java Method Overloading
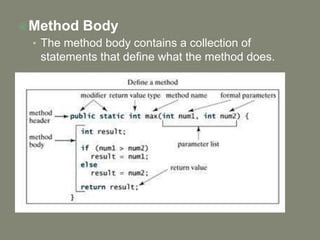
- 3. ïA collection of statements that are grouped together to perform an operation ïA method has the following syntax modifier return_Value_Type Method Name(list of parameters) { // Method body; } ïA method definition consists of a method header and a method body
- 4. 1. Modifiers: âĒ Optional âĒ Tells the compiler how to call the method. âĒ Defines the access type of the method. 2. Return Types âĒ The data type of the value the method returns. âĒ the return type is the keyword void when no value is returned
- 5. ïMethod Name âĒ The actual name of the method. âĒ Method name and the parameter list together constitute the method signature. ïParameters âĒ Act as a placeholder. âĒ When a method is invoked, a value is passed to parameter. âĒ This value is referred to as actual parameter or argument. âĒ The parameter list refers to the type, order, and number of the parameters of a method. âĒ Parameters are optional; that is,
- 6. ïMethod Body âĒ The method body contains a collection of statements that define what the method does.
- 7. ïA concept in Java which allows programmer to declare method with same name but different behavior. ïMethod with same name co-exists in same class but they must have different method signature ïWhen you overload a method in Java its method signature gets changed
- 8. ïIf you have two methods with same name in one Java class with different method signature than its called overloaded method in Java ïGenerally overloaded method in Java has different set of arguments to perform something based on different number of input ïTo overload a Java method just changes its signature.
- 9. ïTo change signature, either change number of argument, type of argument or order of argument ïSince return type is not part of method signature changing return type will result in duplicate method and you will get compile time error in Java
- 10. public class MethodOverLoading { // Method 1 public static int Addition(int a, int b) { System.out.println(âMethod 1 is calledâ); return a + b; } // Method 2 public static int Addition(int a, int b, int c) { System.out.println(âMethod 2 is calledâ); return a + b + c; } }
- 11. public static void main(String[] args) { int Answer1 = Addition(5, 6); // In this case Method 1 will be called System.out.println(âAnswer 1 = â + Answer1); System.out.println(â----------------------------â); int Answer2 = Addition(5, 6, 7); // In this case Method 2 will be called System.out.println(âAnswer 2 = â + Answer2); }
- 12. Output of the code Method 1 is called Answer 1 = 11 ---------------------------- Method 2 is called Answer 2 = 18










![public static void main(String[] args)
{
int Answer1 = Addition(5, 6);
// In this case Method 1 will be called
System.out.println(âAnswer 1 = â + Answer1);
System.out.println(â----------------------------â);
int Answer2 = Addition(5, 6, 7);
// In this case Method 2 will be called
System.out.println(âAnswer 2 = â + Answer2);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/omkarjava-170404053039/85/java-Method-Overloading-11-320.jpg)
