Java Object Orientend Programming 1.pptx
Download as pptx, pdf0 likes13 views
This document discusses programming language foundations and provides information about mathematical functions, characters, and strings in Java. It includes a case study on computing triangle angles from user-entered coordinate points. It also covers the character and string data types in Java, encoding schemes like Unicode and ASCII, character testing and comparison methods, and basic string methods.
1 of 19
Download to read offline










Ad
Recommended
LiangChapter4 Unicode , ASCII Code .ppt
LiangChapter4 Unicode , ASCII Code .pptzainiiqbal761
╠²
The document discusses Java character and string data types. It covers the char data type, Unicode encoding, ASCII character codes, escape sequences, methods in the Character class, the String type as a reference type, simple string methods like length(), concatenation, conversion methods, comparing strings, and substring methods.11-ch04-3-strings.pdf
11-ch04-3-strings.pdfAndreaBatholomeo
╠²
This document provides information about strings and characters in Java. It includes definitions of strings and characters, examples of using string methods like length(), substring(), indexOf(), and equals(). It also discusses formatting output with printf and comparing/modifying strings and characters. The document is from a textbook on building Java programs and is copyrighted material. It contains exercises for students to complete.Chapter 4 Mathematical Functions, Characters, and Strings.pptx
Chapter 4 Mathematical Functions, Characters, and Strings.pptxssusere3b1a2
╠²
This document provides an overview of mathematical functions, characters, and strings in Java. It describes the Math class and its common mathematical methods for trigonometric, exponent, rounding, and other functions. It also covers the char data type, escape sequences, Unicode encoding, and methods for comparing and testing characters. Finally, it discusses the String class and methods for string length, concatenation, comparison, substring extraction, and searching.Lecture 3.pptx
Lecture 3.pptxShehabEldinSaid
╠²
This document provides a detailed overview of Java programming concepts, covering primitive types, characters, strings, objects, methods, and input handling using the Scanner class. It explains the properties of various data types, how string manipulation works, and introduces basic arithmetic operations using the Math class. Example code snippets demonstrate these concepts, emphasizing the differences between primitive types and objects, and the interactivity of programs via user input.04slide Update.pptx
04slide Update.pptxAdenomar11
╠²
This document covers objectives and content about mathematical functions, characters, and strings in Java. It discusses topics like the Math class and its static methods for mathematical operations, the char type for representing single characters, the String class for representing text as objects, and methods for manipulating and comparing strings. Examples are provided throughout to demonstrate various string and character operations in Java like concatenation, extraction of characters and substrings, conversion between char and int types, and comparing strings.Java c─ān bß║Żn - Chapter9
Java c─ān bß║Żn - Chapter9Vince Vo
╠²
This document provides an overview of character and string processing in Java, including defining and manipulating character data, using the String, StringBuilder, and StringBuffer classes, regular expressions for pattern matching, and examples of counting vowels, finding words, and replacing characters in strings. It also describes writing an application to build a word concordance from a document by reading a file, creating a word list, and saving the output.Java string handling
Java string handlingGaneshKumarKanthiah
╠²
This document discusses string handling in Java. Some key points:
- Strings are immutable sequences of characters represented by the String class. StringBuffer allows mutable strings.
- Constructors can initialize strings from arrays of characters or other strings. Methods like length(), charAt(), and compareTo() operate on strings.
- Strings can be concatenated, searched, extracted, modified, and converted between cases. StringBuffer supports mutable operations like insertion and deletion.21CS642 Module 3 Strings PPT.pptx VI SEM CSE
21CS642 Module 3 Strings PPT.pptx VI SEM CSEVENKATESHBHAT25
╠²
21CS642 Module 2 Generics PPT.pptx VI SEM CSE 2021 Batch StudentsChapter 9 - Characters and Strings
Chapter 9 - Characters and StringsEduardo Bergavera
╠²
This document provides an overview of character and string processing in Java. It discusses character data types, string classes like String, StringBuilder and StringBuffer, regular expressions for pattern matching, and examples of string manipulation methods. The document then presents a problem statement and overall plan to build a word concordance program that counts word frequencies in a given text document. It outlines a 4-step process to develop the program, including defining class structures, opening/saving files, building the word list, and finalizing the code.Chapter 2 java
Chapter 2 javaahmed abugharsa
╠²
Chapter 2 covers fundamental programming concepts in Java, focusing on character strings, primitive data types, variable declaration, and expressions. It explains the use of various techniques like string concatenation, assignment statements, operator precedence, and data conversions. The chapter also introduces boolean values, escape sequences, and provides examples illustrating these concepts.String Method.pptx
String Method.pptxDreime Estandarte
╠²
