Islamic banking
Download as ppt, pdf0 likes481 views
1) Islamic banking provides interest-free banking products that comply with Sharia law, including profit and loss sharing arrangements. It emerged in the 1970s due to factors like Arab nationalism, oil wealth, and individual choice. 2) Common Islamic banking products include short-term working capital financing, medium-term sales financing, syndicated financing, and sukuk (Islamic bonds). Mortgages are offered through diminishing musharakah, where the bank and customer jointly purchase a property. 3) The Islamic finance market has grown significantly, with over $700 billion in assets and $100-200 billion in liquid funds seeking Sharia-compliant investments. The industry is working to develop new
1 of 26
Downloaded 25 times














![Issuer
Dar Al-Arkan International Sukuk Company (a limited liability
company incorporated in the Cayman Islands)
Guarantor Dar Al-Arkan Real Estate Development Company (Dar Al-Arkan)
Issue 5 Year US$[*] Trust Certificates due 2012
Maturity 5 years, bullet
Floating Rate 3-month US$ LIBOR
Coupon US$ LIBOR plus 225bps
Public Listing
Application made to Dubai International Financial Exchange (DIFX)
and Labuan International Financial Exchange (LFX)
Issue Type Sukuk Al-Ijara
Governing Law
Saudi law for property-related documents
English law for Trust Deed and Certificates
Joint Lead Managers
and Joint Bookruners
ABC Islamic Bank (E.C.); Arab National Bank; Deutsche Bank AG;
Dubai Islamic Bank PJSC; Gulf International Bank B.S.C.; Kuwait
Finance House (Malaysia) Berhad; Unicorn Investment Bank,
B.S.C. (c)
(4) SUKUK SUMMARY](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/islamicbanking-130717103310-phpapp02/85/Islamic-banking-18-320.jpg)






Ad
Recommended
Duncan Smiths Presentation
Duncan Smiths PresentationISEConsult
╠²
The document provides an overview of Islamic banking products and operations. It discusses key concepts like prohibiting interest and requiring profit and loss sharing. Common Islamic banking products described include murabaha for working capital, equipment financing, syndicated financing, sukuk bonds, mortgages, and investment funds. The concluding remarks note the growth opportunities for Islamic banking given the large Muslim population and its compatibility with their religious beliefs.Islamic Finance 3
Islamic Finance 3Nuradli Ridzwan Shah Bin Mohd Dali
╠²
The document discusses two types of riba that are prohibited in Islamic banking:
1) Riba-un-Nasiyah (or Riba-al-Jahiliya), which refers to loans with interest or excess repayment amounts predetermined. Scholars define it as any loan with interest.
2) Riba-al-Fadl, which refers to an excess received when exchanging specific commodities like gold for gold. Scholars differ on which commodities apply, but most say commodities must be edible, storable, or act as a medium of exchange.
The key difference between Islamic and conventional banking is that Islamic banking prohibits riba and is based on profit/loss sharingIfs
IfsMayank Arora
╠²
The document lists several names and entities involved in the money market: Stuti, Kanika, Parag, Kush, Abhinav, Mayank Arora, Reserve Bank of India, Discount and Finance House of India, mutual funds, corporate investors, non-banking finance companies, Securities Trading Corporation of India, commercial banks, co-operative banks, non-banking financial institutions, indigenous banks, money lenders.
It then lists several money market instruments: treasury bills, call/notice money, commercial paper, certificates of deposits, commercial bills, collateralized borrowing and lending obligation.
It provides details on treasury bills, commercial paper, and the Liquidity Adjustment Facility whichHandbook Of Islamic Banking
Handbook Of Islamic BankingAshik Iqbal
╠²
This document provides a summary of the Handbook of Islamic Banking edited by M. Kabir Hassan and Mervyn K. Lewis. The handbook contains 25 chapters contributed by various experts in the field of Islamic banking and finance. It covers the foundations, operations, instruments and markets, systems and globalization of Islamic banking. The handbook aims to provide comprehensive coverage of the principles, practices and contemporary issues related to Islamic banking and finance.Covid-19 drives demand for short term rentals in UAE
Covid-19 drives demand for short term rentals in UAEHina Navin Freelance Journalist/Designer - Dubai
╠²
The COVID-19 pandemic has heightened demand for short-term rentals in the UAE, particularly in areas like Barsha, Barsha Heights, and JVC, as residents seek flexible housing options amidst job uncertainties. Rental prices for studios and one-bedroom units have dropped significantly, leading to increased occupancy in these properties as renters prioritize hygiene and affordability. Hotel staycations are also on the rise, with customers seeking private amenities and safety measures, illustrating a shift in preferences towards short-term accommodations.Ctu 351 bab 2 framework of islamic banking
Ctu 351 bab 2 framework of islamic bankingNor Ila Che Man
╠²
This document provides an overview of the framework of the Islamic financial system. It discusses key concepts like Islam, Islamic economics, banking and finance. The core principles of Islamic banking are outlined, including a prohibition of riba (usury) and risk sharing. The objectives of Islamic banking are described as promoting products and services based on shariah principles, upholding brotherhood and providing facilities to communities. Ethics like avoiding abuse of power and maintaining secrecy are also emphasized. Sources of Islamic law that guide the system are mentioned.Islamic Mutual Trust
Islamic Mutual TrustFarhanah Noah
╠²
Islamic unit trust funds have become increasingly popular investments in Malaysia. They allow investors to invest in a diversified portfolio of Shariah-compliant securities while being professionally managed. The Malaysian government and Securities Commission regulate Islamic unit trusts and oversee fund managers and trustees to protect investors. Recent trends show investors increasingly choosing Islamic funds over conventional funds.Introduction to CTU351
Introduction to CTU351Mahyuddin Khalid
╠²
This document outlines the syllabus for a course on the fundamentals of Islamic banking. The course aims to introduce students to Islamic banking principles and how they differ from conventional banking. Key topics covered include the framework of the Islamic financial system, compliance with Shariah laws, principles of Islamic banking, sources and application of funds through various Islamic financing facilities. Assessment consists of continuous assessments like tests, assignments and presentations, as well as a final exam. Presentations should be in PowerPoint format and last 30 minutes, followed by a 20-minute Q&A session. References are to be formatted in APA style.Chapter 3
Chapter 3WanBK Leo
╠²
The document provides an overview of Islamic economic systems, including its key principles, structures, and implementation. It discusses that Islamic economics is based on principles from Islamic sources that offer an alternative set of parameters for economic activity focused on human welfare. The main objectives of Islamic economy are social and economic justice, equality, and ensuring wealth circulation to prevent concentration.Unit trust
Unit trustHafizul Mukhlis
╠²
Unit trusts allow investors to pool their money into a single fund which is then professionally managed. The fund manager invests the pooled money into a variety of securities and assets. Individual investors purchase units in the fund, becoming beneficial owners of the assets in proportion to the number of units they hold. A trust deed governs the roles of the trustee, who holds the legal title to the assets, and the fund manager, who manages the investments and makes decisions on behalf of unit holders.Fundamental of Islamic Banking - Principles of Islamic Banking
Fundamental of Islamic Banking - Principles of Islamic BankingMahyuddin Khalid
╠²
This document provides an overview of Islamic banking and finance principles. It discusses permissible and prohibited activities for Islamic investment and financing. Key concepts covered include profit and loss sharing, trade-based financing vs interest-based loans, and the prohibition of riba (interest), gharar (uncertainty) and maisir (gambling). It also outlines the payment of zakat and some major Islamic legal maxims.ISLAMIC UNIT TRUST AND ETF
ISLAMIC UNIT TRUST AND ETFZainora Hayari
╠²
The document discusses Islamic unit trusts and Islamic exchange-traded funds (ETFs). It provides an overview of Islamic unit trusts, including their history, structure, types of funds, and issues related to speculation, diversity of underlying equities, and global investments. It also discusses Islamic ETFs, defining them, comparing them to conventional ETFs, and outlining their structure and operation. Finally, it discusses some potential issues for Islamic ETFs regarding purification of earnings, liquidity, technical issues, compliance limitations, and asset allocation.Type of unit trusts
Type of unit trustsTio Sheng Chiat
╠²
Types of unit trust funds available in Malaysia include equity funds, fixed income funds, money market funds, real estate investment trusts, exchange traded funds, balanced funds, and Syariah funds. Equity funds provide exposure to companies listed on Bursa Malaysia and come in forms like aggressive growth funds and index funds. Fixed income and money market funds invest in bonds and short-term instruments. Real estate investment trusts allow investment in property markets. Balanced funds maintain a mix of equities, bonds and cash. Syariah funds exclude companies incompatible with Islamic principles.Islamic trade financing
Islamic trade financingan nur
╠²
1. Islamic trade financing provides Shariah-compliant financing options to support international trade. Common tools include letters of credit, bank acceptances, and shipping guarantees.
