shilpa
- 1. Fundamentals of Watermarking and Data Hiding Pierre Moulin University of Illinois at UrbanaâChampaign Dept of Electrical and Computer Engineering moulin@ifp.uiuc.edu July 9, 2006 ISIT Tutorial, Seattle c 2006 by Pierre Moulin. All rights reserved. 1
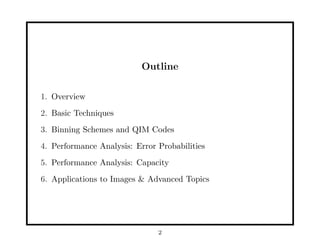
- 2. Outline 1. Overview 2. Basic Techniques 3. Binning Schemes and QIM Codes 4. Performance Analysis: Error Probabilities 5. Performance Analysis: Capacity 6. Applications to Images & Advanced Topics 2
- 3. SESSION 1: OVERVIEW âĒ Data hiding, watermarking, steganography âĒ Basic properties: ïŽdelity, payload, robustness, security 3
- 4. Some Reading âĒ Books: Digital Watermarking, by I. Cox, M. Miller, J. Bloom, Morgan-Kaufmann, 2002 Information Hiding Techniques for Steganography and Digital Watermarking, by S. Katzenbeisser and F. Petitcolas, Eds., Artech House, 2000 Information Hiding: Steganography and Watermarking, by N. Johnson, Z. Duric and S. Jajodia, Kluwer, 2000 4
- 5. âĒ New IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security (quarterly, inaugural issue in March 2006) âĒ Special issues of various IEEE journals, 1999 â 2005 âĒ Annual Information Hiding Workshops âĒ Watermarking newsletter: www.watermarkingworld.org âĒ www.ifp.uiuc.edu/Ëmoulin âĒ Tutorial paper âData Hiding Codesâ by P. Moulin and R. Koetter, Proceedings IEEE, December 2005. 5
- 6. Multimedia Security âĒ Dissemination of digital documents âĒ Owner identiïŽcation âĒ Forgery detection âĒ IdentiïŽcation of illegal copies âĒ Intellectual protection 6
- 8. 8
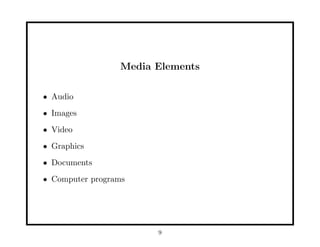
- 9. Media Elements âĒ Audio âĒ Images âĒ Video âĒ Graphics âĒ Documents âĒ Computer programs 9
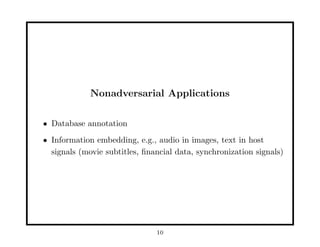
- 10. Nonadversarial Applications âĒ Database annotation âĒ Information embedding, e.g., audio in images, text in host signals (movie subtitles, ïŽnancial data, synchronization signals) 10
- 11. Data Hiding âĒ Embed data in covertext (high payload) âĒ Perceptual similarity requirement âĒ Multimedia database management âĒ Covert communications (military, spies, etc.) âĒ Steganography (ÏÏ ÎģÎąÎ―Ï ÎģÏÎąÏÏ, covert writing): conceal existence of hidden message 11
- 12. Watermarking âĒ Hide a few bits of information âĒ Original and modiïŽed signals should be perceptually similar âĒ Application to digital cameras, TV, DVD video, audio âĒ Authentication âĒ Transaction tracking âĒ Broadcast monitoring 12
- 13. Fingerprinting âĒ Fingerprinter marks several copies of original and distributes copies to users 1, 2, · · · , L âĒ Each mark is diïŽerent âĒ Users may collude to âremoveâ watermarks âĒ Applications: copy control, traitor tracing 13
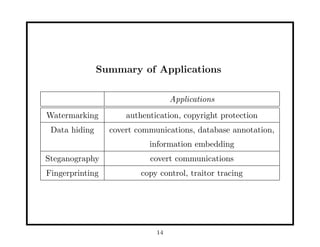
- 14. Summary of Applications Applications Watermarking authentication, copyright protection Data hiding covert communications, database annotation, information embedding Steganography covert communications Fingerprinting copy control, traitor tracing 14
