Java lecture
- 1. Java Swing - Lecture 1 An Introduction Milena Radenkovic (mvr@cs.nott.ac.uk) slides originally by Chris Coleman
- 2. 2 Timeline • 26th Oct (Now) - Java Necessaries, Swing Basics • 27th Oct - Components and Containers • 3rd Oct - Layout Management • 9th Nov - Event Handling and Listeners • 10th Nov - Graphics with Swing • Java Labs TBA
- 3. 3 Before we Start… (1) • Swing is all Java. • You must know about, and understand:  Classes / Objects  Method Overloading  Inheritance  Polymorphism  Interfaces  How to read the Java2 API Documents
- 4. 4 Before We Start… (2) • If Java is a problem – learn NOW, not later when the coursework is due!  Labs  Come to the labs and help is there for both Java and Swing.  Web  Use the Sun/Java tutorials  Plenty of web resources out there, even the PRG notes  Read a book?
- 5. 5 2D interface programming toolkits • Tcl/Tk • Motif/UIL • IDEs (e.g. VB, MSVC++/MFC) • Java AWT – the beginnings • Java JFC Swing (Java2 - JDK >= 1.2) • JBuilder and other Java IDEs • etc…
- 6. 6 What is Swing? • A part of The Java Foundation Classes  Swing  Look and feel  Accessibility  Java 2D (Java 2 onwards)  Drag and Drop  etc • Can be used to build Standalone Apps as well as Servlets and Applets
- 7. 7 On-line reading and reference • The Java Swing trail: http://java.sun.com/docs/books/tutorial/uiswing/ • Swing articles: http://java.sun.com/javase/technologies/desktop/articles.jsp • Developer Technical Articles & Tips: http://java.sun.com/developer/technicalArticles/GUI/
- 8. 8 Books • Java Swing (1998), Robert Eckstein, Mark Loy, Dave Wood, O'Reilly • JFC Swing Tutorial, The: A Guide to Constructing GUIs, 2nd Edition (2004); K. Walrath and M. Campione, Addison Wesley
- 9. 9 Getting started with Swing (1) • Compiling & running programs  Swing is standard in Java 2 (JDK >= 1.2)  Use:  ‘javac <program.java>’ && ‘java <program>’  Or JCreator / IDE
- 10. 10 Getting started with Swing (2) • Computer Science Department Stuff…  PCs  Java 2 (1.5.0) on hard disk at csjava  Unix (tuck and much):  Java 2 (1.5.0) in /usr/bin (or /usr/java)  Differences between previous versions  http://java.sun.com/j2se/1.4.2/docs/guide/swing/SwingChanges.html  http://java.sun.com/j2se/1.5.0/docs/guide/swing/SwingChanges.html  Coursework marked on Win XP & JDK 1.5.0
- 11. 11 Getting started with Swing (3) • Swing, like the rest of the Java API is subdivided into packages:  javax.swing, javax.accessibility, javax.swing.border … • At the start of your code - always  import javax.swing;  import javax.swing.event; • Most Swing programs also need  import java.awt.*;  import java.awt.event.*;
- 12. 12 Differences between Swing and AWT (1) • Never mix Swing and AWT components • If you know AWT, put ‘J’ in front of everything  AWT: Button  Swing: JButton • Swing does all that AWT does, but better and there’s much more of it.
- 13. 13 Differences between Swing and AWT (2) • Buttons and labels can display images • Behaviour and appearance of components • Component shape • Borders • Assistive technologies • Look and feel of the program’s GUI  Windows – (but only on Windows, M$ issues….)  UNIX  GTK  etc
- 14. 14 A typical Swing program • Consists of multiple parts  Containers  Components  Events  Graphics  (Threads) • Now look at each in turn
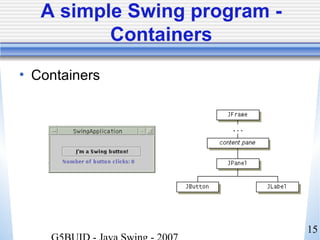
- 15. 15 A simple Swing program - Containers • Containers
- 16. 16 Remember this about Containers: • The structure of containers is your design decision and should always be thought through in advance  particularly for managing components  nesting containers • Failure to do so usually either results in a messy interface, messy code or both.
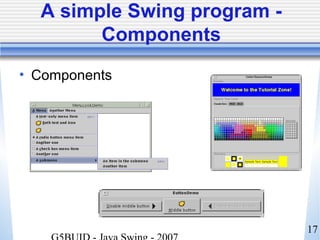
- 17. 17 A simple Swing program - Components • Components
- 18. 18 Remember this about Components: • There are many components that make your job much easier. • Often, you will be able to customise an existing Swing component to do a job for you, instead of having to start from scratch  Eg can extend (inherit from) the JButton class and ‘paint’ a new button over the top
- 19. 19 A simple Swing program - Events • Events
- 20. 20 Remember this about events: • ‘Events’ as seen by GUIs do not happen all that often in an application • Consider what is happening between events as well as during them
- 21. 21 A simple Swing program - Graphics • Graphics • Complex drawing and shading API. • Can do far more than display images.
- 22. 22 Remember this about Graphics: • There are many aspects of Swing that allow you to achieve graphics-like things without actually using ‘Graphics’. • Therefore, you don’t have to use them most of the time, and it is often easier not to.
- 23. 23 A simple Swing program - Threads • Most simple Swing GUI applications don’t require use of any (extra) threads • As Swing creates event-driven programs, all code is executed on the event- dispatching thread
- 24. 24 Remember this about Threads: The single-thread rule “Once a Swing component has been realized, all code that might affect or depend on the state of that component should be executed in the event-dispatching thread” (with some exceptions)
- 25. 25 How to Learn Swing • Don’t even try. • Learn general framework principles and design styles. • Then use the API reference, and Swing Tutorials to discover detailed usage of each component.
- 26. 26 How to read Java Docs (1) • Java 2 (J2SE 1.5.0) API Reference:  http://java.sun.com/j2se/1.5.0/docs/api/ • Split into 3 Sections (html frames):  Top Left: Packages  Bottom Left: Classes in Packages  Main Frame: Information about selected Class
- 27. 27 How to read Java Docs (2) • General idea is find class, and examine main frame for information. • Main frame pages split into sections:  Package hierarchy & implemented interfaces  Class Description, and links to more info  Nested Class Summary – Detail in separate page  Fields - 2 types Class (static) and instance, plus fields inherited from parent classes / interfaces  Constructor Summary  Method Summary & inherited methods from parents  Detailed info on all summary sections
- 28. 28 Summary • Do you know enough Java? • 2D interface programming toolkits • JFC/Swing • AWT and Swing • Getting started with Swing • Parts of a simple Swing program • Tomorrow: Components and Containers • Some source code, and design styles