2. There are several methods for settling trade transactions, including cash in advance (where the importer pays before shipment), open account (where payment is made after shipment on agreed terms), and documentary collection (where documents and payment are handled through banks).
3. For Islamic banks, common settlement methods include cash in advance, where a percentage is paid upfront, and documentary collection, where documents and payment are routed through correspondent banks following Shariah guidelines. This allows trade to be financed while managing risks for both importers and exporters.20161103 technical programme 2 financing_products_djibouti_2016
20161103 technical programme 2 financing_products_djibouti_2016Abubaker Mayanja
╠²
Islamic banks make money through various Sharia-compliant financing contracts that do not involve interest, including deferred sales contracts like murabaha and istisna'a, and profit-and-loss sharing contracts like mudaraba and musharaka. Murabaha involves the bank purchasing an asset for a customer and reselling it at a markup. Mudaraba is a partnership between the bank and an entrepreneur where profits are shared according to a predetermined ratio but losses are borne solely by the bank. These contracts allow Islamic banks to finance various products and services like mortgages, working capital, and car/equipment purchases in a way that is permissible under Islamic law.Islamic markets
Islamic marketsalco7001
╠²
The document outlines various Islamic investment and financing structures including debts-based structures like murabaha, bai al-inah, and bay salam; equity-based structures like musharakah and mudarabah; leasing structures like ijara and ijara-wa-iqtina; and services like hawala and kafala. It provides details on how each structure works in accordance with Shariah principles like risk-sharing and prohibition of interest.Cross-Border Sukuk Issues
Cross-Border Sukuk IssuesISEConsult
╠²
This document summarizes WestLB's involvement in Islamic financing deals since 2005 and discusses opportunities for continued growth in the Islamic finance market. It outlines two case studies of cross-border Sukuk issues arranged by WestLB, including the first GCC sovereign Sukuk in 2001 and a $600 million Sukuk for Dar Al-Arkan. It also discusses expansion of Islamic finance into new regions like the UK and innovations in Sukuk structures.Islamic Banking
Islamic Banking Muzamil Rehman
╠²
This document provides an overview of Islamic banking through a presentation by several members. It begins with an introduction to Islamic banking principles such as prohibiting interest and encouraging profit and loss sharing. It then discusses various Islamic financing modes like murabaha, ijara, musharakah, and sukuk. The document also covers the history and development of Islamic banking, current practices in countries like the UK, and challenges related to standardization and a shortage of qualified scholars and professionals.Financial Accounting
Financial Accounting mastergaming51
╠²
Islamic banking is a system that allows Muslims to deal with their finances according to their faith. It is based on avoiding interest (riba), which is forbidden. Common Islamic financing modes include mudarabah (profit-sharing), murabaha (cost-plus), ijara (leasing), musharaka (joint venture), takaful (Islamic insurance), and sukuk (Islamic bonds). The main differences between conventional and Islamic banks are that conventional banks lend money and charge interest, while Islamic banks engage in asset-backed trading and business partnerships based on profit/loss sharing.Fundamentals of Islamic Finance explained through Islamic Contracts
Fundamentals of Islamic Finance explained through Islamic Contractstiesinfo
╠²
The document provides an overview of Islamic banking and finance principles, focusing on the prohibition of interest (riba), risk sharing, and the types of Islamic contracts including equity-based, sale-based, and lease-based. It details specific contracts like mudarabah, musharakah, sukuk, salaam, murabahah, and ijarah, explaining their applications and suitability in contexts such as India. Additionally, it outlines the basic rules for judging the validity of conditions in Islamic contracts.Islamic Finance Its Concepts, Models, Growth & Opportunities
Islamic Finance Its Concepts, Models, Growth & OpportunitiesIndoAsia Partners
╠²
This document provides an overview of Islamic finance, including its key concepts, models, and growth opportunities. It discusses how Islamic finance works using models like murabaha and ijara that avoid interest, the principles of prohibiting riba (interest), gharar (uncertainty), and investing in certain sectors. It outlines major contracts like mudaraba, musharaka, sukuk, and the role of Sharia boards in approving Islamic financial products and transactions to ensure compliance.Islmic banking
Islmic bankingIndoAsia Partners
╠²
This document provides an overview of Islamic finance, including its key concepts, models, and growth opportunities. It discusses how Islamic finance works using models like murabaha and ijara that avoid interest, the principles of prohibiting riba (interest), gharar (uncertainty), and investing in certain sectors. It outlines major Islamic finance contracts and products like mudaraba, sukuk, and takaful. It also explains the roles of mudaraba, sukuk, and Sharia boards in ensuring compliance with Islamic principles.Islamic-banking
Islamic-bankingmastergaming51
╠²
Islamic banking is based on Islamic law and prohibits interest. It operates using profit-and-loss sharing contracts instead of interest-based loans. The two main principles are sharing of profit/loss and prohibition of interest. Islamic banks have grown significantly around the world, especially in the Middle East, Southeast Asia, and some parts of Europe. They offer products like mudarabah, musharaka, murabaha, and ijara. The key difference from conventional banks is the prohibition of interest and focus on risk-sharing rather than guaranteed returns. Morocco is encouraging the growth of Islamic banking by establishing new Islamic banks and windows and developing its Islamic financial market.Islamic Banking and Various Contracts
Islamic Banking and Various ContractsMaryam Khan
╠²
This document provides an overview of Islamic banking products and services offered by Bank Islami Pakistan Limited. It discusses various Shariah compliant financing modes like Mudarabah, Musharakah, and Diminishing Musharakah used in Islamic home financing. The document also describes different Sukuk structures like Ijarah, Murabahah, Musharakah and their key features. Finally, it summarizes the key features and requirements for opening Islami Bachat and Islami Dollar Bachat accounts.ISLAMIC PRESENTATION AND BANKING DECISION
ISLAMIC PRESENTATION AND BANKING DECISIONIqtidarAli6
╠²
The document presents an overview of Islamic banking, defining it as a system based on Islamic law that prohibits interest and promotes profit-sharing. It discusses the global landscape of Islamic banks, their specific operational principles, and various products and services like mudarabah, musharakah, and murabaha. Additionally, the presentation highlights the differences between Islamic and conventional banking, and the status of Islamic banking in Pakistan, emphasizing its role in economic development and stability.Al Alawi Co Islamic Finance Presentation - Final - 13 01 16
Al Alawi Co Islamic Finance Presentation - Final - 13 01 16Arsalan Buriro (Bar-at-Law)
╠²
Banking plays an important role in modern economies by facilitating investment opportunities for individuals and businesses. Islamic finance provides alternatives to conventional banking that are compliant with Shariah principles such as prohibitions on riba (interest) and gharar (excessive uncertainty). Some of the main Islamic finance contracts and instruments discussed include mudaraba, musharaka, murabaha, ijara, sukuk, and istisna/salam which are based on principles of profit/loss sharing and asset-backed transactions.Alhuda CIBE - Present Trends and Future Prospects of Sukuk
Alhuda CIBE - Present Trends and Future Prospects of SukukAlhuda Centre of Islamic Banking & Economics
╠²
1) The document discusses the growth of the Islamic bond (sukuk) market, providing examples of notable sukuk deals from 2003-2006 in the Middle East.