The document discusses the String class in Java. It covers string literals, immutability of strings, common string methods like length(), charAt(), substring(), and concatenation. It also discusses converting between strings and numbers, formatting strings, and the StringBuffer mutable string class. The Character class is described as having useful methods for classifying characters.Charcater and Strings.ppt Charcater and Strings.ppt
Charcater and Strings.ppt Charcater and Strings.pptmulualem37
╠²
The document provides an in-depth overview of Java's character and string handling classes, focusing on Character, String, and StringBuffer. It explains the characteristics of each class, methods for creating and manipulating characters and strings, as well as important concepts such as immutability, string concatenation, and methods for searching and modifying strings. Additional examples illustrate the practical applications of these classes in Java programming.Week02
Week02hccit
╠²
This document discusses topics covered in Chapter 2 of a Java programming textbook, including character strings, primitive data types, variables, expressions, and operator precedence. The chapter focuses on strings, primitive data like integers and floating-point numbers, declaring and assigning variables, and arithmetic expressions. It also covers string concatenation, escape sequences, constants, numeric ranges of different data types, and the order that operators are evaluated according to precedence rules.String and string buffer
String and string bufferkamal kotecha
╠²
The document discusses String handling in Java. It describes how Strings are implemented as objects in Java rather than character arrays. It also summarizes various methods available in the String and StringBuffer classes for string concatenation, character extraction, comparison, modification, and value conversion. These methods allow extracting characters, comparing strings, modifying strings, and converting between string and other data types.Chapter i(introduction to java)
Chapter i(introduction to java)Chhom Karath
╠²
Java is a cross-platform language originally developed by James Gosling at Sun Microsystems. It enables writing programs for many operating systems using a C/C++-like syntax but with a simpler object model and fewer low-level facilities. Java programs are compiled to bytecode that can run on any Java Virtual Machine (JVM) regardless of computer architecture. Common Java development tools include Eclipse and NetBeans integrated development environments.Dr. Rajeshree Khande : Programming concept of basic java
Dr. Rajeshree Khande : Programming concept of basic javajalinder123
╠²
This document provides an overview of data types, variables, and expressions in Java. It discusses the different primitive data types in Java like int, float, boolean, and char. It explains how to declare variables of different types and assign values to them. The document also covers string concatenation, escape sequences, type conversion, and arithmetic expressions in Java. Key concepts covered include compatible data types for assignments, implicit type casting in expressions, and operator precedence rules.Dr. Rajeshree Khande : Java Basics
Dr. Rajeshree Khande : Java BasicsDrRajeshreeKhande
╠²
This document provides an overview of data types, variables, and constants in Java. It discusses the primitive data types like int, float, boolean and char. It describes how to declare variables, assign values, and the rules for compatible data types. The document also covers strings, literals, escape sequences and constants. It explains implicit and explicit type casting, operator precedence and mixed-type arithmetic expressions. Finally, it provides an introduction to arrays, including how to declare, assign values to, and access array elements.Java String class
Java String classDrRajeshreeKhande
╠²
The document discusses the String class in Java. It states that a String represents a sequence of characters and belongs to the java.lang package. Character sequences can be represented using character arrays, but character arrays do not support the full range of string operations. In Java, strings are class objects implemented using the String and StringBuffer classes. Strings are immutable while StringBuffers are mutable and support modifying string contents.String classes and its methods.20
String classes and its methods.20myrajendra
╠²
The document summarizes the String class and its methods in Java. It discusses that String is an immutable sequence of characters represented by the String class. It lists some key methods of the String class like length(), charAt(), equals() for comparing Strings. It also covers String constructors and how to initialize Strings.Cso gaddis java_chapter10
Cso gaddis java_chapter10mlrbrown
╠²
This document summarizes Chapter 10 of the textbook "Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Data Structures" which discusses text processing and wrapper classes in Java. The chapter covers introduction to wrapper classes, the Character class for character testing and conversion, additional String methods for searching and extracting substrings, the StringBuilder class, and wrapper classes for numeric primitive data types. Example code is provided to demonstrate various string and character methods.Programming fundamental
Programming fundamentalMukesh Thakur
╠²
The document discusses Java character sets, tokens, keywords, identifiers, literals, and data types. It provides details on:
1. Java uses the Unicode character set which supports characters from many languages.
2. The smallest individual units in a Java program are called tokens, which include keywords, identifiers, literals, punctuators, and operators.
