Java
- 1. 13-05-2013Rajavel DRajavel D Java Summer Internship – 2013 (Indian Institute of Technology Bombay)
- 2. Java ÔÇ® Object-Oriented ÔÇ® Platform independent ÔÇ® Simple ÔÇ® Secure ÔÇ® Multi-threaded ÔÇ® High Performance Rajavel D Java IITB-CSE-Internship 2013
- 4. Basic terms ÔÇ® Object - Objects have states and behaviors. ÔÇ® Class - A class can be defined as a blue print that describe the behaviors/states that object. ÔÇ® Methods - A method is basically a behavior. ÔÇ® Instance Variables - States of an objects, each object has its unique set of instance variables. Rajavel D Java IITB-CSE-Internship 2013
- 5. Keep in Mind ÔÇ® Case Sensitivity - Hello and hello would have different meaning in Java. ÔÇ® Class Names - For all class names the first letter should be in Upper Case. Example : class MyFirstJavaClass ÔÇ® Method Names - All method names should start with a Lower Case letter and each inner word's first letter should be in Upper Case. Example : public void myMethodName() ÔÇ® Program File Name - Name of the program file should exactly match the class name. Rajavel D Java IITB-CSE-Internship 2013
- 6. Simple Program class HelloWorldApp { public static void main(String[] args) { HelloWorldApp hello = new HelloWorldApp(); hello.sayHello(); } public void sayHello(){ System.out.println(“Hello”); } } O/P : Hello Rajavel D Java IITB-CSE-Internship 2013
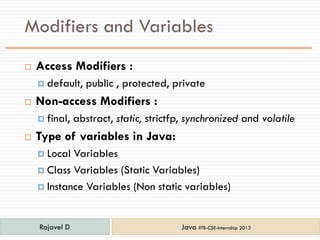
- 7. Modifiers and Variables  Access Modifiers :  default, public , protected, private  Non-access Modifiers :  final, abstract, static, strictfp, synchronized and volatile  Type of variables in Java:  Local Variables  Class Variables (Static Variables)  Instance Variables (Non static variables) Rajavel D Java IITB-CSE-Internship 2013
- 8. public static void main ? ÔÇ® java program processing starts from the main() method. ÔÇ® Public ? ÔÇ® Static? ÔÇ® Void? Rajavel D Java IITB-CSE-Internship 2013
- 9. Object Oriented Principles  Abstraction  Hiding the implementation (abstract class and interface)  Encapsulation  Wrapping up of data into single unit. (data hiding)  Inheritance  Reusable the properties of existing class  Polymorphism  Overloading and Overriding Rajavel D Java IITB-CSE-Internship 2013
- 10. Thread ÔÇ® Create Thread by implements Runnable interface or extends Thread class Rajavel D Java IITB-CSE-Internship 2013
- 11. Exception Handling ÔÇ® Problem that arises during the execution of a program. ÔÇ® try{} ÔÇ® catch{} ÔÇ® finally{} Rajavel D Java IITB-CSE-Internship 2013
- 12. Some important concepts ÔÇ® Constructor ÔÇ® Package ÔÇ® Multithreading ÔÇ® Synchronized ÔÇ® This keyword ÔÇ® finally Rajavel D Java IITB-CSE-Internship 2013
- 13. Any Doubts ??? Rajavel D Java IITB-CSE-Internship 2013
- 14. References ÔÇ® http://download.oracle.com/javase/tutorial/ ÔÇ® http://www.tutorialspoint.com/java ÔÇ® www.java2s.com/Tutorial/Java/CatalogJava.h tm Rajavel D Java IITB-CSE-Internship 2013





![Simple Program
class HelloWorldApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HelloWorldApp hello = new HelloWorldApp();
hello.sayHello();
}
public void sayHello(){
System.out.println(“Hello”);
}
}
O/P : Hello
Rajavel D Java IITB-CSE-Internship 2013](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-130514103014-phpapp02/85/Java-6-320.jpg)