Kingdom protista
- 2. General Characteristics ïŽ Protists are very diverse and have few traits in common ïŽ Most are single-celled organisms, but some are many cells, and others live in colonies ïŽ Some produce own food, others eat other organisms or decaying matter ïŽ Some can control own movement, others cannot
- 3. ïŽ Characteristics that protists DO share: ïŽ Eukaryotic(have a nucleus), but are less complex than other eukaryotic organisms ïŽ Do not have specialized tissues ïŽ Members of the kingdom Protista are related more by how they differ from members of other kingdoms than by how they are similar to other protists
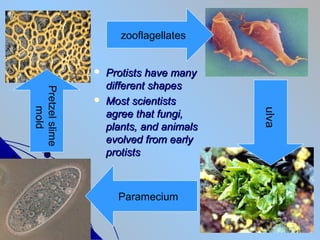
- 4. zooflagellates ïŽ Protists have many different shapes Pretzel slime ïŽ Most scientists mold ulva agree that fungi, plants, and animals evolved from early protists Paramecium
- 5. Protists and Food ïŽ Protists can get food many ways: ïŽ Can make own food ïŽ Can eat other organisms ïŽ Can eat parts or products of other organisms ïŽ Can eat remains of other organisms ïŽ Some use more than one way to get food ïŽ Some produce foodâthey use chloroplasts to produce food through photosynthesis
- 6. ïŽ Finding Food ïŽHeterotroph: organism that cannot make own food ïŽSome are decomposersâthey get energy by breaking down dead organic matter
- 7. Asexual Reproduction ïŽ Most protists reproduce asexually ïŽ Offspring come from just one parent ïŽ Binary fission: a single-celled protist divides into two cells ïŽ Each new cell is a single-celled protist
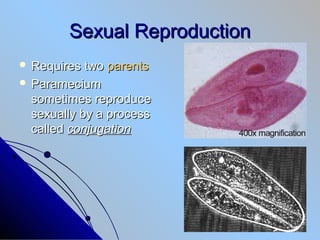
- 8. Sexual Reproduction ïŽ Requires two parents ïŽ Paramecium sometimes reproduce sexually by a process called conjugation
- 9. ïŽ Algae Kinds of Protists ïŽ Allalgae have the green pigment chlorophyll, which is used to make food through photosynthesis ïŽ Almost all algae live in water ïŽ Free-floating, single- celled algae are called phytoplankton, which produce much of the worldâs oxygen
- 10. ïŽ Amoebas ïŽ Soft,jellylike protozoans ïŽ Found in fresh and salt water, soil, and in parasites ïŽ Move with pseudopodia, which means âfalse feetâ
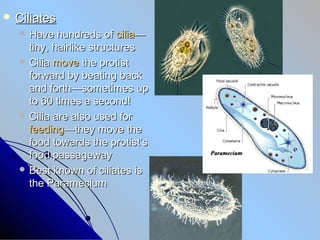
- 11. ïŽ Ciliates ïŽ Have hundreds of ciliaâ tiny, hairlike structures ïŽ Cilia move the protist forward by beating back and forthâsometimes up to 60 times a second! ïŽ Cilia are also used for feedingâthey move the food towards the protistâs food passageway ïŽ Best known of ciliates is the Paramecium
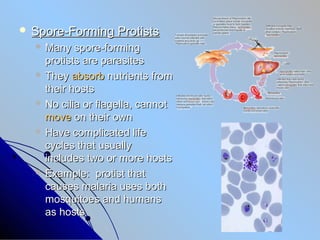
- 12. ïŽ Spore-Forming Protists ïŽ Many spore-forming protists are parasites ïŽ They absorb nutrients from their hosts ïŽ No cilia or flagella, cannot move on their own ïŽ Have complicated life cycles that usually includes two or more hosts ïŽ Example: protist that causes malaria uses both mosquitoes and humans as hosts
- 13. ïŽ Slime Molds ïŽ Heterotrophic and can only move during certain periods of life cycle ïŽ Look like thin, colorful globs of slime ïŽ Use pseudopodia to move and eat fungi and yeast ïŽ When environmental conditions are stressful, slime molds grow stalks with knobs, which contain spores
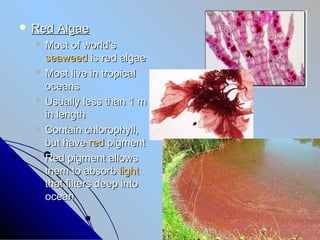
- 14. ïŽ Red Algae ïŽ Most of worldâs seaweed is red algae ïŽ Most live in tropical oceans ïŽ Usually less than 1 m in length ïŽ Contain chlorophyll, but have red pigment ïŽ Red pigment allows them to absorb light that filters deep into ocean
- 15. ïŽ Brown algae ïŽ Most seaweed in cool climates are brown algae ïŽ Attach to rocks or form large floating beds in ocean waters ïŽ Have chlorophyll and yellow-brown pigment ïŽ Many are very largeâup to 60 meters
- 16. ïŽ Green algae ïŽ Most diverse of protist producers ïŽ Green because chlorophyll is main pigment ïŽ Most live in water or moist soil ïŽ Others live in melting snow, on tree trunks, and inside other organisms
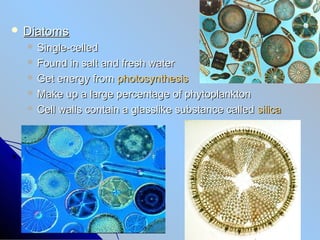
- 17. ïŽ Diatoms ïŽ Single-celled ïŽ Found in salt and fresh water ïŽ Get energy from photosynthesis ïŽ Make up a large percentage of phytoplankton ïŽ Cell walls contain a glasslike substance called silica