2) It describes various sukuk structures that have been used, including sukuk al-ijara, sukuk al-istisna, and sukuk al-musharakah.
3) Factors that fueled the growth of Islamic bond markets are also summarized, such as the use of "mainstream" Islamic structures and higher demand from investors.islamic-banking-170223203820.pdf
islamic-banking-170223203820.pdfEnglish1013
╠²
Islamic banking is a system based on Islamic law that prohibits interest and involves profit/loss sharing. It has grown strongly in recent years across Asia, the Middle East, Europe and Africa. Islamic banks offer products like mudarabah, musharaka, and murabaha that comply with Shariah law. They differ from conventional banks in their risk sharing approach and prohibition of interest and speculative activities. Morocco has encouraged the growth of Islamic banking by allowing new Islamic banks and windows and plans to develop its Islamic financial market.Presentation1 (1)
Presentation1 (1)Shahana Khan
╠²
This document discusses the principles of Islamic finance. It states that Islamic finance is based on Shariah law, which governs religious and secular aspects of life. Some key principles discussed are the prohibition of riba (interest), gharar (uncertainty), investing in haram activities, and speculation. It also discusses common Islamic financial instruments like mudarabah (profit-sharing project financing), musharakah (profit-sharing partnership), murabaha (cost-plus sale), ijarah (leasing), and different types of accounts in Islamic banks.Islamic banking
Islamic bankingImane SBAI
╠²
The document provides an overview of Islamic banking, which operates under Islamic law principles like profit and loss sharing and prohibiting interest. It outlines various Islamic banking products and services, such as mudarabah, musharakah, murabaha, and ijara, while comparing Islamic banking practices to conventional banking. Additionally, it discusses the status of Islamic banking in Morocco, including partnerships to establish Islamic bank subsidiaries and efforts to promote investment stability and economic development.More Related Content
Viewers also liked (6)
Chapter 3
Chapter 3WanBK Leo
╠²
The document provides an overview of Islamic economic systems, including its key principles, structures, and implementation. It discusses that Islamic economics is based on principles from Islamic sources that offer an alternative set of parameters for economic activity focused on human welfare. The main objectives of Islamic economy are social and economic justice, equality, and ensuring wealth circulation to prevent concentration.Unit trust
Unit trustHafizul Mukhlis
╠²
Unit trusts allow investors to pool their money into a single fund which is then professionally managed. The fund manager invests the pooled money into a variety of securities and assets. Individual investors purchase units in the fund, becoming beneficial owners of the assets in proportion to the number of units they hold. A trust deed governs the roles of the trustee, who holds the legal title to the assets, and the fund manager, who manages the investments and makes decisions on behalf of unit holders.Fundamental of Islamic Banking - Principles of Islamic Banking
Fundamental of Islamic Banking - Principles of Islamic BankingMahyuddin Khalid
╠²
This document provides an overview of Islamic banking and finance principles. It discusses permissible and prohibited activities for Islamic investment and financing. Key concepts covered include profit and loss sharing, trade-based financing vs interest-based loans, and the prohibition of riba (interest), gharar (uncertainty) and maisir (gambling). It also outlines the payment of zakat and some major Islamic legal maxims.ISLAMIC UNIT TRUST AND ETF
ISLAMIC UNIT TRUST AND ETFZainora Hayari
╠²
The document discusses Islamic unit trusts and Islamic exchange-traded funds (ETFs). It provides an overview of Islamic unit trusts, including their history, structure, types of funds, and issues related to speculation, diversity of underlying equities, and global investments. It also discusses Islamic ETFs, defining them, comparing them to conventional ETFs, and outlining their structure and operation. Finally, it discusses some potential issues for Islamic ETFs regarding purification of earnings, liquidity, technical issues, compliance limitations, and asset allocation.Type of unit trusts
Type of unit trustsTio Sheng Chiat
╠²
Types of unit trust funds available in Malaysia include equity funds, fixed income funds, money market funds, real estate investment trusts, exchange traded funds, balanced funds, and Syariah funds. Equity funds provide exposure to companies listed on Bursa Malaysia and come in forms like aggressive growth funds and index funds. Fixed income and money market funds invest in bonds and short-term instruments. Real estate investment trusts allow investment in property markets. Balanced funds maintain a mix of equities, bonds and cash. Syariah funds exclude companies incompatible with Islamic principles.Islamic trade financing
Islamic trade financingan nur
╠²
1. Islamic trade financing provides Shariah-compliant financing options to support international trade. Common tools include letters of credit, bank acceptances, and shipping guarantees.
2. There are several methods for settling trade transactions, including cash in advance (where the importer pays before shipment), open account (where payment is made after shipment on agreed terms), and documentary collection (where documents and payment are handled through banks).
