Journal Publication.pptx
- 1. Outline of the Presentation • Concept of Citations • Citation Indexing • Webof Sciencedatabases • Limitations of WoSDatabases • Indian Citation Index (ICI) • WhyWeNeed ICI? • Benefits of ICI • The Impact Factor • Tools for measuring Impact Analysis • JCR (Journal Citation Report) • Other tools for Measuring the Impact analysis • Example of Google Scholar andScholarometer
- 3. • Research Methodology Rig Veda • Literature Review Shyam Veda • Conclusion Yajur Veda Atharva Veda • Reference
- 5. How To Select A Journal Search Journal Of your Discipline Check Impact Factor Check the journal’s credentials Select Database to submit Find the Key word Check h-index
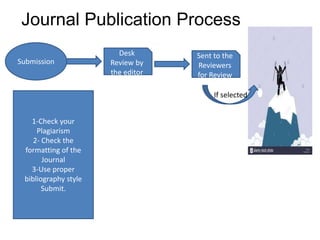
- 6. Journal Publication Process Submission Desk Review by the editor Sent to the Reviewers for Review If selected 1-Check your Plagiarism 2- Check the formatting of the Journal 3-Use proper bibliography style Submit.
- 7. What is Indexing Q4 Q3 Q2 Q1 Scopus
- 8. Concept of Citations citations symbolize the conceptual association of scientific ideas as recognized by publishing research authors . Bythe references they cite in their papers, authors make explicit linkages between their current research and prior work in the archive of scientificliterature.
- 9. distinction between "citation" and "reference" • If Paper R contains a bibliographic footnote using and describing Paper C, then – R contains a referenceto C, – C has a citationfrom R. • The number of references a paper has is measured by the number of items in its bibliography as endnotes, footnotes, etc., • The number of citations a paper has is found by looking it up [in a]citation index and seeing how many others papers mention it." Source:PriceD.J.D.Little science,bigscience.andbeyond.NewYork:ColumbiaUniversityPress,1986.
- 10. …..Tostart, it isimportant toclarify the terminological distinction between "citation“[6] and "reference".In hisclassic book Little Science, Big Science, Derek Price gave a clear definition of both terms. He said: "It seems to me a great pity to waste a good technical term by using the words citation and reference interchangeably. I therefore propose and adopt the convention that if Paper R contains a bibliographic footnote using and describing PaperC,then R contains… R contains a reference to C, [6] The concept of citation indexing: A unique and innovative tool for navigating the research literature. Current Contents, January 3, 1994. Paper C Paper R Little science, big science...and beyond. This is my first Current Contents® (CC®) essay under the rubric of Citation Comments. As discussed in last week's CC, this new monthly feature will focus on the applications of the Institute for Scientific Information's (ISI's) databases. 1 An appropriate topic to launch this new series is perhaps the most rudimentary -- the basic concept of citation indexing. To start, it is important to clarify the terminological distinction between "citation" and "reference". In his classic book Little Science, Big Science, Derek Price gave a clear definition of both terms. He said: "It seems to me a great pity to waste a good technical term by using the words citation and reference interchangeably. I therefore propose and adopt the convention that if Paper R contains a bibliographic footnote using and describing Paper C, then R contains a. C has a citation from R. adopted from : Mathew, N. (n.d.). Citation indexing. Retrieved from http://ist.psu.edu/faculty_pages/giles/IST497/presentations/Mathew.ppt
- 11. Citation Indexing • Introduced by Dr. Eugene Garfield of Institute of Scientific Information (Webof Science) in 1950s. • Citation indexing makes links between books and articles that were written in the past and articles that make reference to ("cite") these older publications. In other words, it is a technique that allows us to trace the use of an idea (an earlier document) forward to others who have used ("cited") it. • The citation indexes were originally designed primarily for information retrieval. Helps for identifying the relevant research papers independent of language, title words, or author keywords
- 14. The Impact Factor • The impact factor is a measure of the frequency with which the average article in a journal has been cited in a particular year or period. • JCR (Journal Citation Report) of WoShas been major tool for measuring the Impact factor of journals.
