Java findamentals2
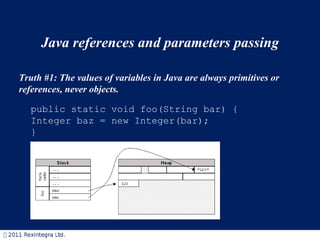
- 1. Java references and parameters passing Truth #1: The values of variables in Java are always primitives or references, never objects. public static void foo(String bar) { Integer baz = new Integer(bar); }
- 2. Java references and parameters passing Truth #2: Everything in Java is passed by value. Objects, however, are never passed at all. 1. public void foo(Dog d) { 2.  d.name == "Max"; // true 3.  d = new Dog("Fifi"); 4.  d.name == "Fifi"; // true 5. } 6. 7. public static void main(String [] args){ 9. Dog aDog = new Dog("Max"); 10. foo(aDog); 11. aDog.name == "Max"; // true 12. }
- 3. Java references and parameters passing Java references vs. C++ pointers Pointers in C++ must be referenced and dereferenced using the *, whereas the referencing and dereferencing of objects is handled for you automatically by Java. C++ int *num = new int(1); std::cout << num; //result 00345948 Java Integer num = new Integer(1); System. out .print(num); //result 1
- 4. Java references and parameters passing Java references vs. C++ pointers Java does not allow you to do pointer arithmetic . C++ class Number { public: int num; Number( int n um ) { this -> num = n um ; } }; void main (){ Number * ptr = new Number(1); // ptr==00345948 std::cout << (*(++ ptr )).num; // ptr==0034594C delete ptr ; //explicitly heap cleaning } //The value of â (*(++ ptr )).num â is address with //an uninitialized value(-33686019).We got a Bug. Java public class Number { public int num; public Number( int num) { this .num = num; } } public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Number ref = new Number(1); System. out .print(++(ref.num)); } } //Result is 2
- 5. Some Java Basics â finalâ keyword A final class  cannot be extended. This is done for reasons of security and efficiency and all methods in a final class are implicitly final. Many of the Java standard library classes are final , for example java.lang.System and java.lang.String . A final method  cannot be overridden by subclasses. This is used to prevent unexpected behavior from a subclass altering a method that may be crucial to the function or consistency of the class. A final variable  can only be initialized once, either via an initializer or an assignment statement. It need not be initialized at the point of definition: this is called a 'blank final' variable.
- 6. Some Java Basics The three forms of Polymorphism Instance methods and overriding An instance method in a subclass with the same signature (name, plus the number and the type of its parameters) and return type as an instance method in the superclass overrides  the superclass's method. Overloading Overloaded methods are methods with the same name signature but either a different number of parameters or different types in the parameter list. Dynamic (or late) method binding Dynamic (or late) method binding is the ability of a program to resolve references to subclass methods at runtime .Â
- 7. Some Java Basics The three forms of Polymorphism Dynamic (or late) method binding - Example public abstract class Employee { abstract void printPosition(); } public class Slave extends Employee { public void printPosition() { System. out .println("I am the Slave!"); } } public class Manager extends Employee { public void printPosition() { System. out .println("I am the Boss!"); } } public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Employee ref; Slave aSlave = new Slave(); ref = aSlave; ref.printPosition();//I am the Slave! Manager aManager = new Manager(); ref = aManager; ref.printPosition();//I am the Boss! } }
- 8. Some Java Basics Variables Instance Variables (Non-Static Fields) Non-static fields are also known as instance variables  because their values are unique to each instance  of a class (to each object, in other words). Class Variables (Static Fields)  A class variable  is any field declared with the static modifier; this tells the compiler that there is exactly one copy of this variable in existence, regardless of how many times the class has been instantiated. Local Variables  Similar to how an object stores its state in fields, a method will often store its temporary state in local variables . These are only visible to the methods in which they are declared. Parameters are variables that are passed to the methods.
- 9. Some Java Basics Constants The  static  modifier, in combination with the final  modifier, is also used to define constants. The final modifier indicates that the value of this field cannot change. String Class The String  class represents character strings. All string literals in Java programs, such as "abc", are implemented as instances of this class. Since strings are instances of the String class, max size of a String class object could be the available heap memory.
- 10. Some Java Basics â finalâ keyword A final class  cannot be extended. This is done for reasons of security and efficiency and all methods in a final class are implicitly final. Many of the Java standard library classes are final , for example java.lang.System and java.lang.String . A final method  cannot be overridden by subclasses. This is used to prevent unexpected behavior from a subclass altering a method that may be crucial to the function or consistency of the class. A final variable  can only be initialized once, either via an initializer or an assignment statement. It need not be initialized at the point of definition: this is called a 'blank final' variable.
![Java references and parameters passing Truth #2: Everything in Java is passed by value. Objects, however, are never passed at all. 1. public void foo(Dog d) { 2.  d.name == "Max"; // true 3.  d = new Dog("Fifi"); 4.  d.name == "Fifi"; // true 5. } 6. 7. public static void main(String [] args){ 9. Dog aDog = new Dog("Max"); 10. foo(aDog); 11. aDog.name == "Max"; // true 12. }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javafindamentals2-110517032733-phpapp01/85/Java-findamentals2-2-320.jpg)

![Java references and parameters passing Java references vs. C++ pointers Java does not allow you to do pointer arithmetic . C++ class Number { public: int num; Number( int n um ) { this -> num = n um ; } }; void main (){ Number * ptr = new Number(1); // ptr==00345948 std::cout << (*(++ ptr )).num; // ptr==0034594C delete ptr ; //explicitly heap cleaning } //The value of â (*(++ ptr )).num â is address with //an uninitialized value(-33686019).We got a Bug. Java public class Number { public int num; public Number( int num) { this .num = num; } } public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Number ref = new Number(1); System. out .print(++(ref.num)); } } //Result is 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javafindamentals2-110517032733-phpapp01/85/Java-findamentals2-4-320.jpg)


![Some Java Basics The three forms of Polymorphism Dynamic (or late) method binding - Example public abstract class Employee { abstract void printPosition(); } public class Slave extends Employee { public void printPosition() { System. out .println("I am the Slave!"); } } public class Manager extends Employee { public void printPosition() { System. out .println("I am the Boss!"); } } public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Employee ref; Slave aSlave = new Slave(); ref = aSlave; ref.printPosition();//I am the Slave! Manager aManager = new Manager(); ref = aManager; ref.printPosition();//I am the Boss! } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javafindamentals2-110517032733-phpapp01/85/Java-findamentals2-7-320.jpg)