3. Keywords are reserved words with special meanings, identifiers name variables and other items, and literals are fixed data values like integers and strings.JAVA PROGRAMMING : Data types
JAVA PROGRAMMING : Data typesKongu Engineering College, Perundurai, Erode
╠²
The document discusses Java data types including primitive and non-primitive types. It describes the eight primitive types - byte, short, int, long, float, double, boolean and char. It provides the size, range of values, and examples for each primitive type. The document also discusses ASCII, Unicode/UTF encodings and how characters are represented in Java using the char data type.Eo gaddis java_chapter_08_5e
Eo gaddis java_chapter_08_5eGina Bullock
╠²
This document discusses text processing and wrapper classes in Java. It covers wrapper classes for primitive data types like int and double. Character testing and conversion using the Character class is described. Methods of the String and StringBuilder classes for string manipulation are outlined, including searching, extracting substrings, and modifying strings. The StringTokenizer class is introduced for tokenizing strings into tokens based on delimiters.Eo gaddis java_chapter_08_5e
Eo gaddis java_chapter_08_5eGina Bullock
╠²
This document discusses text processing and wrapper classes in Java. It covers wrapper classes for primitive data types like int and char, and how they allow primitive values to be wrapped in objects. It also discusses the String, StringBuilder, and Character classes, describing their methods for string manipulation like searching, extracting substrings, modifying strings, and concatenation. The StringBuilder class is introduced as a mutable alternative to String for performing string operations.String in java, string constructors and operations
String in java, string constructors and operationsmanjeshbngowda
╠²
The document provides an overview of string handling in Java, detailing the definition of strings, their creation using constructors, and methods for measuring length and performing operations like concatenation and comparison. It discusses key string methods such as length(), equals(), compareTo(), and how to manipulate strings with methods like substring() and replace(). Additionally, it covers searching for substrings and modifying strings, showcasing various examples for practical understanding.ITFT-Constants, variables and data types in java
ITFT-Constants, variables and data types in javaAtul Sehdev
╠²
The document provides an introduction to constants, variables, and data types in programming, specifically within the Java language. It details different types of constants: integer (decimal, octal, hexadecimal), real (floating point), character, and string constants, along with their syntax. Additionally, it explains Java's data types, including integer types (byte, short, int, long), floating-point types (float, double), character type (char), and boolean type.BUSINESS QUIZ PRELIMS | QUIZ CLUB OF PSGCAS | 9 SEPTEMBER 2024
BUSINESS QUIZ PRELIMS | QUIZ CLUB OF PSGCAS | 9 SEPTEMBER 2024Quiz Club of PSG College of Arts & Science
╠²
THE QUIZ CLUB OF PSGCAS BRINGS T0 YOU A FUN-FILLED, SEAT EDGE BUSINESS QUIZ
DIVE INTO THE PRELIMS OF BIZCOM 2024
QM: GOWTHAM S
BCom (2022-25)
THE QUIZ CLUB OF PSGCAS
More Related Content
Similar to Java Object Orientend Programming 1.pptx (20)
21CS642 Module 3 Strings PPT.pptx VI SEM CSE
21CS642 Module 3 Strings PPT.pptx VI SEM CSEVENKATESHBHAT25
╠²
21CS642 Module 2 Generics PPT.pptx VI SEM CSE 2021 Batch StudentsChapter 9 - Characters and Strings
Chapter 9 - Characters and StringsEduardo Bergavera
╠²
This document provides an overview of character and string processing in Java. It discusses character data types, string classes like String, StringBuilder and StringBuffer, regular expressions for pattern matching, and examples of string manipulation methods. The document then presents a problem statement and overall plan to build a word concordance program that counts word frequencies in a given text document. It outlines a 4-step process to develop the program, including defining class structures, opening/saving files, building the word list, and finalizing the code.Chapter 2 java
Chapter 2 javaahmed abugharsa
╠²
Chapter 2 covers fundamental programming concepts in Java, focusing on character strings, primitive data types, variable declaration, and expressions. It explains the use of various techniques like string concatenation, assignment statements, operator precedence, and data conversions. The chapter also introduces boolean values, escape sequences, and provides examples illustrating these concepts.String Method.pptx
String Method.pptxDreime Estandarte
╠²
The document discusses the String class in Java. It covers string literals, immutability of strings, common string methods like length(), charAt(), substring(), and concatenation. It also discusses converting between strings and numbers, formatting strings, and the StringBuffer mutable string class. The Character class is described as having useful methods for classifying characters.Charcater and Strings.ppt Charcater and Strings.ppt
Charcater and Strings.ppt Charcater and Strings.pptmulualem37
╠²
The document provides an in-depth overview of Java's character and string handling classes, focusing on Character, String, and StringBuffer. It explains the characteristics of each class, methods for creating and manipulating characters and strings, as well as important concepts such as immutability, string concatenation, and methods for searching and modifying strings. Additional examples illustrate the practical applications of these classes in Java programming.Week02
Week02hccit
╠²
This document discusses topics covered in Chapter 2 of a Java programming textbook, including character strings, primitive data types, variables, expressions, and operator precedence. The chapter focuses on strings, primitive data like integers and floating-point numbers, declaring and assigning variables, and arithmetic expressions. It also covers string concatenation, escape sequences, constants, numeric ranges of different data types, and the order that operators are evaluated according to precedence rules.String and string buffer
String and string bufferkamal kotecha
╠²
The document discusses String handling in Java. It describes how Strings are implemented as objects in Java rather than character arrays. It also summarizes various methods available in the String and StringBuffer classes for string concatenation, character extraction, comparison, modification, and value conversion. These methods allow extracting characters, comparing strings, modifying strings, and converting between string and other data types.Chapter i(introduction to java)
Chapter i(introduction to java)Chhom Karath
╠²
Java is a cross-platform language originally developed by James Gosling at Sun Microsystems. It enables writing programs for many operating systems using a C/C++-like syntax but with a simpler object model and fewer low-level facilities. Java programs are compiled to bytecode that can run on any Java Virtual Machine (JVM) regardless of computer architecture. Common Java development tools include Eclipse and NetBeans integrated development environments.Dr. Rajeshree Khande : Programming concept of basic java
