Jatin sharma (42162)
- 1. Jatin Sharma 42162 Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering
- 2. CONTENTS • Introduction • Definition • History • Technology Used • Working • Vehicular Communication • Google Driverless Car • Potential Advantages • Potential Obstacles • Conclusion
- 3. INTRODUCTION • Autonomous car is an automated or autonomous vehicle capable of fulfilling the main transportation capabilities of a traditional car without human input. • Suggested by Forbes magazine as one of the Five Most Disruptive Innovation of 2015. • Autonomous vehicles have enormous potential to allow for more productive use of time spent in a vehicle and to reduce crashes, costs of congestion, energy consumption, and pollution.
- 4. DEFINITION • Autonomous means having the power for self-government. • National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) has created a five-level hierarchy to help clarify the concept of autonomous vehicles.
- 5. HISTORY • Experimentation started in 1920s; • The first truly autonomous cars appeared in the 1980s, with Carnegie Mellon University’s Navlab and ALV projects in 1984. • DARPA (Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency) Grand Challenge 2005 fueled the development and research. • Google has done notable work in this field for past few years.
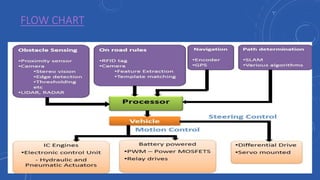
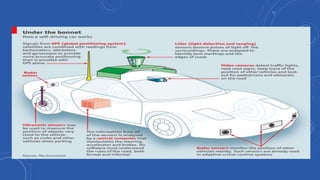
- 6. TECHNOLOGY USED • Various technologies work in conjunction with each other to make a car autonomous. • LIDAR Sensors • RADAR Detectors • GPS • INS • Electromechanical Systems • Software and Algorithm
- 7. LIDAR (LIGHT DETECTION AND RANGING) • LIDAR is a remote-sensing technology that measures distance by illuminating a target with a laser and analyzing the reflected light. • There are several major components to a Lidar system: 1. Laser (600nm-1000nm) 2. Scanner and Optics 3. Photodetector and receiver electronics. 4. Position and Navigation System.
- 8. RADAR (RADIO DETECTION AND RANGING) • Radar is the use of radio waves to detect and monitor various objects. • Automotive radar systems in the 77 GHz domain are used in car . • There are two primary methods : 1. The direct propagation method 2. The indirect propagation method or the Frequency Modulated Continuous Wave (FMCW) .
- 9. GPS (GLOBAL POSITIONING SYSTEM) • Global Positioning System is a space-based satellite navigation system that provides location and time information anywhere on earth where there is an unobstructed line of sight to four or more satellites. • The current GPS consists of three major segments. These are Space segment (SS), a control segment (CS), and a User segment (US). • All satellites broadcast at the same two frequencies, 1.57542 GHz and 1.2276 GHz.
- 10. INS (INERTIAL NAVIGATION SYSTEM) • Inertial navigation system (INS) is a navigation aid that uses a computer, motion sensors and rotation sensors to continuously calculate the position, orientation, and velocity of a moving object without the need for external references. • Includes computer, gyroscopes, and accelerometers • Initially used in spacecraft, ships and airplanes.
- 11. ELECTROMECHANICAL SYSTEMS • Electromechanical systems used to manipulate the steering, throttle and breaking systems of the car by receiving instruction from the computer. • These system employs the use of solid state relay for switching purposes, • servo motors for gearing purpose, • and pneumatic and hydraulic controls for breaking.
- 12. SOFTWARE AND ALGORITHMS • Various software and algorithms are used in autonomous car One such technique is SLAM which is abbreviation for Simultaneous Localization and Map Building. • Used for solving a problem as to if it is possible for an autonomous vehicle to start in an unknown location in an unknown environment and then to incrementally build a map of this environment while simultaneously using this map to compute absolute vehicle location.
- 13. WORKING • Autonomous car use many technologies and different type of sensors to sense the environment around it and make appropriate decision. • Many systems are already available that assist human driver like ABS (Automatic Breaking System) , ACC (Automatic Cruise Control) etc. • Various technologies discussed above are used in conjunction to control the car.
- 14. LIDAR SENSOR • An array of laser beams is emitted by the system in all directions and reflected scattered waves are sensed by on board sensor. • This data is fed in to the computer which generates high precision 3D map of the surrounding environment. • This accuracy of this map is in centimeters because the wavelength of light used is very small and is able to reflect of all types of surfaces and small objects. • Mounted on the top of the car on a cylindrical enclosure which rotates 360 degree .
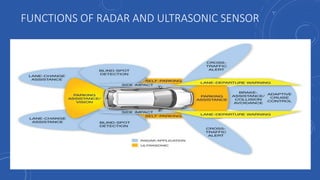
- 15. RADAR DETECTORS • There are usually RADAR detectors provides various functions like Lane- change assistance, blind spot detection, side impact warning, cross- traffic alert, and adaptive cruise control. • The radar detectors are usually mounted on both ends of the car. • 3 detectors in front of the car, 1 detector on rear end.
- 16. GPS • It is used in determining the position of the car and creating route to selected destination. It is the basis of all the maps that car uses while on the road. • GPS alone can’t be used to determine the location as it can be wrong by several meters; the bad weather conditions such as rain and fog also harm the precision. • So along with GPS other systems are used to determine the complete position.
- 17. INS • Inertial navigation system in fitted in to the car. • Uses accelerometers and gyroscopes to measure acceleration and angular movement of car. • Sometimes position estimator is also used with these two sensor for more precision.
- 18. DIGITAL CAMERAS • Cameras are used in the cars for motives other than finding the right path for the car. • The cameras help in identifying traffic signal, unexpected things like animals or pedestrians. Cameras also help in recognizing certain gestures which other sensors can’t comprehend like hand waving, stop sign, and traffic cones. • The camera is usually mounted on the rear view mirror.
