J2ee and web services
- 1. JAVA PLATFORMS âĒJ2SE â Java 2 Standard Edition ï Java for the desktop / workstation âĒ âĒJ2ME â Java 2 Micro Edition ï Java for the consumer device âĒJ2EE - Java 2 Enterprise Edition ï Java for the server
- 2. J2ee J2se J2me
- 3. J2EE Supports âĒ Extensible Markup Language âĒ Web Applications âĒ Web Services Support / WSDL Standard Format âĒ UDDI and ebXML Standard Formats âĒ HTTP-SOAP Transport Protocol
- 4. âĒJ2EE comes with a built in application server âĒJ2EE defines Java API for XML Processing (JAXP) API for processing XML âĒUses SAX and DOM standards
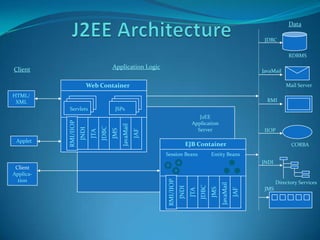
- 5. âĒJ2EE does not specify the nature and structure of the runtime. âĒJ2EE Container â capability of the runtime to manage application components. âĒJ2EE APIs specifies the contract between the applications and the container.
- 6. Data JDBC RDBMS Client Application Logic JavaMail Web Container Mail Server HTML/ XML RMI Servlets JSPs J2EE RMI/IIOP JavaMail Application JDBC JNDI Server JMS IIOP JTA JAF Applet EJB Container CORBA Session Beans Entity Beans JNDI Client Applica- tion RMI/IIOP Directory Services JavaMail JDBC JNDI JMS JMS JTA JAF
- 7. âĒThe Component technologies â to hold the business logic. (JSP, Servlets and EJB) âĒThe Service technologies â to provide supported services to application components (JDBC, JTA, JNDI) âĒThe Communication technologies â transparent to appln programmer, provide the mechanism for communication among different parts of the appln. (JMS, JavaMail, RMI-IIOP) âĒThey are re-usable software units containing business logic. âĒ An EJB is just a collection of Java classes and an XML file, bundled into a single unit.
- 8. âĒ They are re-usable software units containing business logic. âĒ An EJB is just a collection of Java classes and an XML file, bundled into a single unit. âĒ Java classes must follow certain rules and provide certain callback methods.
- 9. âĒ Session Beans âĒ Entity Beans âĒ Message-driven Beans
- 10. âĒ Intended for the use of a single client. âĒ Lifespan is limited to that of its client. âĒ When the client leaves the web site or the application is shut down, the session bean disappears.
- 11. Can keep information on behalf of its client across method calls. For example, Full information of the client is stored in every transactions example , credit card
- 12. âĒ This bean implements a particular business logic, though its created for a particular client, it doesnât have to remember anything about the client. âĒ Can be considered as a remote procedure that gets executed on behalf of the client, taking some parameters and returns the result (of calculation in a particular business rule context).
- 13. âĒPersistence is its basic property. âĒIt stays around even after the program is terminated until it is deleted. âĒWhen the program is restarted, it can gain access to this bean again. âĒIt can be used by any program on the network. âĒIt is executed remotely. âĒIt is identified by a primary key. âĒIts nothing but the object representation of records in RDBMS tables.
- 14. Advantages âĒ J2EE provides a complete architecture for developing - Distributed systems including object persistence, session tracking, transaction management, âĶ âĒSeparation of technical and application-specific code - Deployment descriptors - Container Managed Persistence
- 15. Disadvantages âĒ Very complex technology Even simple examples require many interfaces, bean classes, deployment descriptors. âĒ Many errors occur only at runtime (several steps required until the application is running) - Compilation - Packaging - Deployment - Running the application
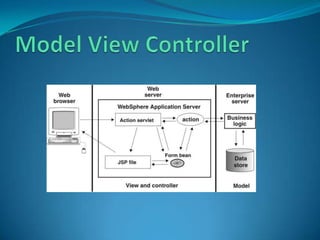
- 16. A Web Application Framework (WAF) is a reusable, skeletal, semi-complete modular platform that can be specialized to produce custom web applications , which commonly serve the web browsers via the Http's protocol. WAF usually implements the Model-View-Controller (MVC) design pattern, typically in the Model 2 architecture to develop request-response web-based applications on the Java EE and .NET models.
- 18. Request-based Framework : Struts WebWork Beehive , Stripes Component-based Framework Jave Server Faces (JSF) Tapestry Wicket Hybrid â Meta Framework RIFE Spring Framework RIA-based Framework DWR Echo2 JSON-RPC-Java