Dr. Rajeshree Khande : Programming concept of basic javajalinder123
╠²
This document provides an overview of data types, variables, and expressions in Java. It discusses the different primitive data types in Java like int, float, boolean, and char. It explains how to declare variables of different types and assign values to them. The document also covers string concatenation, escape sequences, type conversion, and arithmetic expressions in Java. Key concepts covered include compatible data types for assignments, implicit type casting in expressions, and operator precedence rules.Dr. Rajeshree Khande : Java Basics
Dr. Rajeshree Khande : Java BasicsDrRajeshreeKhande
╠²
This document provides an overview of data types, variables, and constants in Java. It discusses the primitive data types like int, float, boolean and char. It describes how to declare variables, assign values, and the rules for compatible data types. The document also covers strings, literals, escape sequences and constants. It explains implicit and explicit type casting, operator precedence and mixed-type arithmetic expressions. Finally, it provides an introduction to arrays, including how to declare, assign values to, and access array elements.Java String class
Java String classDrRajeshreeKhande
╠²
The document discusses the String class in Java. It states that a String represents a sequence of characters and belongs to the java.lang package. Character sequences can be represented using character arrays, but character arrays do not support the full range of string operations. In Java, strings are class objects implemented using the String and StringBuffer classes. Strings are immutable while StringBuffers are mutable and support modifying string contents.String classes and its methods.20
String classes and its methods.20myrajendra
╠²
The document summarizes the String class and its methods in Java. It discusses that String is an immutable sequence of characters represented by the String class. It lists some key methods of the String class like length(), charAt(), equals() for comparing Strings. It also covers String constructors and how to initialize Strings.Cso gaddis java_chapter10
Cso gaddis java_chapter10mlrbrown
╠²
This document summarizes Chapter 10 of the textbook "Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Data Structures" which discusses text processing and wrapper classes in Java. The chapter covers introduction to wrapper classes, the Character class for character testing and conversion, additional String methods for searching and extracting substrings, the StringBuilder class, and wrapper classes for numeric primitive data types. Example code is provided to demonstrate various string and character methods.Programming fundamental
Programming fundamentalMukesh Thakur
╠²
The document discusses Java character sets, tokens, keywords, identifiers, literals, and data types. It provides details on:
1. Java uses the Unicode character set which supports characters from many languages.
2. The smallest individual units in a Java program are called tokens, which include keywords, identifiers, literals, punctuators, and operators.
3. Keywords are reserved words with special meanings, identifiers name variables and other items, and literals are fixed data values like integers and strings.JAVA PROGRAMMING : Data types
JAVA PROGRAMMING : Data typesKongu Engineering College, Perundurai, Erode
╠²
The document discusses Java data types including primitive and non-primitive types. It describes the eight primitive types - byte, short, int, long, float, double, boolean and char. It provides the size, range of values, and examples for each primitive type. The document also discusses ASCII, Unicode/UTF encodings and how characters are represented in Java using the char data type.Eo gaddis java_chapter_08_5e
Eo gaddis java_chapter_08_5eGina Bullock
╠²
This document discusses text processing and wrapper classes in Java. It covers wrapper classes for primitive data types like int and double. Character testing and conversion using the Character class is described. Methods of the String and StringBuilder classes for string manipulation are outlined, including searching, extracting substrings, and modifying strings. The StringTokenizer class is introduced for tokenizing strings into tokens based on delimiters.Eo gaddis java_chapter_08_5e
Eo gaddis java_chapter_08_5eGina Bullock
╠²
This document discusses text processing and wrapper classes in Java. It covers wrapper classes for primitive data types like int and char, and how they allow primitive values to be wrapped in objects. It also discusses the String, StringBuilder, and Character classes, describing their methods for string manipulation like searching, extracting substrings, modifying strings, and concatenation. The StringBuilder class is introduced as a mutable alternative to String for performing string operations.String in java, string constructors and operations
String in java, string constructors and operationsmanjeshbngowda
╠²
The document provides an overview of string handling in Java, detailing the definition of strings, their creation using constructors, and methods for measuring length and performing operations like concatenation and comparison. It discusses key string methods such as length(), equals(), compareTo(), and how to manipulate strings with methods like substring() and replace(). Additionally, it covers searching for substrings and modifying strings, showcasing various examples for practical understanding.ITFT-Constants, variables and data types in java
ITFT-Constants, variables and data types in javaAtul Sehdev
╠²
The document provides an introduction to constants, variables, and data types in programming, specifically within the Java language. It details different types of constants: integer (decimal, octal, hexadecimal), real (floating point), character, and string constants, along with their syntax. Additionally, it explains Java's data types, including integer types (byte, short, int, long), floating-point types (float, double), character type (char), and boolean type.Recently uploaded (20)
BUSINESS QUIZ PRELIMS | QUIZ CLUB OF PSGCAS | 9 SEPTEMBER 2024
BUSINESS QUIZ PRELIMS | QUIZ CLUB OF PSGCAS | 9 SEPTEMBER 2024Quiz Club of PSG College of Arts & Science
╠²
THE QUIZ CLUB OF PSGCAS BRINGS T0 YOU A FUN-FILLED, SEAT EDGE BUSINESS QUIZ
DIVE INTO THE PRELIMS OF BIZCOM 2024
QM: GOWTHAM S
BCom (2022-25)
THE QUIZ CLUB OF PSGCAS
FIRST DAY HIGH orientation for mapeh subject in grade 10.pptx
FIRST DAY HIGH orientation for mapeh subject in grade 10.pptxGlysdiEelesor1
╠²
basic orientation of the first day highHow to Manage Multi Language for Invoice in Odoo 18
How to Manage Multi Language for Invoice in Odoo 18Celine George
╠²
Odoo supports multi-language functionality for invoices, allowing you to generate invoices in your customersŌĆÖ preferred languages. Multi-language support for invoices is crucial for businesses operating in global markets or dealing with customers from different linguistic backgrounds. Paper 109 | Archetypal Journeys in ŌĆśInterstellarŌĆÖ: Exploring Universal Themes...
