Irrigation engineering -River gauging
- 2. DEFINITION The process of gauging a river flow is called river gauging. It helps in determining characteristics of a stream flow at different times during a year It is a technique used to measure the discharge or the volume of water moving through a channel per unit time of a stream The height of water in a stream channel is called stage or gage height
- 3. IMPORTANCE ŌŚÅ To distribute uniformly the irrigation water among the cultivators ŌŚÅ To determine the coefficient of roughness of lined and unlined canals and to find the amount of absorption losses ŌŚÅ To forecast the normal and highest water supplies for designing the various irrigation structures ŌŚÅ Flood warnings can be issued at times of excess flow in the rivers ŌŚÅ To know the dependable supplies in a river
- 4. SITE SELECTION ŌŚÅ The river should have a straight reach length of which should not be less than 20 times the width of the water ŌŚÅ The river should not be wide and shallow ŌŚÅ No hydraulic structure should exist near the gauging site ŌŚÅ The river section line should be at right angles to the flow of the river ŌŚÅ There should not be any chance for silting and scouring at the gauging site
- 5. OPEN GAUGE WELL ŌŚÅ Gauges fixed in open areas and kept exposed, water level cannot be read with accuracy as the currents against the gauge piller affect the water levels due to waves and surgings which cause constant variations in depth. ŌŚÅ A gauge well is a well sunk on the margin of the river and provided with a gauge to show the level of water inside the gauge well ŌŚÅ One or more pipes or openings or narrow slits in the side connect the well with the water of the stream and thus the level of water in the well is kept at the true level of the surface of the stream ŌŚÅ Wherever A gauge well is installed there must be two gauges with their zero at the same level one in the well and the other in the stream and readings of both gauges must be recorded. ŌŚÅ Pipes connecting gauge well with the stream must be more than 10 cms in diameter and each pipe should be without bend
- 6. ŌŚÅ The lowest pipe must be fully submerged below the level stage of flow to be recorded.
- 8. Gauging of river 1. By actually measuring the discharge at the outlet of the catchment basin 2. By determining the area and velocity of a river
- 9. 1. By actual measurement 1. For a rectangular weir L length of weir H head of water over crest
- 10. 2. For a triangular notch fixed over small rivers and channels H head of water over sill of notch Cd co efficient of discharge of the notch
- 11. For a broad crested weir L length of weir H head of water over crest
- 12. 2. By area velocity method ŌŚÅ It involves the measuring area and average velocity of flow ŌŚÅ As it is difficult to correctly measure the average velocity the stream or river should be divided into sections ŌŚÅ If V is the velocity in m/sec and A is the sectional area of the stream then volume of water through stream Q= AxV ŌŚÅ In this method both quantities are measured at a suitable site when the discharge is steady ŌŚÅ Area is the product of width and depth ŌŚÅ Flow section is divided into no pf equal compartments ŌŚÅ The depth of water is measured in the middle of each compartment whose area is then calculated by multiplying the depth with its width ŌŚÅ The total cross sectional area of flow is the sum of areas of all compartments
- 14. MEASUREMENT OF VELOCITY- SURFACE FLOATS ŌŚÅ The floats are pieces of wood or hollow metallic cylinders or bottles etc ŌŚÅ Good for measuring small discharges of stream with an uneven bed ŌŚÅ can be used in absence of current meters and velocity rods ŌŚÅ The velocity is obtained by dividing the length of run in meters by the time in seconds ŌŚÅ Floats are easily affected by winds ŌŚÅ Mean velocity Vm= 0.85 Vs Vs observed velocity
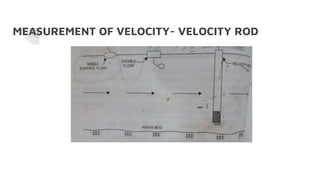
- 16. MEASUREMENT OF VELOCITY- VELOCITY ROD
- 17. ŌŚÅ A circular wooden rode of 5cm diameter with a hook at the topand of length that it floats only a few cms above the bed with its lower end at 0.94d from the top ŌŚÅ It is weighed at the bottom by piecesof metal to keep it in vertical position while floating ŌŚÅ Not affected by winds ŌŚÅ Not suited for measuring velocity in a stream with weed growth
- 18. MEASUREMENT OF VELOCITY- CURRENT METER ŌŚÅ Accurate results ŌŚÅ Operate by a dry battery cell ŌŚÅ Two types cup meters and propeller meters ŌŚÅ In cup meters 6or 8 cups rotate on a vertical axis due to the velocity of flow when the meter is immersed in water ŌŚÅ In propeller meters there are vanes revolving round a horizontal axis ŌŚÅ
- 20. MAXIMUM FLOOD DISCHARGE The maximum flood discharge is also called as maximum rate of run off during a peak flow or maximum flood 1. By indication of past floods 2. By empirical formulae 3. By unit hydrograph method 4. By flood frequency analysis
- 21. By empirical formuale 1. RYVEŌĆÖS FORMULA FOR SOUTH INDIAN CATCHMENTS Q= CM2/3 Q MAX FLOOD DISCHARGE IN CUMECS M IS CATCHMENT AREA IN SQ.KM C RYVEŌĆÖS COEFFICIENT
- 22. 2. DickenŌĆÖs formula Q= CM3/4 Q MAX FLOOD DISCHARGE IN CUMECS M IS THE CATCHMENT AREA IN SQ.KM C DICKENS COEFFICIENT
- 23. INGLIS FORMULA Q= 124A ŌłÜ(A+10.4) Q MAXIMUM FLOOD DISCHARGE CUMECS A CATCHMENT AREA IN SQ.KMS