Kertas penerangan
- 1. JABATAN PEMBANGUNAN KEMAHIRAN KEMENTERIAN SUMBER MANUSIA ARAS 7 & 8 BLOK D4, KOMPLEKS D PUSAT PENTADBIRAN KERAJAAN PERSEKUTUAN 62502 PUTRAJAYA KERTAS PENERANGAN KOD DAN NAMA PROGRAM / PROGRAM H-176-2 AUTOMATION TECHNICIAN CODE AND NAME NO DAN TAJUK MODUL/ M09 ROBOT MAINTENANCE MODULE NO AND TITLE NO DAN PERNYATAAN 09.01 CARRY OUT ROBOTS CONDITION CHECK TUGASAN / TASK(S) NO 09.02 CARRY OUT ROBOT SAFETY CHECK AND STATEMENT NO. DAN PENGALAMAN LE01 IDENTIFY TYPES OF ROBOT PEMBELAJARAN / LE02 PREPARE CHECKING TOOL & LANGKAH / EQUIPMENT LE03 CHECK ROBOT CONDITIONS AND SAFETY NO. AND LEARNING EXPERIENCE/ STEPS LE04 RECORD ROBOT CONDITIONS PERFORM MAINTENANCE OF ROBOT USING MANUFACTURER’S SPECIFICATION,ROBOT PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE,PROGRAMMING MANUALS AND DATA BOOK,LOGBOOK,CHECKLIST,HAND OBJEKTIF MODUL / TOOLS,SPECIAL TOOLS,REPORT FORMS ETC.SO THAT MODULE OBJECTIVE TYPES OF ROBOT IDENTIFIED,CONDITION AND SAFETY CONDITION CHECKED AND RECORDED IN ACCORDANCE WITH JOB SPECIFICATION REQUIREMENT AND STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURES. NO. KOD / CODE NO H-176-2/M09/KP(1/4) Muka : 01 Drp : TITLE : TYPES OF ROBOT AIM : This explanatory paper is intended to describe the preparations needed to identify the types of robots, symbols, terminology, specifications Robot, schematic / block diagram, Programming Language, and Function Robot. By the trainees will acquire the information, skills and knowledge base robot.
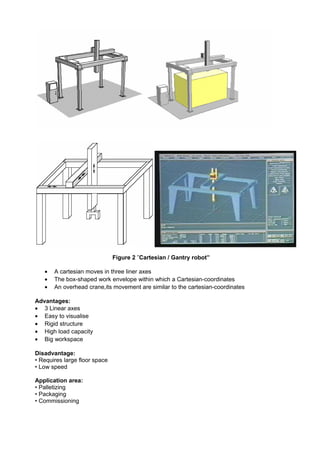
- 2. CLASIFICATION OF INDUSTRIAL ROBOTS There are 6 different types of robots classification found in usage today .There are: 1. Cartesian / Gantry robot 2. Cylindrical robot 3. Spherical / Polar robot 4. SCARA robot 5. Articulated robot (joint-arm, revolute) and 6. Parallel robot Robotic Joints • A robot joint is a mechanism that permits relative motion between parts of a robot arm. • Relative Motion: Rotational, Radial, Vertical • These basic movements, independently or in combination with others, define the complete motion of the end effector… Joints • Prismatic (sliding, linear) “L”: The cross section of the joint is considered as a generalized prism. • Revolute “R”, “T”, ”V”: Angular motion between links Figure 1 ”Joints” 1.Cartesian / Gantry robot It is used for pick and place work, application of sealant, assembly operations,handling machine tools and arc welding.It’s a robot whose arm has three prismatic / linear joints whose axes are coincident with a cartesian coordinator.
- 3. Figure 2 ”Cartesian / Gantry robot” • A cartesian moves in three liner axes • The box-shaped work envelope within which a Cartesian-coordinates • An overhead crane,its movement are similar to the cartesian-coordinates Advantages: • 3 Linear axes • Easy to visualise • Rigid structure • High load capacity • Big workspace Disadvantage: • Requires large floor space • Low speed Application area: • Palletizing • Packaging • Commissioning
- 4. Chip Handling Palletizing / Handling Figure 3 ”Cartesian / Gantry robot” 2. Cylindrical robot It is used for assembly operations, handling at machine tools, spot welding, and handling at die- casting machines.Its a robot whose axes form a cylindrical coordinate system. Figure 4 “Cylindrical robot” Advantages: • 2 Linear axes, one rotating axis • Can reach all around itself • Reach and height axes rigid • Rotational axis easy to seal
- 5. Disadvantage: • Cannot reach above itself • Base rotation axis is less rigid than a linear axis • Horizontal motion is circular 3. Spherical / Polar robot It is used for handling tools, spot welding, die-casting, fettling machines,gas welding and arc welding. Its a robot whose axes form a polar coordinate system. This type of robot is rarely used today. Figure 5 “Spherical / Polar robot” 4. SCARA robot (Selective Compliance Assembly Robot Arms) SCARA is an acronym for Selective Compliance Assembly Robot Arm. It is used for pick and place work, application of sealant, assembly operations and handling machine tools. It’s a robot which has two parallel rotary joints to provide compliance in a plane. Figure 6 “SCARA robot (Selective Compliance Assembly Robot Arms)”
- 6. Figure 7 “Configuration: 2-3 rotational joints, 1 linear joint” Advantages: • very fast horizontal movements • One linear axis,two rotating axes • High stiffnes in the vertical direction/Height axis is rigid • Very high repeatability • Large work area for floor space Disadvantages: • Working area only in a plane • Low load capacity • Difficult to program off-line • Highly complex arm Application area: • Palletizing • Commissioning Figure 8 “SCARA ROBOT”
- 7. 5. Articulated robot / Revolute robot This is the robot which we will study further in this class. It is used for assembly operations, die-casting, gas welding, arc welding, and spray painting. Its a robot whose arm has at least three rotary axes. Figure 9 “Articulated robot / Revolute robot”
- 8. Configuration: 5-6 rotational joints Advantages: • 3-dimensional workspace • high accuracy • fast movements • high load capacity • arbitrary ( 6 joints) orientation of gripper Applications: • palletizing • assembly • welding • painting • surface processing • workpiece and tool handling • quality control 6. Parallel robot One use of this robot is a mobile platform handling cockpit flight simulators. It’s a robot arms have concurrent prismatic/linear or rotary joints. Figure 10 “Parallel robot”
- 9. EXERCISE: 1. List down Industrial Robot classification 2. Explain the configuration of SCARA and GANTRY robot 3. In your opinion, which robot configuration will give a big impact for the long term investment of robot usage in any production line? If you say that so, please explain why it can be REFERENCES : 1 Yaakup Bin Saad, Mohammad Afiq dan Sahidan Tahir (2001), “Pengenalan Sistem Robot”, Venton Publishing, Kuala Lumpur, ISBN: 983-2031-32-X. 2 M. Manimaran (2003), “Jenis-jenis Robot”, Kings Information Co. Ltd Taiwan, ISBN: 957-466- 981-5. 3 www.notakom.tripod.com, Spesifikasi Robot, 15 Feb 2010, 3.15 pm