3. For Islamic banks, common settlement methods include cash in advance, where a percentage is paid upfront, and documentary collection, where documents and payment are routed through correspondent banks following Shariah guidelines. This allows trade to be financed while managing risks for both importers and exporters.Similar to Islamic banking (20)
20161103 technical programme 2 financing_products_djibouti_2016
20161103 technical programme 2 financing_products_djibouti_2016Abubaker Mayanja
╠²
Islamic banks make money through various Sharia-compliant financing contracts that do not involve interest, including deferred sales contracts like murabaha and istisna'a, and profit-and-loss sharing contracts like mudaraba and musharaka. Murabaha involves the bank purchasing an asset for a customer and reselling it at a markup. Mudaraba is a partnership between the bank and an entrepreneur where profits are shared according to a predetermined ratio but losses are borne solely by the bank. These contracts allow Islamic banks to finance various products and services like mortgages, working capital, and car/equipment purchases in a way that is permissible under Islamic law.Islamic markets
Islamic marketsalco7001
╠²
The document outlines various Islamic investment and financing structures including debts-based structures like murabaha, bai al-inah, and bay salam; equity-based structures like musharakah and mudarabah; leasing structures like ijara and ijara-wa-iqtina; and services like hawala and kafala. It provides details on how each structure works in accordance with Shariah principles like risk-sharing and prohibition of interest.Cross-Border Sukuk Issues
Cross-Border Sukuk IssuesISEConsult
╠²
This document summarizes WestLB's involvement in Islamic financing deals since 2005 and discusses opportunities for continued growth in the Islamic finance market. It outlines two case studies of cross-border Sukuk issues arranged by WestLB, including the first GCC sovereign Sukuk in 2001 and a $600 million Sukuk for Dar Al-Arkan. It also discusses expansion of Islamic finance into new regions like the UK and innovations in Sukuk structures.Islamic Banking
Islamic Banking Muzamil Rehman
╠²
This document provides an overview of Islamic banking through a presentation by several members. It begins with an introduction to Islamic banking principles such as prohibiting interest and encouraging profit and loss sharing. It then discusses various Islamic financing modes like murabaha, ijara, musharakah, and sukuk. The document also covers the history and development of Islamic banking, current practices in countries like the UK, and challenges related to standardization and a shortage of qualified scholars and professionals.Financial Accounting
Financial Accounting mastergaming51
╠²
Islamic banking is a system that allows Muslims to deal with their finances according to their faith. It is based on avoiding interest (riba), which is forbidden. Common Islamic financing modes include mudarabah (profit-sharing), murabaha (cost-plus), ijara (leasing), musharaka (joint venture), takaful (Islamic insurance), and sukuk (Islamic bonds). The main differences between conventional and Islamic banks are that conventional banks lend money and charge interest, while Islamic banks engage in asset-backed trading and business partnerships based on profit/loss sharing.Fundamentals of Islamic Finance explained through Islamic Contracts
Fundamentals of Islamic Finance explained through Islamic Contractstiesinfo
╠²
The document provides an overview of Islamic banking and finance principles, focusing on the prohibition of interest (riba), risk sharing, and the types of Islamic contracts including equity-based, sale-based, and lease-based. It details specific contracts like mudarabah, musharakah, sukuk, salaam, murabahah, and ijarah, explaining their applications and suitability in contexts such as India. Additionally, it outlines the basic rules for judging the validity of conditions in Islamic contracts.Islamic Finance Its Concepts, Models, Growth & Opportunities
Islamic Finance Its Concepts, Models, Growth & OpportunitiesIndoAsia Partners
╠²
This document provides an overview of Islamic finance, including its key concepts, models, and growth opportunities. It discusses how Islamic finance works using models like murabaha and ijara that avoid interest, the principles of prohibiting riba (interest), gharar (uncertainty), and investing in certain sectors. It outlines major contracts like mudaraba, musharaka, sukuk, and the role of Sharia boards in approving Islamic financial products and transactions to ensure compliance.Islmic banking
Islmic bankingIndoAsia Partners
╠²
This document provides an overview of Islamic finance, including its key concepts, models, and growth opportunities. It discusses how Islamic finance works using models like murabaha and ijara that avoid interest, the principles of prohibiting riba (interest), gharar (uncertainty), and investing in certain sectors. It outlines major Islamic finance contracts and products like mudaraba, sukuk, and takaful. It also explains the roles of mudaraba, sukuk, and Sharia boards in ensuring compliance with Islamic principles.Islamic-banking
Islamic-bankingmastergaming51
╠²
Islamic banking is based on Islamic law and prohibits interest. It operates using profit-and-loss sharing contracts instead of interest-based loans. The two main principles are sharing of profit/loss and prohibition of interest. Islamic banks have grown significantly around the world, especially in the Middle East, Southeast Asia, and some parts of Europe. They offer products like mudarabah, musharaka, murabaha, and ijara. The key difference from conventional banks is the prohibition of interest and focus on risk-sharing rather than guaranteed returns. Morocco is encouraging the growth of Islamic banking by establishing new Islamic banks and windows and developing its Islamic financial market.Islamic Banking and Various Contracts
Islamic Banking and Various ContractsMaryam Khan
╠²
This document provides an overview of Islamic banking products and services offered by Bank Islami Pakistan Limited. It discusses various Shariah compliant financing modes like Mudarabah, Musharakah, and Diminishing Musharakah used in Islamic home financing. The document also describes different Sukuk structures like Ijarah, Murabahah, Musharakah and their key features. Finally, it summarizes the key features and requirements for opening Islami Bachat and Islami Dollar Bachat accounts.ISLAMIC PRESENTATION AND BANKING DECISION
ISLAMIC PRESENTATION AND BANKING DECISIONIqtidarAli6
╠²
The document presents an overview of Islamic banking, defining it as a system based on Islamic law that prohibits interest and promotes profit-sharing. It discusses the global landscape of Islamic banks, their specific operational principles, and various products and services like mudarabah, musharakah, and murabaha. Additionally, the presentation highlights the differences between Islamic and conventional banking, and the status of Islamic banking in Pakistan, emphasizing its role in economic development and stability.Al Alawi Co Islamic Finance Presentation - Final - 13 01 16
Al Alawi Co Islamic Finance Presentation - Final - 13 01 16Arsalan Buriro (Bar-at-Law)
╠²
Banking plays an important role in modern economies by facilitating investment opportunities for individuals and businesses. Islamic finance provides alternatives to conventional banking that are compliant with Shariah principles such as prohibitions on riba (interest) and gharar (excessive uncertainty). Some of the main Islamic finance contracts and instruments discussed include mudaraba, musharaka, murabaha, ijara, sukuk, and istisna/salam which are based on principles of profit/loss sharing and asset-backed transactions.Alhuda CIBE - Present Trends and Future Prospects of Sukuk
Alhuda CIBE - Present Trends and Future Prospects of SukukAlhuda Centre of Islamic Banking & Economics
╠²
1) The document discusses the growth of the Islamic bond (sukuk) market, providing examples of notable sukuk deals from 2003-2006 in the Middle East.
2) It describes various sukuk structures that have been used, including sukuk al-ijara, sukuk al-istisna, and sukuk al-musharakah.