Paper 109 | Archetypal Journeys in ŌĆśInterstellarŌĆÖ: Exploring Universal Themes...Rajdeep Bavaliya
╠²
Get ready to embark on a cosmic quest as we unpack the archetypal power behind Christopher NolanŌĆÖs ŌĆśInterstellar.ŌĆÖ Discover how heroŌĆÖs journey tropes, mythic symbols like wormholes and tesseracts, and themes of love, sacrifice, and environmental urgency shape this epic odyssey. Whether youŌĆÖre a film theory buff or a casual viewer, youŌĆÖll learn why CooperŌĆÖs journey resonates with timeless mythsŌĆöand what it means for our own future. Smash that like button, and follow for more deep dives into cinemaŌĆÖs greatest stories!
M.A. Sem - 2 | Presentation
Presentation Season - 2
Paper - 109: Literary Theory & Criticism and Indian Aesthetics
Submitted Date: April 5, 2025
Paper Name: Literary Theory & Criticism and Indian Aesthetics
Topic: Archetypal Journeys in ŌĆśInterstellarŌĆÖ: Exploring Universal Themes in NolanŌĆÖs Cosmic Odyssey
[Please copy the link and paste it into any web browser to access the content.]
Video Link: https://youtu.be/vHLaLZPHumk
For a more in-depth discussion of this presentation, please visit the full blog post at the following link: https://rajdeepbavaliya2.blogspot.com/2025/04/archetypal-journeys-in-interstellar-exploring-universal-themes-in-nolan-s-cosmic-odyssey.html
Please visit this blog to explore additional presentations from this season:
Hashtags:
#ChristopherNolan #Interstellar #NolanFilms #HeroJourney #CosmicOdyssey #FilmTheory #ArchetypalCriticism #SciFiCinema #TimeDilation #EnvironmentalCinema #MythicStorytelling
Keyword Tags:
Interstellar analysis, Christopher Nolan archetypes, heroŌĆÖs journey explained, wormhole symbolism, tesseract meaning, myth in sci-fi, cinematic archetypes, environmental themes film, love across time, Nolan film breakdownICT-8-Module-REVISED-K-10-CURRICULUM.pdf
ICT-8-Module-REVISED-K-10-CURRICULUM.pdfpenafloridaarlyn
╠²
In this module, you will discover how digital tools, systems, and platforms empower people, businesses, and communities in the modern world. As 21st-century learners, you are part of a generation that lives and learns in a digital environment. This module is designed to guide you in exploring how ICT serves as a powerful toolŌĆönot only for communication but also for innovation, entrepreneurship, and responsible citizenship. Throughout this learning material, you will examine how ICT is used in real-world scenarios such as online marketing, digital citizenship, and legal and ethical issues in technology use. YouŌĆÖll gain practical knowledge and skills, from creating websites and managing e-commerce platforms, to analyzing data and practicing safe and responsible behavior online.
By engaging with the lessons, activities, and performance tasks in this module, you will become more than just a technology userŌĆöyou will be a responsible, informed, and empowered digital citizen ready to thrive in todayŌĆÖs interconnected world.
LetŌĆÖs begin this journey and unlock the full potential of ICT in your everyday life!
Capitol Doctoral Presentation -June 2025.pptx
Capitol Doctoral Presentation -June 2025.pptxCapitolTechU
╠²
║▌║▌▀Żs from a Capitol Technology University presentation covering doctoral programs offered by the university. All programs are online, and regionally accredited. The presentation covers degree program details, tuition, financial aid and the application process.Revista digital preescolar en transformaci├│n
Revista digital preescolar en transformaci├│nguerragallardo26
╠²
EVOLUCI├ōN DEL CONTENIDO DE LA EVALUACI├ōN DE LOS RECURSOS Y DE LA FORMACI├ōN DE LOS DOCENTESROLE PLAY: FIRST AID -CPR & RECOVERY POSITION.pptx
ROLE PLAY: FIRST AID -CPR & RECOVERY POSITION.pptxBelicia R.S
╠²
Role play : First Aid- CPR, Recovery position and Hand hygiene.