- 19. ULTRASONIC SENSORS • Ultrasonic sensors are mounted on various sides of the car to detect objects very near the car. • These sensors provide parking assistance, collision warning, lane departure among other functions.
- 20. FUNCTIONS OF RADAR AND ULTRASONIC SENSOR
- 21. COMPUTER • The data from all the above mentioned system is fed in to an on-board Computer which process this data at high speed and with the help of highly sophisticated software makes the required decision and sends the output to electro-mechanical units like automatic steering, throttle and breaking systems. • This computer is also connected to the internet and GPS system to provide real time monitoring and updates.
- 22. FLOW CHART
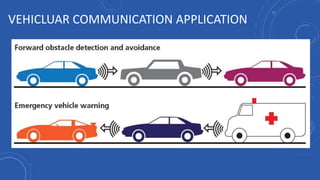
- 23. VEHICULAR COMMUNICATION • Vehicular communication systems are a type of network in which vehicles and roadside units are the communicating nodes, providing each other with information • Contain two types of nodes: vehicles and roadside stations. Both are dedicated short-range communications (DSRC) devices works in 5.9 GHz band with bandwidth of 75 MHz and approximate range of 1000 m. • The network support both private data and public communications but higher priority is given to public communications. • Wireless Access in Vehicular Environments (WAVE) 802.11p.
- 25. GOOGLE DRIVERLESS CAR • Google Self-Driving Car is the real name of the project that involves developing technology for autonomous cars, mainly electric cars. • The software powering Google’s cars is called Google Chauffeur. Lettering on each car identifies it as a “self-driving car”. • The project is led by Google Engineer Chris Urmson. • Google cars have about $150,000 in equipment including a $70,000 LIDAR system. The range finder is mounted on the top is a Velodyne 64-beam laser.
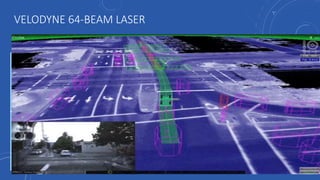
- 26. VELODYNE 64-BEAM LASER Sensor: ď‚· 64 lasers/detectors ď‚· 360 degree field of view ď‚· <2 cm distance accuracy ď‚· 5-15 Hz field of view update ď‚· 50 meter range for pavement ď‚· 120 meter range for other objects ď‚· >1.3 M points per second Laser: ď‚· Class 1- eye safe ď‚· 905 nm wavelength ď‚· ~ 10 ns pulse width ď‚· Dynamic laser power selection for larger dynamic range Mechanical: ď‚· 15V @ 4 amps ď‚· 300 RPM-900 RPM spin rate
- 28. RANGE OF SENSORS The stereo cameras have an overlapping region with a horizontal field of view of approximately 50 degrees, a vertical field of view of approximately 10 degrees, and a maximum distance of approximately 30 meters. The localization camera has a horizontal field of view of approximately 75 degrees, a vertical field of view of approximately 90 degrees and a maximum distance of approximately 10 meters. The laser has a horizontal field of view of approximately 360 degrees, a vertical field of view of approximately 30 degrees, and a maximum distance of 100 meters. The radar has a horizontal field of view of 60 degrees and a maximum distance of 200 meters.
- 29. POTENTIAL ADVANTAGES • Fewer traffic collisions • Roadway capacity will be increased • Higher speed limit can be sets for autonomous cars • Alleviation of parking scarcity • Removal of constraints on the user of cars • Vehicular Communication together with autonomous car system will eliminate the need of traffic signal and other traffic requirement. • Smoother ride • Increased human work efficiency
- 30. POTENTIAL OBSTACLES • First problem is reluctance by individuals to relinquish control of their cars • A car’s computer could potentially be compromised • implementation of legal framework and establishment of government regulations for self-driving cars. • Self-driving cars could potentially be loaded with explosives. • Susceptibility of car’s navigation system to different types of weather. • Current road infrastructure may need changes for autonomous cars. • diminish the use of public transport • High Cost
- 31. CONCLUSION • Future of transportation and mankind. • Competition like DARPA and companies like Google, Mercedes are fueling the development. • The autonomous car have numerous advantages, • Ever decreasing cost of technology, and involvement of big automotive giants. • 4 states in USA namely Nevada, Florida, California, and Michigan, along with District of Columbia who have successfully enacted laws addressing autonomous vehicles .
- 32. REFERENCES • http://spectrum.ieee.org/automaton/robotics/artificial-intelligence/how-google-self-driving-car-works • http://www.telegraph.co.uk/motoring/motoringvideo/11308777/How-do-driverless-cars-work.html • http://www.extremetech.com/extreme/189486-how-googles-self-driving-cars-detect-and-avoid-obstacles • http://www.forbes.com/sites/bigbangdisruption/2015/01/09/the-five-most-disruptive-innovations-at-ces-2015/ • http://www.techworld.com/news/personal-tech/volvo-reveals-how-its-driverless-cars-work-3599076/ • http://www.velodynelidar.com • C. Stiller, U. Ozguner, and K. Redmill, “Systems for Safety and Autonomous Behaviors in cars: The DARPA challenge experience”, February, 2007 • Anderson, James M., Nidhi Kalra, Karlyn D. Stanley, Paul Sorensen, Constantine Samaras and Oluwatobi A. Oluwatola. Autonomous Vehicle Technology: A Guide for Policymakers. Santa Monica, CA: RAND Corporation, 2014.
- 33. Thank You
- 34. Any questions?
- 35. IF CARS WILL DRIVE THEMSELVES WHAT WILL PEOPLE DO?