3) Factors that fueled the growth of Islamic bond markets are also summarized, such as the use of "mainstream" Islamic structures and higher demand from investors.islamic-banking-170223203820.pdf
islamic-banking-170223203820.pdfEnglish1013
╠²
Islamic banking is a system based on Islamic law that prohibits interest and involves profit/loss sharing. It has grown strongly in recent years across Asia, the Middle East, Europe and Africa. Islamic banks offer products like mudarabah, musharaka, and murabaha that comply with Shariah law. They differ from conventional banks in their risk sharing approach and prohibition of interest and speculative activities. Morocco has encouraged the growth of Islamic banking by allowing new Islamic banks and windows and plans to develop its Islamic financial market.Presentation1 (1)
Presentation1 (1)Shahana Khan
╠²
This document discusses the principles of Islamic finance. It states that Islamic finance is based on Shariah law, which governs religious and secular aspects of life. Some key principles discussed are the prohibition of riba (interest), gharar (uncertainty), investing in haram activities, and speculation. It also discusses common Islamic financial instruments like mudarabah (profit-sharing project financing), musharakah (profit-sharing partnership), murabaha (cost-plus sale), ijarah (leasing), and different types of accounts in Islamic banks.Islamic banking
Islamic bankingImane SBAI
╠²
The document provides an overview of Islamic banking, which operates under Islamic law principles like profit and loss sharing and prohibiting interest. It outlines various Islamic banking products and services, such as mudarabah, musharakah, murabaha, and ijara, while comparing Islamic banking practices to conventional banking. Additionally, it discusses the status of Islamic banking in Morocco, including partnerships to establish Islamic bank subsidiaries and efforts to promote investment stability and economic development.Sources of finance
Sources of finance Jamiu Akangbe
╠²
The document provides an overview of various sources of financing, including both conventional and Islamic options. It discusses debt financing through instruments like bonds, sukuk, murabaha, and qard al hassan. It also covers equity financing such as venture capital, public offerings, private placements, and Islamic structures like musharakah and mudarabah. Practical tips are provided for sourcing financing, including factors financiers consider, requirements for applications, and emphasizing the importance of istighfar.A primer on islamic finance & banking by Century Banking Corp
A primer on islamic finance & banking by Century Banking CorpMuniruddeen Lallmahamood (Dr.)
╠²
The document provides an overview of Islamic finance and banking principles. It summarizes that Islamic banking prohibits interest and gambling, and requires profit and risk sharing between parties based on underlying business transactions or assets. It describes common Islamic finance concepts like mudarabah, musharakah, murabaha, and ijara that are used to structure financing. The document also answers frequently asked questions about Islamic deposit accounts, fees, and whether Islamic banking is only for Muslims.Islamic financial system
Islamic financial systemMohamed Ibrahim
╠²
This document discusses the application of Musharakah and Mudarabah contracts in Islamic finance and banking. It defines Musharakah as a partnership contract where both parties contribute capital to a project and share profits, while losses are based on capital contributions. Musharakah can be used in trade financing, project financing, syndicated assets, stocks, and securitization. Mudarabah is defined as a contract where one party provides capital and the other provides labor to generate profits, which are shared according to agreement. Mudarabah can be used in deposits, various types of financing, takaful, and sukuk.ICMAP
ICMAPAlhuda Centre of Islamic Banking & Economics
╠²
The document provides an overview of Islamic banking and finance. It defines key concepts like Riba (interest), outlines major Islamic banking products like Murabahah, Ijarah, Musharakah and Mudarabah. It discusses the differences between Islamic and conventional banking. It also provides information on the progress and growth of the Islamic banking industry globally and in Pakistan, including the number of Islamic banks and branches.Alhuda CIBE - Present Trends and Future Prospects of Sukuk
Alhuda CIBE - Present Trends and Future Prospects of SukukAlhuda Centre of Islamic Banking & Economics
╠²
Ad
Recently uploaded (20)
Code Profiling in Odoo 18 - Odoo 18 ║▌║▌▀Żs
Code Profiling in Odoo 18 - Odoo 18 ║▌║▌▀ŻsCeline George
╠²
Profiling in Odoo identifies slow code and resource-heavy processes, ensuring better system performance. Odoo code profiling detects bottlenecks in custom modules, making it easier to improve speed and scalability.How to Manage Different Customer Addresses in Odoo 18 Accounting
How to Manage Different Customer Addresses in Odoo 18 AccountingCeline George
╠²
A business often have customers with multiple locations such as office, warehouse, home addresses and this feature allows us to associate with different addresses with each customer streamlining the process of creating sales order invoices and delivery orders.SCHIZOPHRENIA OTHER PSYCHOTIC DISORDER LIKE Persistent delusion/Capgras syndr...
SCHIZOPHRENIA OTHER PSYCHOTIC DISORDER LIKE Persistent delusion/Capgras syndr...parmarjuli1412
╠²
SCHIZOPHRENIA INCLUDED TOPIC IS INTRODUCTION, DEFINITION OF GENERAL TERM IN PSYCHIATRIC, THEN DIFINITION OF SCHIZOPHRENIA, EPIDERMIOLOGY, ETIOLOGICAL FACTORS, CLINICAL FEATURE(SIGN AND SYMPTOMS OF SCHIZOPHRENIA), CLINICAL TYPES OF SCHIZOPHRENIA, DIAGNOSIS, INVESTIGATION, TREATMENT MODALITIES(PHARMACOLOGICAL MANAGEMENT, PSYCHOTHERAPY, ECT, PSYCHO-SOCIO-REHABILITATION), NURSING MANAGEMENT(ASSESSMENT,DIAGNOSIS,NURSING INTERVENTION,AND EVALUATION), OTHER PSYCHOTIC DISORDER LIKE Persistent delusion/Capgras syndrome(The Delusion of Doubles)/Acute and Transient Psychotic Disorders/Induced Delusional Disorders/Schizoaffective Disorder /CAPGRAS SYNDROME(DELUSION OF DOUBLE), GERIATRIC CONSIDERATION, FOLLOW UP, HOMECARE AND REHABILITATION OF THE PATIENT, University of Ghana Cracks Down on Misconduct: Over 100 Students Sanctioned
University of Ghana Cracks Down on Misconduct: Over 100 Students SanctionedKweku Zurek
╠²
University of Ghana Cracks Down on Misconduct: Over 100 Students Sanctioned
This is why students from these 44 institutions have not received National Se...
This is why students from these 44 institutions have not received National Se...Kweku Zurek
╠²
This is why students from these 44 institutions have not received National Service PIN codes (LIST)Plate Tectonic Boundaries and Continental Drift Theory
Plate Tectonic Boundaries and Continental Drift TheoryMarie
╠²
This 28 slide presentation covers the basics of plate tectonics and continental drift theory. It is an effective introduction into a full plate tectonics unit study, but does not cover faults, stress, seismic waves, or seafloor spreading.
To download PDF, visit The Homeschool Daily. We will be uploading more slideshows to follow this one. Blessings, Marie Q1_ENGLISH_PPT_WEEK 1 power point grade 3 Quarter 1 week 1
Q1_ENGLISH_PPT_WEEK 1 power point grade 3 Quarter 1 week 1jutaydeonne
╠²
Grade 3 Quarter 1 Week 1 English part 2Birnagar High School Platinum Jubilee Quiz.pptx
Birnagar High School Platinum Jubilee Quiz.pptxSourav Kr Podder
╠²
Birnagar High School Platinum Jubilee Celebration QuizTHE PSYCHOANALYTIC OF THE BLACK CAT BY EDGAR ALLAN POE (1).pdf
THE PSYCHOANALYTIC OF THE BLACK CAT BY EDGAR ALLAN POE (1).pdfnabilahk908
╠²
Psychoanalytic Analysis of The Black Cat by Edgar Allan Poe explores the deep psychological dimensions of the narratorŌĆÖs disturbed mind through the lens of Sigmund FreudŌĆÖs psychoanalytic theory. According to Freud (1923), the human psyche is structured into three components: the Id, which contains primitive and unconscious desires; the Ego, which operates on the reality principle and mediates between the Id and the external world; and the Superego, which reflects internalized moral standards.