Scene 1: Three friends are shopping in a mall
Scene 2: One of the friend becomes victim to electric shock.
Scene 3: Arrival of a first aider
Steps:
Safety First
Evaluate the victimŌĆśs condition
Call for help
Perform CPR- Secure an open airway, Chest compression, Recuse breaths.
Put the victim in Recovery position if unconscious and breathing normally.
Chalukyas of Gujrat, Solanki Dynasty NEP.pptx
Chalukyas of Gujrat, Solanki Dynasty NEP.pptxDr. Ravi Shankar Arya Mahila P. G. College, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi, India.
╠²
This presentation has been made keeping in mind the students of undergraduate and postgraduate level. In this slide try to present the brief history of Chaulukyas of Gujrat up to Kumarpala To keep the facts in a natural form and to display the material in more detail, the help of various books, websites and online medium has been taken. Whatever medium the material or facts have been taken from, an attempt has been made by the presenter to give their reference at the end.
Chaulukya or Solanki was one of the Rajputs born from Agnikul. In the Vadnagar inscription, the origin of this dynasty is told from Brahma's Chauluk or Kamandalu. They ruled in Gujarat from the latter half of the tenth century to the beginning of the thirteenth century. Their capital was in Anahilwad. It is not certain whether it had any relation with the Chalukya dynasty of the south or not. It is worth mentioning that the name of the dynasty of the south was 'Chaluky' while the dynasty of Gujarat has been called 'Chaulukya'. The rulers of this dynasty were the supporters and patrons of Jainism.How to Manage Upselling of Subscriptions in Odoo 18
How to Manage Upselling of Subscriptions in Odoo 18Celine George
╠²
Subscriptions in Odoo 18 are designed to auto-renew indefinitely, ensuring continuous service for customers. However, businesses often need flexibility to adjust pricing or quantities based on evolving customer needs.PEST OF WHEAT SORGHUM BAJRA and MINOR MILLETS.pptx
PEST OF WHEAT SORGHUM BAJRA and MINOR MILLETS.pptxArshad Shaikh
╠²
Wheat, sorghum, and bajra (pearl millet) are susceptible to various pests that can significantly impact crop yields. Common pests include aphids, stem borers, shoot flies, and armyworms. Aphids feed on plant sap, weakening the plants, while stem borers and shoot flies damage the stems and shoots, leading to dead hearts and reduced growth. Armyworms, on the other hand, are voracious feeders that can cause extensive defoliation and grain damage. Effective management strategies, including resistant varieties, cultural practices, and targeted pesticide applications, are essential to mitigate pest damage and ensure healthy crop production.Ray Dalio How Countries go Broke the Big Cycle
Ray Dalio How Countries go Broke the Big CycleDadang Solihin
╠²
A complete and practical understanding of the Big Debt Cycle. A much more practical understanding of how supply and demand really work compared to the conventional economic thinking. A complete and practical understanding of the Overall Big Cycle, which is driven by the Big Debt Cycle and the other major cycles, including the big political cycle within countries that changes political orders and the big geopolitical cycle that changes world orders.Non-Communicable Diseases and National Health Programs ŌĆō Unit 10 | B.Sc Nursi...
Non-Communicable Diseases and National Health Programs ŌĆō Unit 10 | B.Sc Nursi...RAKESH SAJJAN
╠²
This PowerPoint presentation is prepared for Unit 10 ŌĆō Non-Communicable Diseases and National Health Programs, as per the 5th Semester B.Sc Nursing syllabus outlined by the Indian Nursing Council (INC) under the subject Community Health Nursing ŌĆō I.
This unit focuses on equipping students with knowledge of the causes, prevention, and control of non-communicable diseases (NCDs), which are a major public health challenge in India. The presentation emphasizes the nurseŌĆÖs role in early detection, screening, management, and referral services under national-level programs.
¤ö╣ Key Topics Included:
Definition, burden, and impact of NCDs in India
Epidemiology, risk factors, signs/symptoms, prevention, and management of:
Diabetes Mellitus
Hypertension
Cardiovascular Diseases
Stroke & Obesity
Thyroid Disorders
Blindness
Deafness
Injuries and Accidents (incl. road traffic injuries and trauma guidelines)
NCD-2 Cancers:
Breast Cancer
Cervical Cancer
Oral Cancer
Risk factors, screening, diagnosis, early signs, referral & palliative care
Role of nurse in screening, referral, counseling, and continuum of care
National Programs:
National Program for Prevention and Control of Cancer, Diabetes, Cardiovascular Diseases and Stroke (NPCDCS)
National Program for Control of Blindness
National Program for Prevention and Control of Deafness
National Tobacco Control Program (NTCP)
Introduction to Universal Health Coverage and Ayushman Bharat
Use of standard treatment protocols and referral flowcharts
This presentation is ideal for:
Classroom lectures, field assignments, health education planning, and student projects
Preparing for university exams, class tests, and community field postingsABCs of Bookkeeping for Nonprofits TechSoup.pdf
ABCs of Bookkeeping for Nonprofits TechSoup.pdfTechSoup
╠²
Accounting can be hard enough if you havenŌĆÖt studied it in school. Nonprofit accounting is actually very different and more challenging still.
