Isomerism
- 2. What is ISOMERS???? ISOMERS ARE COMPOUND WITH SAME MOLECULAR FORMULA BUT DIFFERENT STRUCTURAL FORMULA THAT IS THEY CONTAIN ATOMS OF THE SAME ELEMENTS BUT THE ELEMENTS ARE ARRANGED IN DIFFERENT WAYS.
- 3. EXAMPLE : BUTANE AND METHYL PROPANE ARE ISOMERS. THEY HAVE THE FOLLOWING CHARACTERISTICS.
- 5. ïIN METHANE ,ETHANE AND PROPANE, THERE IS ONLY ONE POSSIBLE WAY OF JOINING THE CARBON ATOMS AND THE HYDROGEN ATOMS. ïEACH OF THEM WILL HAVE ONLY ONE STRUCTURE.ALL OF THEM DO NOT HAVE ANY OTHER STRUCTURE. ïTHEREFORE, METHANE,ETHANE AND PROPANE DO NOT HAVE ISOMERS. ïALL THE ALKANES ABOVE PROPANE HAVE ISOMERS. THERE ARE 2 DIFFERENT WAYS OF ARRANGING THE FOUR CARBON ATOMS AND TEN HYDROGEN ATOMS FOR BUTANE C4H10. THUS BUTANE HAS TWO ISOMERS AS FOLLOWS :
- 7. ïThere are three different ways of arranging the five carbon atoms and twelve hydrogen atoms for pentane C5H12 ïThus, C5H12 has three isomers. Examples : PENTANE
- 8. METHYLBUTANE
- 10. ïThe number of possible alkane isomers grows rapidly as the number of carbon atoms increases as shown below :
- 12. The IUPAC nomenclature is used to name alkanes of isomers. STEP 1 : Find the longest continuous carbon chain in the molecule. STEP 2 : Give the name for this longest chain.
- 13. STEP 3 : Number the carbon atoms in this longest chain beginning at the end nearer to the branches (alkyl groups).The table below shows the prefixes to name each branch chain
- 14. STEP 4 : Locate and name the attached alkyl groups.The position of each alkyl group is given the number of the carbon atoms to which it is attached on the chain. {Note : If two or more of the same kind of alkyl groups are attached to the same chain, the number of alkyl groups is indicated by the prefixes di-(2), tri-(3), tetra-(4) and so on.In addition, the location of every identical group must ne indicated by a number.}
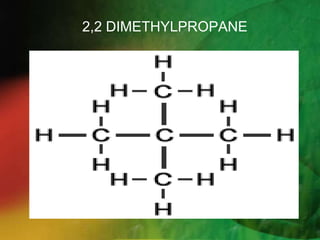
- 15. STEP 5 : Complete the name for the molecules by combining the three component part together.Write the name as a single word.Use hyphens to separate number and words, and commas to separate numbers 2,2-Dimethylbutane A single word . Do not leave any spaces..!
- 17. ïķThe first two members of the alkene series do not have any isomer.That is ethene and propene do not have isomers. ïķAll the other members of the alkenes have isomers. oButene has three isomers oPentene has five iomers. ïķ Isomerism in alkenes are due to: oThe changes in the position of the double bonds. oThe different arrangements of the carbon atoms and hydrogen atoms.
- 18. Example : BUTENE, C4H8 By changing the position of the double bond, we have two isomers. By rearranging the carbon atoms and the hydrogen atoms we have another isomer, 2-methylprop-1-ene. Thus the total number of isomers for C4H8 is three.
- 20. The drawing of alkene isomers is similar to the drawing of alkane isomers. The only diffrence is the positioning of the double bond. STEP 1 : Find the longest continuous carbon chain containing the double bond. STEP 2 : Give the name for this longest chain.
- 21. STEP 3 : Number the carbon atoms in this longest chain beginning at the end nearer the double bond and not nearer to the first alkyl group.This will ensure the carbon atoms joined by the double bond have numbers as low as possible. (numbering from left to right gives the double bond the lowest possible number.) STEP 4 : Locate the double bond by the number of the first carbon atom in the double bond.This number is placed infront of the family name.
- 22. {NOTE : The position of the double bond needs to be indicated only for chains of four or more carbon atoms.} CH3 | CH2=CH - CH - CH3 Double bond is between carbons 1 and 2.
- 23. STEP 5 : Locate and name the attached alkyl group. STEP 6 : Complete the name for the molecule by combining the three component parts together. Write the name as a single word. Name of the molecule: 3-methylbut-1-ene.