In this story, Poe presents a narrator who experiences a psychological breakdown triggered by repressed guilt, aggression, and internal conflict. This analysis focuses not only on the gothic horror elements of the narrative but also on the narratorŌĆÖs mental instability and emotional repression, demonstrating how the imbalance of these three psychic forces contributes to his downfall.BINARY files CSV files JSON files with example.pptx
BINARY files CSV files JSON files with example.pptxRamakrishna Reddy Bijjam
╠²
BINARY FILES, CSV FILESPests of Maize: An comprehensive overview.pptx
Pests of Maize: An comprehensive overview.pptxArshad Shaikh
╠²
Maize is susceptible to various pests that can significantly impact yields. Key pests include the fall armyworm, stem borers, cob earworms, shoot fly. These pests can cause extensive damage, from leaf feeding and stalk tunneling to grain destruction. Effective management strategies, such as integrated pest management (IPM), resistant varieties, biological control, and judicious use of chemicals, are essential to mitigate losses and ensure sustainable maize production.ECONOMICS, DISASTER MANAGEMENT, ROAD SAFETY - STUDY MATERIAL [10TH]
ECONOMICS, DISASTER MANAGEMENT, ROAD SAFETY - STUDY MATERIAL [10TH]SHERAZ AHMAD LONE
╠²
This study material for Class 10th covers the core subjects of Economics, Disaster Management, and Road Safety Education, developed strictly in line with the JKBOSE textbook. It presents the content in a simplified, structured, and student-friendly format, ensuring clarity in concepts. The material includes reframed explanations, flowcharts, infographics, and key point summaries to support better understanding and retention. Designed for classroom teaching and exam preparation, it aims to enhance comprehension, critical thinking, and practical awareness among students.GEOGRAPHY-Study Material [ Class 10th] .pdf
GEOGRAPHY-Study Material [ Class 10th] .pdfSHERAZ AHMAD LONE
╠²
"Geography Study Material for Class 10th" provides a comprehensive and easy-to-understand resource for key topics like Resources & Development, Water Resources, Agriculture, Minerals & Energy, Manufacturing Industries, and Lifelines of the National Economy. Designed as per the latest NCERT/JKBOSE syllabus, it includes notes, maps, diagrams, and MODEL question Paper to help students excel in exams. Whether revising for exams or strengthening conceptual clarity, this material ensures effective learning and high scores. Perfect for last-minute revisions and structured study sessions.Sustainable Innovation with Immersive Learning
Sustainable Innovation with Immersive LearningLeonel Morgado
╠²
Prof. Leonel and Prof. Dennis approached educational uses, practices, and strategies of using immersion as a lens to interpret, design, and planning educational activities in a sustainable way. Rather than one-off gimmicks, the intent is to enable instructors (and institutions) to be able to include them in their regular activities, including the ability to evaluate and redesign them.
Immersion as a phenomenon enables interpreting pedagogical activities in a learning-agnostic way: you take a stance on the learning theory to follow, and leverage immersion to envision and guide your practice.Battle of Bookworms 2025 - U25 Literature Quiz by Pragya
Battle of Bookworms 2025 - U25 Literature Quiz by Pragya Pragya - UEM Kolkata Quiz Club
╠²
Battle of Bookworms is a literature quiz organized by Pragya, UEM Kolkata, as part of their cultural fest Ecstasia. Curated by quizmasters Drisana Bhattacharyya, Argha Saha, and Aniket Adhikari, the quiz was a dynamic mix of classical literature, modern writing, mythology, regional texts, and experimental literary forms. It began with a 20-question prelim round where ŌĆśstar questionsŌĆÖ played a key tie-breaking role. The top 8 teams moved into advanced rounds, where they faced audio-visual challenges, pounce/bounce formats, immunity tokens, and theme-based risk-reward questions. From Orwell and Hemingway to Tagore and Sarala Das, the quiz traversed a global and Indian literary landscape. Unique rounds explored slipstream fiction, constrained writing, adaptations, and true crime literature. It included signature IDs, character identifications, and open-pounce selections. Questions were crafted to test contextual understanding, narrative knowledge, and authorial intent, making the quiz both intellectually rewarding and culturally rich. Battle of Bookworms proved literature quizzes can be insightful, creative, and deeply enjoyable for all.Communicable Diseases and National Health Programs ŌĆō Unit 9 | B.Sc Nursing 5t...
Communicable Diseases and National Health Programs ŌĆō Unit 9 | B.Sc Nursing 5t...RAKESH SAJJAN
╠²
This PowerPoint presentation covers Unit 9 ŌĆō Communicable Diseases and National Health Programs, a core part of the 5th Semester B.Sc Nursing (Community Health Nursing ŌĆō I) syllabus, as outlined by the Indian Nursing Council (INC).
This unit enables nursing students to understand the epidemiology, prevention, control, and nursing management of common communicable diseases in India, while also offering a structured overview of the National Health Programs implemented to address them.
The content is critical for effective field practice, disease surveillance, early detection, referral, and health education, equipping students to participate in public health interventions and outbreak control at community and national levels.
¤ōś Key Topics Covered in the PPT:
Definition and classification of communicable diseases
Modes of transmission and chain of infection
Common communicable diseases in India:
Malaria
Tuberculosis
Leprosy
Dengue
HIV/AIDS
Hepatitis
COVID-19 (if included in the current curriculum)
Diarrheal diseases
Acute Respiratory Infections (ARIs)
Epidemiological factors, causative agents, symptoms, and incubation periods
Prevention and control strategies: primary, secondary, and tertiary levels
Nursing responsibilities in patient care, contact tracing, community surveillance, and outbreak control
Health education and behavior change communication for community awareness
Vaccination schedules and cold chain maintenance
National Health Programs related to communicable diseases:
National Vector Borne Disease Control Program (NVBDCP)
Revised National Tuberculosis Control Program (RNTCP)
National Leprosy Eradication Program (NLEP)
National AIDS Control Program (NACP)
Universal Immunization Program (UIP)
IDSP ŌĆō Integrated Disease Surveillance Program
Overview of standard treatment protocols, referral mechanisms, and community nurseŌĆÖs role in program implementation
This presentation is ideal for:
Nursing students preparing for university exams, class tests, and field projects
Tutors teaching infectious disease nursing and public health interventions
Nurses involved in immunization, outbreak investigation, and contact tracing
It provides a student-friendly breakdown of concepts, aligned with national priorities, including flowcharts, tables, case examples, and simplified text for field-level application.LDMMIA Practitioner Student Reiki Yoga S2 Video PDF Without Yogi Goddess
LDMMIA Practitioner Student Reiki Yoga S2 Video PDF Without Yogi GoddessLDM & Mia eStudios
╠²
A bonus dept update. Happy Summer 25 almost. Do Welcome or Welcome back. Our 10th Free workshop will be released the end of this week, June 20th Weekend. All Materials/updates/Workshops are timeless for future students.