Need help? Join Nonprofit CPA and QuickBooks expert Gregg Bossen in this first-time webinar and learn the ABCs of keeping books for a nonprofit organization.
Key takeaways
* What accounting is and how it works
* How to read a financial statement
* What financial statements should be given to the board each month
* What three things nonprofits are required to track
What features to use in QuickBooks to track programs and grantsBUSINESS QUIZ PRELIMS | QUIZ CLUB OF PSGCAS | 9 SEPTEMBER 2024
BUSINESS QUIZ PRELIMS | QUIZ CLUB OF PSGCAS | 9 SEPTEMBER 2024Quiz Club of PSG College of Arts & Science
╠²
Paper 109 | Archetypal Journeys in ŌĆśInterstellarŌĆÖ: Exploring Universal Themes...
Paper 109 | Archetypal Journeys in ŌĆśInterstellarŌĆÖ: Exploring Universal Themes...Rajdeep Bavaliya
╠²
Chalukyas of Gujrat, Solanki Dynasty NEP.pptx
Chalukyas of Gujrat, Solanki Dynasty NEP.pptxDr. Ravi Shankar Arya Mahila P. G. College, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi, India.
╠²
Ad
Java Object Orientend Programming 1.pptx
- 1. Programming Language Foundation BY Dr. BABAOUSMAIL HASSEN LECTURER AT BINJIANG COLLEGE OF NUIST
- 2. Chapter 4 Mathematical Functions, Characters, and Strings ContinueŌĆ”
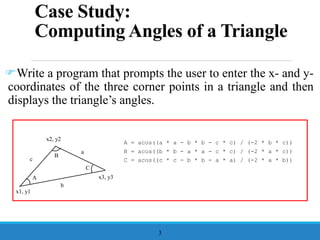
- 3. Case Study: Computing Angles of a Triangle ’üåWrite a program that prompts the user to enter the x- and y- coordinates of the three corner points in a triangle and then displays the triangleŌĆÖs angles. 3 A B C a b c A = acos((a * a - b * b - c * c) / (-2 * b * c)) B = acos((b * b - a * a - c * c) / (-2 * a * c)) C = acos((c * c - b * b - a * a) / (-2 * a * b)) x1, y1 x2, y2 x3, y3
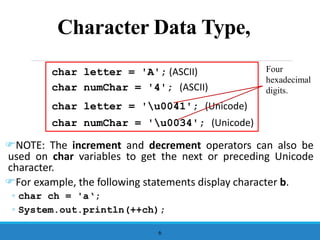
- 4. Character Data Type ’üåIn addition to processing numeric values, you can process characters in Java. ’üåThe character data type, char, is used to represent a single character. ’üåA character literal is enclosed in single quotation marks. Consider the following code: char letter = 'A'; char numChar = '4'; ŌŚ” The first statement assigns character A to the char variable letter. ŌŚ” The second assigns digit character 4 to the char variable numChar. 4
- 5. Character Data Type, ’üåComputers use binary numbers internally. A character is stored in a computer as a sequence of 0s and 1s. ’üåMapping a character to its binary representation is called encoding. There are different ways to encode a character. ŌŚ” Unicode ŌŚ” ASCII code ’üåJava supports Unicode, which was originally designed as a 16-bit character encoding. A 16-bit Unicode takes two bytes, preceded by u, expressed in four hexadecimal digits that run from u0000 to uFFFF. ’üåMost computers use ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange), an 8-bit encoding. ’üåUnicode includes ASCII code, with u0000 to u007F corresponding to the 128 ASCII characters. 5
- 6. Character Data Type, ’üåNOTE: The increment and decrement operators can also be used on char variables to get the next or preceding Unicode character. ’üåFor example, the following statements display character b. ŌŚ” char ch = 'aŌĆś; ŌŚ” System.out.println(++ch); 6 char letter = 'A'; (ASCII) char numChar = '4'; (ASCII) char letter = 'u0041'; (Unicode) char numChar = 'u0034'; (Unicode) Four hexadecimal digits.