- 15. Jjournal Citation Report Impact Factor • The JCRprovides quantitative tools for ranking, evaluating, categorizing, and comparing journals (Thomson Reuters, 2011). • JCR impact factor is a ratio between citations and recent citable items published. • Thus, the impact factor of a journal is calculated by dividing the number of current year citations to the source items published in that journal during the previous two years
- 16. Calculation for journal impact factor A= 2020 cites to articles published in 2018 and 2019 B= Number of articles published in 2018 and 2019 C= A/B= 2020 Impact factor A Cites in 2020 to 2008-2009 articles B Number of articles Published in 2018 and 2019 C Impact Factor (A/B) Journal of Library and Information Science 150 80 1.875
- 17. Reproductive Systems category of the 1992 SCI® Journal Citation Reports®(JCR®) Reprodu ct ive Systems Journals (A/D) JCR Impact Factor A Cites in 1992 to 1990-91 Articles B Self- cites in 1992 to 1990-91 Articles C (A- B) Minu s Self- Cites D Articles Publishe d 1990- 91 E (C/D ) Revise d Impac t Factor AM J REPROD IMMUNO L 1.931 224 54 170 116 1.466 ANIM REPR OD SCI 0.701 110 23 87 157 0.554 BIOL REPR 3.257 726 265 461 530 2.757 Table : Calculation of impact factors without self-citations
- 18. h-Index 1- Institute 2-Journal 3-Author 4-country H-Hirsch(2005) f(A)=10, f(B)=8, f(C)=5, f(D)=4, f(E)=3 ‚Üí h-index=4 f(A)=25, f(B)=8, f(C)=5, f(D)=3, f(E)=3 ‚Üí h-index=3 h-index (f) = max min(f(i),i)}
- 20. i10 index refers to the number of paper with 10 or more citations. It is used by google scholar The g-index is an index for quantifying productivity in science, based on publication record (an author-level metric). It was suggested in 2006 by Leo Egghe.
- 23. TYPES OF PUBLICATIONS YOU CAN USE IN YOUR RESEARCH: PROFESSIONAL OR TRADE PUBLICATIONS
- 24. TYPES OF PUBLICATIONS YOU CAN USE IN YOUR RESEARCH: SCHOLARLY OR ACADEMIC JOURNALS
- 25. ISI Web of Science Databases • Science Citation Index Expanded(SCI) • Social Science Citation Index (SSCI) • Arts and Humanities Citation Index (A&HCI)
- 27. Advantages ofCitation Indexing • SCI, SSCI and A&HCI are multidisciplinary in nature.. • The citation-based associations and connections within the literature are made by authors themselves. • Helps for identifying the core periodicals in a subject. • Helps for quantifying or measuring the research productivity of an institution or individual or country or region.
- 28. Limitations of WoS Databases • Majority of the journals are from US. • Less presence of journals published from third world countries. • Only index journals not monographs • Non-English language journals are not as comprehensively indexed (Mathew, n.d.)
- 30. Why WeNeed Indian Citation Index? Coverage of Web of Science Citation Index No of Journals Science Citation Index 3772 Social Science Citation Index 2995 Arts & Humanities Citation Index 1656 Total =8423 Journal 30.30 of the World Publications 24000 Peer Reviewed Journals (Sale,2007) Only 268 Indian Journals are indexed in WoS
- 31. Indian Citation Index Web Interface http://www.indiancitationindex.com
- 32. Benefits of ICI • Acomprehensive research &evaluation tool for Indian literature • Facilitates comprehensive scientometric and bibliometric studies on Indian literature • Helps to measure & analyze individual, institutional, regional, and national R&D output for strategic planning • An authentic tool to generate complete and comprehensive analytic reports on the health of IndianR&D • ICI can generate national R&D indicators like, Indian Journals Citation Reports, etc. • Catalyze the image & visibility of Indian knowledge contents and publications • Helps decision makers to arrive at some conclusive point to decide the superiority of competitor (s), for some awards, fellowships, recruitments etc. • Provides a boost to Indian publishing industry at global level
- 33. Products of ICI • Indian Science Citation Index (ISCI) • Indian Health Science Citation Index (IHSCI) • Indian Agriculture Citation Index (IACI) India • Social Science & Humanities Citation Index (ISSHCI) • Indian Journals Citation Report (IJCR) • Indian Science &TechnologyAbstracts (ISTA) • Directory of Indian R&D Journals (DoIJ)
- 36. • What are the criteria for adding new journals to ICI? ICI works with its basic intent to cover all scholarly journals from India irrespective of their discipline (s) subject to content selection criteria
- 37. Indexing Research Materials • Research articles • Review articles • Short or brief communications • Editorial and letter to editor • Research notes • Case studies • Case reports • Opinion papers • Observations
- 39. Free Citation Indexing Tool Cited documents 7082 For the Article “TheLarge Scale.. By Hawking S.
