L 22- 23 greek architecture - introduction 14th march
- 1. ARC 044 History of Architecture Lecture ŌĆō 22 Greek Architecture
- 2. Module Outline ŌĆó Lecture ŌĆó Early Greek Period ŌĆō Historical Background ŌĆó Location and period of Greek ŌĆó Social characteristics and beliefs ŌĆó Lecture ŌĆō Architecture of the Civilization ŌĆó Greek Orders ŌĆó Temple Architecture ŌĆó Civic Architecture ŌĆó Lecture ŌĆó Greek City Planning and Design ŌĆó Greek Architecture in Athens ŌĆó Lecture ŌĆō Architectural Characteristics ŌĆó Buildings and other architectural elements ŌĆó Building materials and construction
- 3. Module Learning Outcomes ŌĆó What do we expect to learn from the civilization? ŌĆō Stone construction and decoration ŌĆō The introduction of Proportion in Architecture ŌĆō The introduction of the classical orders of architecture ŌĆō Greek architecture of temples and civic buildings ŌĆō Principles of Greek city Planning and Design ŌĆō Opportunities for women ŌĆō Many Read and Write
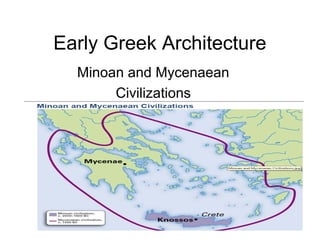
- 4. Early Greek Architecture Minoan and Mycenaean Civilizations
- 5. Minoan Civilization (2000-1400) ŌĆó Seafaring ŌĆó Enjoyed a sense of security ŌĆó Prosperous ŌĆó Their writing has not been deciphered On the Island of Crete
- 7. How the Palace of Minos might have looked:
- 8. The QueenŌĆÖs Quarters, Palace of Minos ’ü« Artifacts and religionArtifacts and religion ’ü« Fertility goddessFertility goddess or priestessor priestess
- 9. Mycenaean Civilization (1600-1100) ŌĆó Militant and aggressive ŌĆó Strong Navy ŌĆó Heavily fortified Citadels ŌĆó Royal tombs have treasures ŌĆó 1200 B.C. they attacked Troy TROY
- 10. Funerary Mask Royal graves of Mycenae (1500 B.C) Mycenaean Lion Gate
- 11. Historical Background Location ŌĆó Greeks lived on rocky mountainous land surrounded by water .The mainland of Greece is a peninsula. ŌĆó Surrounded on three sides by sea. ŌĆó Mountains cover 70 to 80 % of Greece , divide land into many regions. ŌĆó Towards the later or Hellenistic period, Greek civilization spread to other far away places including Asia Minor and Northern Africa Q- What bodies of water surround Greece? Ans - Mediterranean, Ionian, Aegean Seas
- 12. Historical Background Location ŌĆó Rocky land , Only 20 to 30 % good for farming . ŌĆó Greeks therefore lived along the coastline or on islands where the soil was good for farming ŌĆó The Aegean and Mediterranean Seas provided a means of communication and trade with other places. ŌĆó Trade brought an alphabet and coins to Greece. ŌĆó Skilled Shipbuilders and sailors . Question ---How did mountains affect the location of Greek settlements? Hint ----Isolated them and developed their own city- states.
- 13. Period ŌĆó The period of ancient Greek history can be divided into four as follows: ŌĆō 1100 B. C. ŌĆō 750 B. C. Greek Dark Ages ŌĆō 750 B. C. ŌĆō 500 B. C. Archaic Period ŌĆō 500 B. C. ŌĆō 323 B. C. Classical Period ŌĆō 323 B. C. ŌĆō 147 B. C. Hellenistic Period ŌĆó The classical and archaic period are sometimes collectively referred to as Hellenic period
- 14. Period of Greeks ŌĆó Greek Dark Ages (1100-750 BC) ŌĆō The Mycenaean people were Greek in Origin ŌĆō Greek civilization is therefore usually viewed as a continuation of the Mycenaean civilization ŌĆō As Greek people migrated from the mainland, other people from other less prosperous mountain regions of the north migrated to the more fertile coastline regions. ŌĆō They invade the Greek mainland villages and established their rule . ŌĆō Earthquakes destroyed many cities . ŌĆō Greek culture then declined , kept no written records . ŌĆō Period of Warfare and Disorder ŌĆōa period called Dark age
- 15. Period Archaic Period - City states (750 - 500 BC) ŌĆō The revival of Greece from the dark ages started during the eight century BC ŌĆō Started to Join together in small groups for protection & stability . ŌĆō These groups set up independent city ŌĆō Polis. ŌĆō City states are cities which are ruled as independent nations ŌĆō The archaic period saw the renewal interest in overseas trading contact
- 16. Period ŌĆó Archaic Period (750 - 500 BC) ŌĆō Greek societies that were engaged in trade became rich and by joining with other their neighbors, sometimes forcefully, formed large states ŌĆō Early examples of these city states include Athens, Corinth, Argos, Aegean, Miletus , and Sparta. ŌĆō The archaic period marked the beginnings of Greek monumental stone sculpture and architecture . ŌĆō The rising threat of the Persian Empire marked the end of the Greek archaic period . Plan of Athens
- 17. Period ŌĆó Classical period (500 - 323 BC) ŌĆō The Classical period of ancient Greek history occurred between 500 BC, and 323 BC. ŌĆō The period started with the Greek city states coming into conflict with the rising Persian Empire ŌĆō Pericles, the ruler of Athens between 444 and 429 BC became a driving force for the development of temple architecture. ŌĆō Between 431 and 404, Athens entered into a series of wars. with Sparta which left it in ruins. ŌĆō The Macedonian king, Philip rapidly extended Macedonian power and wealth. ŌĆō His son Alexander undertook a lot of military campaigns to extend the Greek empire and founded many new cities. ŌĆō The Death of Alexander marked the end of the classical period of Greece civilization
- 18. Period ŌĆó Hellenistic period (323 - 147 BC) ŌĆō The Hellenistic period of ancient Greek civilization started with the death of Alexander in 323 BC ŌĆō When Alexander died, he did not have a heir to inherit him ŌĆō The Greek empire split into smaller states with AlexanderŌĆÖs generals as their rulers. ŌĆō The period saw the transplanting of Greek art, Civic Buildings , civic life and culture to newly conquered areas . ŌĆō The Hellenistic period ended in 147 BC, when the Roman Empire conquered Greece and incorporated the city states into it
- 19. ŌĆó Religious Belief ŌĆō The ancient Greeks were polytheistic, believing in many different gods and goddesses ŌĆō All aspect of life was under the protection of the gods . ŌĆō All the gods and goddesses had specific roles, controlling one or two major aspects of life . ŌĆō Zeus was, for example, the supreme leader of the gods, Hermes was the messenger of the gods, and Poseidon was the god of the sea. ŌĆō Ancient Greeks believed that religion would make their lives better while they were living and gods would take care of them when they died. ŌĆō Animals were usually sacrificed as a gift to the gods
- 20. ŌĆó Place of Worship ŌĆō Temples were the focus of Greek religious worships . ŌĆō Temples were usually built in the cities of the Gods called ŌĆ£AcropolisŌĆØ ŌĆō Temples were built in every town and city for one or more god or goddess . ŌĆō The most important task for architects was how to make the temple beautiful. ŌĆō The festivals included plays, music, dancing, and then a parade to the temple where they made sacrifices .
Editor's Notes
- Made of gold; Agamemnon?