Kleene's theorem
- 1. COMMONWEALTH OF AUSTRALIA Copyright Regulations 1969 WARNING This material has been reproduced and communicated to you by or on behalf of Monash University pursuant to Part VB of the Copyright Act 1968 (the Act). The material in this communication may be subject to copyright under the Act. Any further reproduction or communication of this material by you may be the subject of copyright protection under the Act. Do not remove this notice.
- 2. Converting Regular ExpressionsConverting Regular Expressions into Finite Automatainto Finite Automata CSE2303 Formal Methods I Lecture 5
- 3. OverviewOverview • Questions • Kleene’s Theorem • Consequences • Convert Regular Expressions to NFA-Λ • Convert NFA-Λ to FA
- 4. QuestionsQuestions • Can every language which is represented by a regular expression be described by a finite automaton? • Can every language which is described by a finite automaton be represented by a regular expression? • Can every language be represented by a regular expression or a finite automaton?
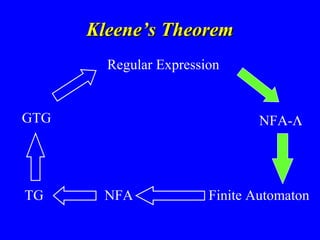
- 5. Kleene’s TheoremKleene’s Theorem Any language which can be defined by – Regular Expressions – Finite Automaton – Nondeterministic Finite Automaton (NFA) – NFA-Λ – Transition Graphs – Generalised Transistion Graphs can be defined by any of the other methods
- 6. The Complement of RegularThe Complement of Regular Language is a Regular LanguageLanguage is a Regular Language Outline of Proof: – Suppose we have a Regular Language. – Therefore we have a regular expression that defines the language. – So, by Kleene’s Theorem, there is a FA that defines this language. – We can convert this FA into one that defines the complement the language. – So, by Kleene’s Theorem, there is a regular expression that defines the complement.
- 7. Kleene’s TheoremKleene’s Theorem Regular Expression Finite Automaton NFA-ΛGTG TG NFA
- 8. How to convert aHow to convert a Regular ExpressionRegular Expression into ainto a NFA-NFA-ΛΛ
- 9. Converting Regular ExpressionConverting Regular Expression to NFA-to NFA-ΛΛ Start with the graph. - + Regular Expression
- 10. Apply the following rules until all edges are labeled with a letter or Λ. 1. Delete any edge labeled with φ. 2. Transform any edge like RS R into S
- 11. 3. Transform any edge like: into R + S R S
- 12. 4. Transform any edge like: into R* R Λ Λ
- 13. 1- a b Λ 2 3+ 4 5 Λ Λ Λ 6 7 Λ Λ a a (a* + aa*b)*(a* + aa*b)*
- 14. How to convert aHow to convert a NFA-NFA-ΛΛ into ainto a FAFA
- 15. a bb - a,b a,ba 3 2 41 + a b Start {1} {1,2} {1,3} {1,2} {1,2,4} {1,3} {1,3} {1,2} {1,3,4} Final {1,2,4} {1,2,4} {1,3,4} Final {1,3,4} {1,2,4} {1,3,4}
- 16. 1- a b Λ 2 3 4 5+ Λ Λ Λ a b Start/Final {1,2,3,4,5} {2,3,4,5} {4,5} Final {2,3,4,5} {2,3,4,5} {4,5} Final {4,5} φ {4,5} φ φ φ
- 17. 1- a b Λ 2 3+ 4 5 Λ Λ Λ 6 7 Λ Λ a a a b Start /Final{1,2,3,4} {5,4,6,7,2,3} φ Final {2,3,4,5,6,7} {5,4,6,7,2,3} {2,3,4} Final {2,3,4} {5,4,6,7,2,3} φ φ φ φ
- 18. RevisionRevision • Understand Kleene’s Theorem • Be able to convert Regular Expressions into NFA-Λ • Be able to convert NFA-Λ into a Finite Automaton • Read – Text Book Chapter 8