- 15. A Brief History âĒ Tattoo hidden message on head of slave (ancient Greeks) âĒ Invisible ink âĒ Secret point patterns âĒ Watermarks in paper (Italy, 13th century) âĒ Digital watermarking: early 1990âs âĒ Standardization attempts: SDMI (music), ISO (MPEG video) 15
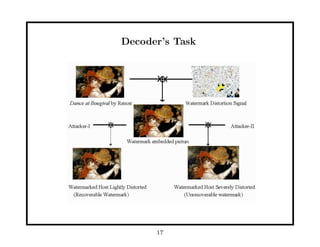
- 16. Hiding Data in Images secret key k Encoder original image S watermarked image X Picture taken by Alice on January 1, 2000. This message is going to be embedded forever in this picture. I challenge you to remove the message without substantially altering the picture. 1001001101001110100...............101 binary representation Decoder Picture taken by Alice on January 1, 2000. This message is going to be embedded forever in this picture. I challenge you to remove the message without substantially altering the picture. Decoded message 1001001101001110100...............101 Decoded binary message secret key k Attack Pirate 11011000...01 16
- 18. Attacks on Images Original JPEG, QF=10 4 à 4 median ïŽltering Gaussian ïŽlter (Ï = 3) Rotated by 10 degrees Random bend 18
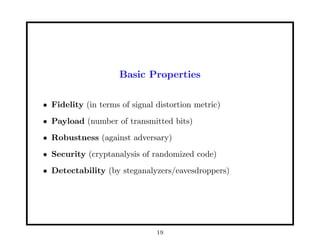
- 19. Basic Properties âĒ Fidelity (in terms of signal distortion metric) âĒ Payload (number of transmitted bits) âĒ Robustness (against adversary) âĒ Security (cryptanalysis of randomized code) âĒ Detectability (by steganalyzers/eavesdroppers) 19
- 20. System Issues âĒ System complexity âĒ Does decoder know host signal? (public vs private watermarking) âĒ Security level? âĒ Reliance on private or public cryptographic system? 20
- 21. Attack Models âĒ No attack âĒ Deterministic attacks (reversible & irreversible) âĒ Stochastic attacks (memoryless & stationary) âĒ Code breaking âĒ System attacks (e.g., ambiguity, sensitivity & scrambling) âĒ Benchmarking (e.g., Stirmark) 21
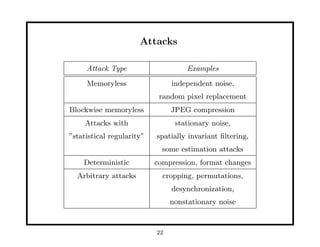
- 22. Attacks Attack Type Examples Memoryless independent noise, random pixel replacement Blockwise memoryless JPEG compression Attacks with stationary noise, âstatistical regularityâ spatially invariant ïŽltering, some estimation attacks Deterministic compression, format changes Arbitrary attacks cropping, permutations, desynchronization, nonstationary noise 22
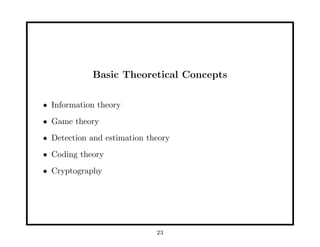
- 23. Basic Theoretical Concepts âĒ Information theory âĒ Game theory âĒ Detection and estimation theory âĒ Coding theory âĒ Cryptography 23
- 24. Purposes of an Information-Theoretic Approach âĒ make appropriate simplifying assumptions to understand fundamental limits of IH and optimally design algorithms âĒ provide new insights into IH âĒ provide a precise framework for evaluating any IH algorithm âĒ develop approach that generalizes easily to related problems Caution: cost of mismodeling may be severe in game with opponent! 24