- 7. Unicode Format ’üåUnicode takes two bytes, preceded by u, expressed in four hexadecimal numbers that run from 'u0000' to 'uFFFF'. ’üåUnicode can represent 65534 characters. 7 Unicode u03b1 u03b2 u03b3 for three Greek letters
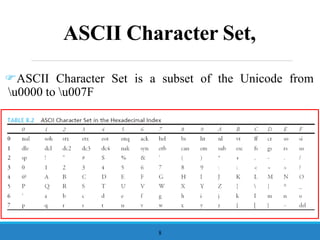
- 8. ASCII Character Set, ’üåASCII Character Set is a subset of the Unicode from u0000 to u007F 8
- 9. ASCII Code for Commonly Used Characters 9 Characters Code Value in Decimal Unicode Value '0' to '9' 48 to 57 u0030 to u0039 'A' to 'Z' 65 to 90 u0041 to u005A 'a' to 'z' 97 to 122 u0061 to u007A
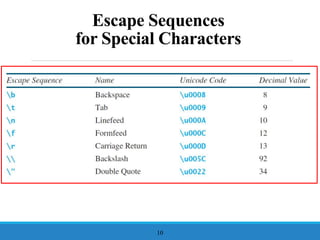
- 10. Escape Sequences for Special Characters 10
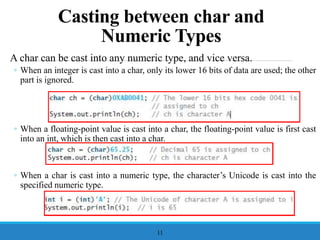
- 11. A char can be cast into any numeric type, and vice versa. ŌŚ” When an integer is cast into a char, only its lower 16 bits of data are used; the other part is ignored. ŌŚ” When a floating-point value is cast into a char, the floating-point value is first cast into an int, which is then cast into a char. ŌŚ” When a char is cast into a numeric type, the characterŌĆÖs Unicode is cast into the specified numeric type. 11 Casting between char and Numeric Types
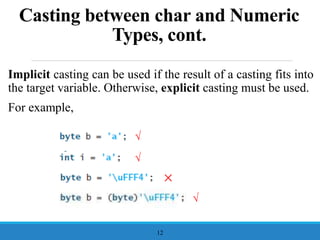
- 12. Casting between char and Numeric Types, cont. Implicit casting can be used if the result of a casting fits into the target variable. Otherwise, explicit casting must be used. For example, 12 ŌłÜ ŌłÜ ├Ś ŌłÜ
- 13. Comparing and Testing Characters ’üåTwo characters can be compared using the relational operators just like comparing two numbers. This is done by comparing the Unicodes of the two characters. ’üåFor example, if (ch >= 'A'&& ch <= 'Z') System.out.println(ch + " is an uppercase letter"); else if (ch >= 'a' && ch <= 'z') System.out.println(ch + " is a lowercase letter"); else if (ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') System.out.println(ch + " is a numeric character"); 13
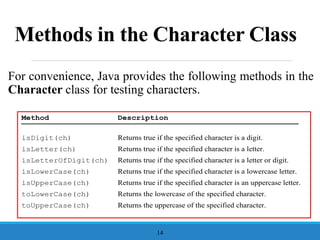
- 14. Methods in the Character Class For convenience, Java provides the following methods in the Character class for testing characters. 14 Method Description isDigit(ch) Returns true if the specified character is a digit. isLetter(ch) Returns true if the specified character is a letter. isLetterOfDigit(ch) Returns true if the specified character is a letter or digit. isLowerCase(ch) Returns true if the specified character is a lowercase letter. isUpperCase(ch) Returns true if the specified character is an uppercase letter. toLowerCase(ch) Returns the lowercase of the specified character. toUpperCase(ch) Returns the uppercase of the specified character.
- 15. The String Type ’üåThe char type only represents one character. To represent a string of characters, use the data type called String. ’üåFor example, String message = "Welcome to Java "; ’üåThe String type is not a primitive type. It is known as a reference type. Any Java class can be used as a reference type for a variable. Reference data types will be thoroughly discussed in Chapter 9. ’üåFor the time being, you just need to know ŌŚ” how to declare a String variable, ŌŚ” how to assign a string to the variable, ŌŚ” how to concatenate strings, ŌŚ” to perform simple operations for strings. 15
- 16. Simple Methods for String Objects 16 Method Description Returns the number of characters in this string. Returns the character at the specified index from this string. Returns a new string that concatenates this string with string s1. Returns a new string with all letters in uppercase. Returns a new string with all letters in lowercase. Returns a new string with whitespace characters trimmed on both sides. length() charAt(index) concat(s1) toUpperCase() toLowerCase() trim()
- 17. Simple Methods for String Objects ’üåStrings are objects in Java. The methods in the preceding table can only be invoked from a specific string instance. For this reason, these methods are called instance methods. ’üåThe syntax to invoke an instance method is referenceVariable.methodName(arguments) ’üå A non-instance method is called a static method. A static method can be invoked without using an object. ’üå The syntax to invoke a static method can be ClassName.methodName(arguments) ’üå All the methods defined in the Math class are static methods. They are not tied to a specific object instance. For example, the pow method in the Math class can be invoked using. Math.pow(2, 2.5) 17
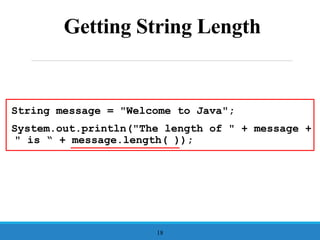
- 18. Getting String Length String message = "Welcome to Java"; System.out.println("The length of " + message + " is ŌĆ£ + message.length( )); 18
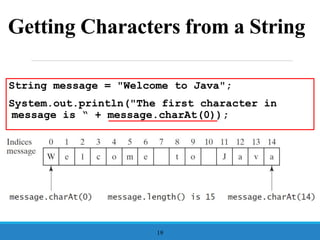
- 19. Getting Characters from a String String message = "Welcome to Java"; System.out.println("The first character in message is ŌĆ£ + message.charAt(0)); 19