO Cut Offs: ’éŚ M<13g/dl ’éŚ F<12gm/dl ’éó Anemia in pregnancy: ’éŚ 1st Trimester Hb< 11 ’éŚ 2nd trimester Hb <10.5 ’éŚ 3rd trimester Hb<11 ’éŚ Post partum Hb <10
- 5. IRON HOMEOSTASIS ’éó 1-2mg of iron ŌĆōabsorbed and lost every day ’éó Most absorption- Duodenum ’éó 2 forms- Ferrous and ferric ’éó Ferric iron ’āĀFerrous iron at brush border ’éó Iron ’āĀBlood ’āĀtransferrin’āĀBone marrow’āĀ2/3rd in Hb
- 6. ’éó Storage: 1. Reticulo Endothelial System 2. Liver ’éó Key Regulator: Hepcidin ’éó Hepcidin blocks Ferroportin ’āĀ Reduced iron absorption from gut and stores
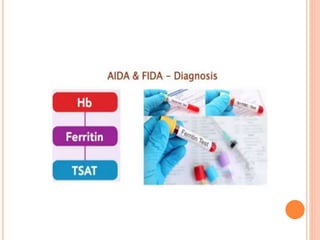
- 9. Diagnosis
- 10. SCREENING FOR IDA ’éó Ferritin <30ng/ml ’éó Transferrin saturation <20%.
- 13. Treatment
- 14. ORAL IRON ’éó Ferrous form is better absorbed ’éó Most commonly available : Ferrous sulphate, ferrous fumarate, ferrous gluconate, ferrous ascorbate. ’éó Any of these is acceptable.
- 15. Advantages: ’éó Efficacious for most patients ’éó Low risk of serious side effects ’éó Low cost Disadvantages: ’éó GI toxicity ’éó Compliance
- 17. SOME QUERIES
- 18. IV iron
- 19. INDICATIONS OF IV IRON ’éó Failure/intolerance of oral iron ’éó Noncompliance ’éó Rapid response required ’éó Malabsorption ’éó Continuous bleeding
- 20. D. Girelli et al 2017
- 21. CONTRAINDICATIONS TO IV IRON ’éó Pregnancy <12 weeks ’éó Lack of facilities of managing allergic reaction ’éó Anaphylaxis to any parenteral iron preparation ’éó Iron overload
- 22. APPROVALS
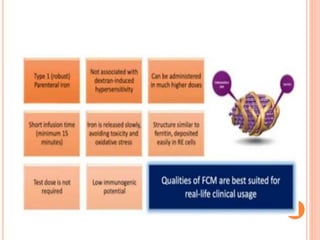
- 23. D. Girelli et al 2017
- 25. D. Girelli et al 2017
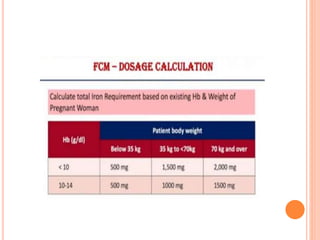
- 28. DILUTION AND DURATION ’éó Dilute FCM 500mg in 100ml NS and 1gm in 250ml NS. Concentration of FCM <2mg/ml is not permissible. ’éó Infuse 500mg in minimum 6minutes and 1gm in minimum 15minutes ’éó Long duration of infusion and excess dilution can lead to destabilization of iron complex and adverse effects
![TREATMENT OF IRON DEFICIENCY ANEMIA WITH
FERRIC CARBOXYMALTOSE
Dr. Kunal Chhattani
MBBS MD DrNB [Clinical Hematology]
Hematologist and Hemato-Oncologist,
Chhattani Hematology Clinic, Nagpur](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/irondeficiencyanemiappt-240111022527-fd40e817/85/Iron-Deficiency-Anemia-FCM-in-brief-pptx-1-320.jpg)