Javascript under the hood 1
- 1. >< nextprevious Javascript Under The Hood The Mysterious Parts Tran Duc Thang Framgia Vietnam - Business Strategy Office - Human Development Section Demystifying Javascript’s “First-class functions”, “Scope”, “Closure”, and “this” keyword binding 1
- 2. >< nextprevious “Javascript is the World's Most Misunderstood Programming Language!” ~ Douglas Crockford ~ 2
- 3. >< nextprevious 3 Too much to remember, too weird to understand? first-class functions lexical scope function scope closure IIFE prototype function statement function expression hoisting this function constructor new block scope
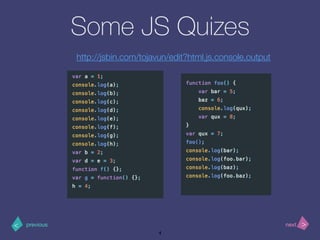
- 4. >< nextprevious Some JS Quizes 4 http://jsbin.com/tojavun/edit?html,js,console,output
- 5. >< nextprevious Some JS Quizes 5 http://jsbin.com/wabedaf/3/edit?html,js,output
- 6. Table of Contents 01 Basic Introductions ‚Ä£ First-class functions ‚Ä£ IIFE ‚Ä£ Hoisting 02 03 04 >< nextprevious Scope ‚Ä£ Lexical Scope ‚Ä£ Function Scope vs Block Scope Closure ‚Ä£ Understanding Closure ‚Ä£ Fixing the problems with Closure this keyword binding ‚Ä£ Understanding this keyword ‚Ä£ Binding this 6
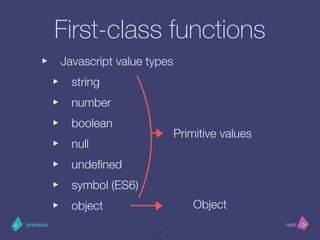
- 7. >< nextprevious First-class functions ‣ Javascript value types ‣ string ‣ number ‣ boolean ‣ null ‣ undefined ‣ symbol (ES6) ‣ object 7 Primitive values Object
- 8. >< nextprevious First-class functions ‚Ä£ Everything which is not primitive is object. ‚Ä£ Function (and even Class in ES6) in Javascript is actually object. 8
- 10. >< nextprevious First-class functions ‚Ä£ First-class citizen (also type, object, entity, or value) is an entity which supports all the operations generally available to other entities. ‚Ä£ These operations typically include being passed as an argument, returned from a function, and assigned to a variable 10
- 11. >< nextprevious First-class functions ‣ A programming language is said to have first- class functions if it treats functions as first- class citizens. ‣ Javascript has first-class functions! 11
- 13. >< nextprevious First-class functions ‚Ä£ Function Statement ‚Ä£ Function Expression 13
- 14. >< nextprevious First-class functions 14 Function Statement Function Expression Defines function. Also known as function declaration. Defines a function as a part of a larger expression syntax Must begins with “function” keyword Must not begin with “function” keyword Must have a name Can have a name or not (can be anonymous)
- 16. >< nextprevious First-class functions ‣ IIFE: Immediately Invoked Function Expression is a Javascript function that runs as soon as it is defined. 16
- 18. >< nextprevious Hoisting ‚Ä£ Hoisting: The ability to use variable, function before they are declared. ‚Ä£ Javascript only hoists declarations, not initializations 18
- 20. >< nextprevious Scope ‚Ä£ Scope is the set of variables, objects, and functions you have access to ‚Ä£ 2 ways to create a Scope: Function and Block* 20
- 21. >< nextprevious Scope ‣ Lexical Scope vs Dynamic Scope ‣ Lexical Scope, or Static Scope: The scope of a variable is defined by its location within the source code and nested functions have access to variables declared in their outer scope. ‣ Dynamic Scope: The scope of a variable depends on where the functions and scopes are called from ‣ Lexical Scope is write-time, whereas Dynamic Scope is runtime ‣ Javascript has Lexical Scope! 21
- 22. >< nextprevious Scope 22 ‚Ä£ Global Scope ‚Ä£ Local Scope ‚Ä£ Nested Scope ‚Ä£ Outer Scope ‚Ä£ Inner Scope ‚Ä£ Function Scope ‚Ä£ Block Scope
- 23. >< nextprevious Scope 23 IIFE can be used to create a new scope!
- 24. >< nextprevious Closure ‚Ä£ Closure is a function that can remember and access its lexical scope even when it's invoked outside its lexical scope 24
- 25. >< nextprevious Closure 25 Unravel the problems http://jsbin.com/wabedaf/3/edit?html,js,output
- 26. >< nextprevious “this” keyword ‣ “this” does not refer to the function itself. ‣ “this” does not refer to the function’s lexical scope. ‣ In most cases, the value of “this” is determined by how a function is called. ‣ “this” may be different each time the function is called. 26
- 27. >< nextprevious “this” keyword ‣ “this” does not refer to the function itself. 27
- 28. >< nextprevious “this” keyword ‣ Default binding: Standalone function invocation. “this” is bind to global object (in non-strict mode) 28
- 29. >< nextprevious “this” keyword ‣ Implicit binding: Function is invoked from a containing object. “this” is bind to the containing object. 29
- 30. >< nextprevious “this” keyword ‣ Explicit binding: Function is called with call, apply or bind method. “this” is bind to the object passed to the binding method. 30
- 31. >< nextprevious “this” keyword ‣ new keyword binding: “this” is bind to the new object that is created 31
- 32. >< nextprevious “this” keyword ‣ Arrow function: “this” is lexically adopted from the enclosing scope 32
- 33. >< nextprevious “this” keyword ‣ Binding priority ‣ Arrow function ‣ new keyword ‣ Explicit binding, by using call, apply and bind ‣ Implicit binding ‣ Default binding 33
- 34. >< nextprevious Some best practices ‚Ä£ Try to avoid Global variables ‚Ä£ Always declare variables ‚Ä£ Put variables declaration on top 34 Use Strict Mode
- 35. >< nextprevious References ‣ You don’t know JS (https://github.com/getify/You- Dont-Know-JS) ‣ Speaking JS (http://speakingjs.com/) ‣ Exploring ES6 (http://exploringjs.com/es6/) ‣ http://www.2ality.com/ JavaScript and more ‣ Mozilla Developer Network (https:// developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/ JavaScript) ‣ Tìm hiểu về Strict Mode trong Javascript (https:// viblo.asia/thangtd90/posts/jaqG0QQevEKw) 35
- 36. >< nextprevious Thank you for listening! Q&A For any discussion, you can refer this post on Viblo https://viblo.asia/thangtd90/posts/WApGx3P3M06y 36