ŌÖź Your Attendance is valued.
We hit over 5k views for Spring Workshops and Updates-TY.
ŌÖź Coming to our Shop This Weekend.
Timeless for Future Grad Level Students.
Practitioner Student. Level/Session 2 Packages.
* ŌÖźThe Review & Topics:
* All virtual, adult, education students must be over 18 years to attend LDMMIA eClasses and vStudio Thx.
* Please refer to our Free Workshops anytime for review/notes.
* Orientation Counts as S1 on introduction. Sold Separately as a PDF. Our S2 includes 2 Videos within 2 Mp4s. Sold Separately for Uploading.
* Reiki Is Japanese Energy Healing used Globally.
* Yoga is over 5k years old from India. It hosts many styles, teacher versions, and itŌĆÖs Mainstream now vs decades ago.
* Teaching Vod, 720 Res, Mp4: Yoga Therapy is Reviewed as a Hatha, Classical, Med Yoga (ND) Base. Take practice notes as needed or repeat videos.
* Fused Teaching Vod, 720 Res, Mp4: Yoga Therapy Meets Reiki Review. Take Practice notes as needed or repeat videos.
* Video, 720 Res, Mp4: Practitioner Congrats and Workshop Visual Review with Suggestions.
ŌÖź Bonus Studio Video, 720 Res, Mp4: Our 1st Reiki Video. Produced under Yogi Goddess, LDM Recording. As a Reiki, Kundalini, ASMR Spa, Music Visual. For Our Remastered, Beatz Single for Goddess Vevo Watchers. https://www.reverbnation.com/yogigoddess
* ŌÖź Our Videos are Vevo TV and promoted within the LDMMIA Profiles.
* Scheduled upload for or by Weekend Friday June 13th.
* LDMMIA Digital & Merch Shop: https://ldm-mia.creator-spring.com
* ŌÖź As a student, make sure you have high speed connections/wifi for attendance. This sounds basic, I know lol. But, for our video section. The High Speed and Tech is necessary. Otherwise, any device can be used. Our Zip drive files should serve MAC/PC as well.
* ŌÖź On TECH Emergency: I have had some rare, rough, horrid timed situations as a Remote Student. Pros and Cons to being on campus. So Any Starbucks (coffee shop) or library can be used for wifi hot spots. You can work at your own speed and pace.
* ŌÖź We will not be hosting deadlines, tests/exams.
* ŌÖźAny homework will be session practice and business planning. Nothing stressful or assignment submissions.
How to Manage Inventory Movement in Odoo 18 POS
How to Manage Inventory Movement in Odoo 18 POSCeline George
╠²
Inventory management in the Odoo 18 Point of Sale system is tightly integrated with the inventory module, offering a solution to businesses to manage sales and stock in one united system.Ad
Islamic banking
- 1. Islamic Banking ŌĆō Products & Operations A practical introduction
- 2. CONTENT OF PRESENTATION ŌĆó Understanding the context ŌĆó Looking at the products ŌĆó Concluding Remarks
- 3. ŌĆó What is Islamic Banking? ŌĆó What prompted Islamic Banking? ŌĆó Origins of Islamic Banking ŌĆó Islamic Finance Perspectives UNDERSTANDING THE CONTEXT
- 4. WHAT IS ISLAMIC BANKING? ŌĆó Interest free banking? ŌĆó Profit and loss sharing? ŌĆó Ethical banking? ’ā╝ ’ā╝ ’ā╝
- 5. WHAT PROMPTED ISLAMIC BANKING? ŌĆó Emergence of Arab nationalism and the search for identity ŌĆó Oil shocks and petrodollars ŌĆó Privatization and the individualŌĆÖs right to choose
- 6. Quran Hadith & Sunna Interpretation by Shariaa Scholars Sayings of the Prophet Teachings & Life style of the Prophet i) Sahih Al-Bokhari ii) Sahih Muslim 1) Hanbaly 2) Shafei 3) Hanafi 4) Maliki Two Sects of Islam Sunnah ShiaŌĆÖh 5) Ithna-Ashriah Qiyas - Ijtehad ŌĆō IjmaŌĆÖa Surah Verse(s) Al-BAQARRAH (#2) 275-279 AN-NESSA (#4) AL-EMRAN (#3) AR-RUM (#30) 130 161 39 ORIGINS OF ISLAMIC BANKING
- 7. ISLAMIC FINANCE PERSPECTIVES ŌĆó 1.5 billion Muslims (20% of population) ŌĆó Fastest growing and one of most active religions ŌĆó Modern Islamic Banking started in the mid-70s, although financing principles pre-date Islam ŌĆó Financial assets now around US$ 700 billion ŌĆó Liquid Funds in the Islamic Markets looking for quality assets are around US$ 100 ŌĆō 200 billion ŌĆó Market is growing at 15% pa
- 8. LOOKING AT THE PRODUCTS ŌĆó Islamic Finance Principles ŌĆó Short Term Working Capital ŌĆó Medium Term Sales Financing ŌĆó Syndication ŌĆó Islamic Securitization ŌĆó Islamic ABS ŌĆó Islamic Mortgages ŌĆó Islamic Funds
- 9. ISLAMIC FINANCE PRINCIPLES ŌĆó Financiers are linked to the underlying transaction ŌĆó Not permitted finance of activity related to: - alcohol, pork, drugs, gambling, etc - speculation or unjustified enrichment ŌĆó Money is not a ŌĆ£CommodityŌĆØ in itself, merely reflecting ŌĆ£Time ValueŌĆØ for a return ŌĆó Hence, no receipt or payment of Interest (Riba) ŌĆó Transactions must be transparent with all details agreed in advance and ownership undisputed
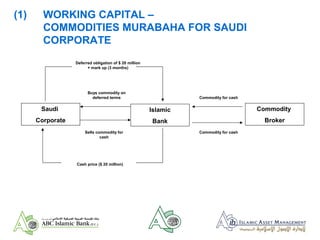
- 10. (1) WORKING CAPITAL ŌĆō COMMODITIES MURABAHA FOR SAUDI CORPORATE ŌĆó Saudi Corporate (SC) requires US$ 20 million from Islamic Bank (IB) for 3 months under Master Agreement which sets out procedures and means of fixing pricing ŌĆó SC contracts to buy via IB an amount of a commodity with a cash price of US$ 20 million on deferred term of 3 months ŌĆó IB contracts to sell the commodity on behalf of SC for US$ 20 million cash and passes cash to SC ŌĆó SC contracts to pay IB for the commodity after 3 months at the cash price plus an agreed mark up
- 11. Saudi Corporate Islamic Bank Commodity Broker Deferred obligation of $ 20 million + mark up (3 months) Buys commodity on deferred terms Sells commodity for cash Cash price ($ 20 million) Commodity for cash Commodity for cash (1) WORKING CAPITAL ŌĆō COMMODITIES MURABAHA FOR SAUDI CORPORATE