- 40. How do we measure Impact Analysis of Individual/ Institutions Name of the Software Features Web address Bibexcel Freely available Uses SCI, SSCI as underlying data Support for visualization http://www8.umu.se/inforsk/Bibexcel/ Network Workbench Freely available Support of larger scale network analysis(Wikipedia) Used very much in Biomedical, Social Science andPhysics Research http://nwb.cns.iu.edu/index.html Pajek Freely available Support for larger scale network analysis andvisualization http://pajek.imfm.si/doku.php?id=pajek Publish or Perish Freely available Uses Google Scholar as underlyingdata Support for citation analysis (author impact analysis, journal impact analysisetc) http://www.harzing.com Scholarometer Freely available A browser add-ons Uses Google Scholar as underlyingdata Support citation analysis (Author impactanalysis) http://scholarometer.indiana.edu/
- 43. Thank You








![distinction between "citation" and
"reference"
• If Paper R contains a bibliographic footnote using
and describing Paper C, then
– R contains a referenceto C,
– C has a citationfrom R.
• The number of references a paper has is measured
by the number of items in its bibliography as
endnotes, footnotes, etc.,
• The number of citations a paper has is found by
looking it up [in a]citation index and seeing how
many others papers mention it."
Source:PriceD.J.D.Little science,bigscience.andbeyond.NewYork:ColumbiaUniversityPress,1986.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/journalpublication-230625075202-32cc90a6/85/Journal-Publication-pptx-9-320.jpg)
![…..Tostart, it isimportant toclarify the
terminological distinction between
"citation“[6] and "reference".In hisclassic
book Little Science, Big Science, Derek
Price gave a clear definition of both
terms. He said: "It seems to me a great
pity to waste a good technical term by
using the words citation and reference
interchangeably. I therefore propose
and adopt the convention that if Paper
R contains a bibliographic footnote
using and describing PaperC,then R
contains…
R contains a reference
to C,
[6] The concept of citation indexing: A unique
and innovative tool for navigating the
research literature. Current Contents,
January 3, 1994.
Paper
C
Paper
R
Little science, big science...and beyond.
This is my first Current Contents® (CC®)
essay under the rubric of Citation Comments.
As discussed in last week's CC, this new
monthly feature will focus on the applications
of the Institute for Scientific Information's
(ISI's) databases. 1 An appropriate topic to
launch this new series is perhaps the most
rudimentary -- the basic concept of citation
indexing.
To start, it is important to clarify the
terminological distinction between "citation"
and "reference". In his classic book Little
Science, Big Science, Derek Price gave a
clear definition of both terms. He said: "It
seems to me a great pity to waste a good
technical term by using the words citation and
reference interchangeably. I therefore propose
and adopt the convention that if Paper R
contains a bibliographic footnote using and
describing Paper C, then R contains a.
C has a citation
from R.
adopted from : Mathew, N. (n.d.). Citation indexing. Retrieved from
http://ist.psu.edu/faculty_pages/giles/IST497/presentations/Mathew.ppt](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/journalpublication-230625075202-32cc90a6/85/Journal-Publication-pptx-10-320.jpg)
































