Km bs process
- 1. The Toyota Production System A Transition from Mass Production to Lean Manufacturing and Supply Chain Management Gunjan Tiwari D-19 SIMS MBA 2015-17
- 2. TOYOTA âĒ Toyota Motor Corporation is a Japanese automotive manufacturer headquartered in Toyota, Aichi, Japan. âĒ In March 2014 the multinational corporation consisted of 338,875 employees worldwideand, as of November 2014, is the fourteenth-largest company in the world by revenue. âĒ Toyota was the largest automobile manufacturer in 2012 (by production) ahead of the Volkswagen Group and General Motors. âĒ Toyota is the world's first automobile manufacturer to produce more than 10 million vehicles per year. âĒ As of July 2014, Toyota was the largest listed company in Japan by market capitalization and by revenue.
- 3. Major Revolutions in Manufacturing âĒ 1776, Adam Smith âThe Wealth of Nationsâ âĒ 1910, Henry Ford and Mass Manufacturing. âĒ 1980, The Toyota Production System. âĒ Lean Manufacturing. âĒ Supply Chain Management.
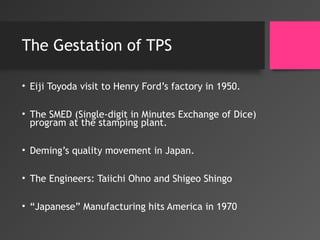
- 4. The Gestation of TPS âĒ Eiji Toyoda visit to Henry Fordâs factory in 1950. âĒ The SMED (Single-digit in Minutes Exchange of Dice) program at the stamping plant. âĒ Demingâs quality movement in Japan. âĒ The Engineers: Taiichi Ohno and Shigeo Shingo âĒ âJapaneseâ Manufacturing hits America in 1970
- 5. Main Features of TPS âĒ Greater Product Variety âĒ Fast Response (Flexibility) âĒ âStableâ Production Schedules âĒ Supply Chain Integration âĒ Demand Management
- 6. Elements of TPS âĒ The SMED Program. âĒ Highlight Problems (Jidoka). âĒ Gradual Elimination of Waste. âĒ Continuous Improvement (Kaizen), Root-Cause Analysis (5-whys?) and Fool- proofing (Poka-Yoke). âĒ Cross-Trained Workers. âĒ Just-In-Time Production. âĒ Stable Production Schedules (Heijunka)
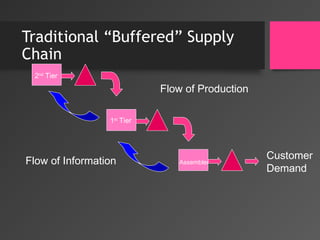
- 7. Traditional âBufferedâ Supply Chain Assembler 2nd Tier 1st Tier Flow of Production Flow of Information Customer Demand
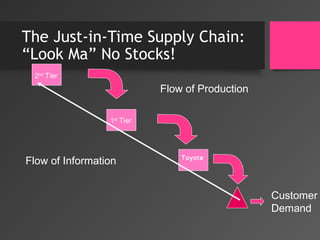
- 8. The Just-in-Time Supply Chain: âLook Maâ No Stocks! Toyota 2nd Tier 1st Tier Flow of Production Flow of Information Customer Demand
- 9. Expectations from Suppliers âĒ Frequent deliveries. âĒ Hours (not days) lead time. âĒ Rapid response capability (not from stocks). âĒ Delivery to assembly line at the right time in the right sequence without inspection. âĒ Reliability (quality and timing).
- 10. Supplier Relationships âĒ Long-term, steady relationships with a few suppliers. âĒ Negotiation based on a long term commitment to productivity and quality improvement. âĒ Interested in supplier capabilities. âĒ Continuous improvement. âĒ Product/process technology. âĒ Design for manufacturability.
- 11. Whatâs in it for a supplier? âĒ A Stable Manufacturing Environment. âĒ Steady production volume. âĒ Leaner Processes. âĒ Cost/Flexibility/Quality âĒ Profits.
- 12. âĒTHANK YOU