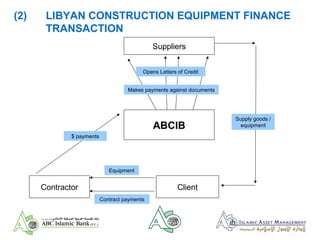
- 12. (2) LIBYAN CONSTRUCTION EQUIPMENT FINANCE TRANSACTION ŌĆó A $ 40 million facility to finance equipment for a project in Libya ŌĆó LCŌĆÖs issued initially to finance the purchase and import of construction equipment from Italy and elsewhere used on the project ŌĆó LCŌĆÖs converted into Murabaha leverage financing during 2007 ŌĆó Was initially to be an Islamic lease/Ijara contract but there were tax and legal uncertainties surrounding this ŌĆó Facility amortization over 5 years commenced July 2007
- 13. (2) LIBYAN CONSTRUCTION EQUIPMENT FINANCE TRANSACTION ABCIB Suppliers ClientContractor Equipment Contract payments Opens Letters of Credit $ payments Makes payments against documents Supply goods / equipment
- 14. (3) SYNDICATED FINANCING ŌĆō REVOLVING MURABAHA FOR KUWAITI CORPORATE ŌĆó 3 year revolving facility ŌĆó $ 100 million with ABC Islamic Bank as Investment Agent (underwriter and arranger) ŌĆó Series of individual murabaha transactions with payment of profit only on individual transactions; conventionally a ŌĆ£bulletŌĆØ payment of principal at maturity
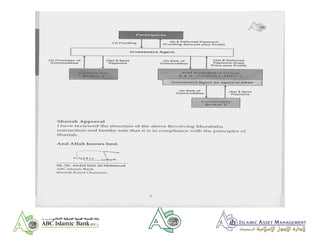
- 17. (4) SUKUK ISSUE ŌĆō ŌĆ£ISLAMIC ABSŌĆØ; SAUDI HOUSEBUILDER ŌĆó Dar Al-Arkan is a major Saudi builder ŌĆó Requirement for raising finance to develop houses to meet underserved Saudi market ŌĆó In 2007 raised $ 1.6 billion in two sukuk issue ŌĆó Complexity because of Saudi law on property ownership ŌĆó Total market of approx $ 100 billion of sukuk in issue end 2007
- 18. Issuer Dar Al-Arkan International Sukuk Company (a limited liability company incorporated in the Cayman Islands) Guarantor Dar Al-Arkan Real Estate Development Company (Dar Al-Arkan) Issue 5 Year US$[*] Trust Certificates due 2012 Maturity 5 years, bullet Floating Rate 3-month US$ LIBOR Coupon US$ LIBOR plus 225bps Public Listing Application made to Dubai International Financial Exchange (DIFX) and Labuan International Financial Exchange (LFX) Issue Type Sukuk Al-Ijara Governing Law Saudi law for property-related documents English law for Trust Deed and Certificates Joint Lead Managers and Joint Bookruners ABC Islamic Bank (E.C.); Arab National Bank; Deutsche Bank AG; Dubai Islamic Bank PJSC; Gulf International Bank B.S.C.; Kuwait Finance House (Malaysia) Berhad; Unicorn Investment Bank, B.S.C. (c) (4) SUKUK SUMMARY
- 19. Sale Proceeds (US$) Sale of Real Estate Assets (Transfer of Title Deeds) Issue Proceeds (US$) Guarantee 5 Year Lease (Use of Real Estate Assets) Lease Payments On-shoreOffshore Certificates Payment for Real Estate Rights (US$) Transfer of Real Estate Rights SAUDI SPV Dar Al-Arkan ISSUER (Dar Al-Arkan International Sukuk Co.) SUKUK HOLDERS (4) TRANSACTION STRUCTURE (SUKUK AL IJARA)
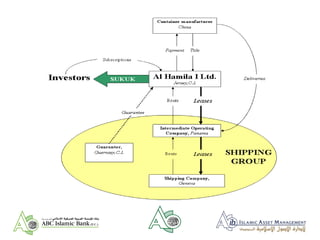
- 20. (5) CONTAINER SUKUK ISSUE ŌĆó Al Hamila is an ABC ŌĆō established SPV which owns shipping containers ŌĆó Al Hamila finances its purchases through the issue of floating rate and fixed rate sukuk. The sukuk ŌĆ£couponsŌĆØ match the profit of underlying leases ŌĆó Client (shipping company) gets lease finance with funds raised from Arab and International markets
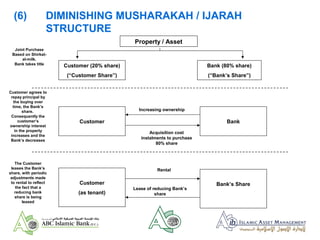
- 22. (6) ISLAMIC MORTGAGES ŌĆō DIMINISHING MUSHARAKA ŌĆó Requirement for British Muslims to buy their own houses without borrowing at interest ŌĆó Approximately 2 million Muslims in UK with potential ŌĆ£mortgageŌĆØ market size of ┬Ż 6 billion ŌĆó Marketed under the ŌĆ£alburaqŌĆØ brand ŌĆó Bank and customer buy the property jointly and over period Bank sells its share to customer; Bank charges rent on the share that it owns ŌĆó Rent re-fixed semi-annually vs. Libor benchmark
- 23. Property / Asset Customer (20% share) (ŌĆ£Customer ShareŌĆØ) Bank (80% share) (ŌĆ£BankŌĆÖs ShareŌĆØ) (6) DIMINISHING MUSHARAKAH / IJARAH STRUCTURE Customer Bank Customer (as tenant) BankŌĆÖs Share Increasing ownership Acquisition cost instalments to purchase 80% share Joint Purchase Based on Shirkat- al-milk. Bank takes title Customer agrees to repay principal by the buying over time, the BankŌĆÖs share. Consequently the customerŌĆÖs ownership interest in the property increases and the BankŌĆÖs decreases The Customer leases the BankŌĆÖs share, with periodic adjustments made to rental to reflect the fact that a reducing bank share is being leased Rental Lease of reducing BankŌĆÖs share
- 24. ISLAMIC INVESTMENT PRODUCTS ŌĆō 320 Worldwide; top 93 Islamic Equity Funds 31 Islamic Income Funds 18 Islamic Real Estate Funds 10 Islamic Balanced Funds 7 Islamic Leasing Funds 5 Islamic Commodity Funds 4 Islamic Funds of Funds 3 Islamic Index Funds 3 Islamic Murabaha Funds 3 Islamic Growth Funds 3 Islamic Hedge Funds 2 Islamic Hybrid Funds 1 Islamic Infrastructure Funds 1 Islamic Mutual Funds 1 Non Investment Islamic Fund 1
- 25. CONCLUDING REMARKS ŌĆó Matching needs of surplus with shortage ŌĆó Oil price, available Sharia technology, volatility in home markets create supply ŌĆó Credit crunch (possibly short tem), desire for diversification as a strategy, more familiarity with Sharia compliance create appetite ŌĆó Potentially more benign regulatory treatment ŌĆó Potential for investment products and serving local market needs (10 million-plus Muslims in Western Europe)
- 26. AIMAN MUJTABA
