La
Download as pptx, pdf2 likes525 views
This document defines key terms related to local anesthesia and describes the ideal properties, constituents, and administration methods of local anesthetic agents. It discusses that local anesthetics work by reversibly blocking nerve impulses, lists important properties like potency, safety, and rapid onset, and describes common agents like lidocaine and bupivacaine. It also outlines techniques for maxillary and mandibular anesthesia, including inferior alveolar nerve blocks and other regional methods.
1 of 27
Downloaded 12 times

















![Tips for painless injection
Control
Communication
Confidence
slow injection[slower still in tense tissue]
Pre-anesthesia
Needle insertion[sharp &slow]
Distraction
Small guage needles
Solution warming](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/la-141021100531-conversion-gate02/85/La-18-320.jpg)








Ad
Recommended
Local anaesthesia- composition and dosage in dentistry
Local anaesthesia- composition and dosage in dentistryVikram Perakath
Ã˝
The document defines local anesthesia and describes the desirable properties of local anesthetics, including that they should not be irritating, cause permanent nerve damage, or have high systemic toxicity. It also discusses the components, actions, dosages, techniques, and complications of various local anesthetic injections used to anesthetize the maxillary teeth and surrounding tissues, such as infiltration, posterior superior alveolar nerve block, and anterior superior alveolar nerve block injections. Contraindications to local anesthetics include allergies and risk of overdose.Local Anesthesia - Paedodontics
Local Anesthesia - Paedodontics Dr Reem Ayesha
Ã˝
The document provides an overview of local anesthesia in pediatric dentistry, detailing its definition, classification, constituents, maximum recommended doses, and various techniques for administration. It highlights the use of common local anesthetic agents like lignocaine, the importance of vasoconstrictors, and the detailed procedures for various injection techniques in both maxillary and mandibular areas. Additionally, it outlines potential complications and precautions to minimize adverse effects during anesthesia administration in children.Local anaesthesia _pedo_
Local anaesthesia _pedo_Moola Reddy
Ã˝
This document discusses various techniques for achieving local anesthesia in dental procedures. It describes common methods such as local infiltration, field block, nerve block, intraligamentary injection, intraseptal injection, intrapulpal injection, intraosseous injection, jet injection, computer-controlled local anesthetic delivery systems, and electronic dental anesthesia. It also discusses topical anesthesia and provides details on the principles, indications, contraindications, advantages and disadvantages of each technique. The goal is to outline options for effectively achieving anesthesia for different dental treatments and patient situations.Anaesthetic Techniques
Anaesthetic TechniquesUrfeya Mirza
Ã˝
The document discusses various anaesthetic techniques used in veterinary practice including general anaesthesia, local anaesthesia, and other methods. General anaesthesia involves injectable and inhalation techniques. Local anaesthesia includes topical, field block, regional nerve block techniques. Specific nerve blocks are described such as auriculopalpebral nerve block, retrobulbar nerve block, maxillary nerve block. Intravenous regional anaesthesia, spinal anaesthesia techniques are also summarized. Other anaesthetic routes mentioned include electronarcosis, acupuncture, hypothermia.Local anesthesia in animals
Local anesthesia in animalsDR AMEER HAMZA
Ã˝
Local anesthesia involves applying numbing drugs to specific parts of the body to temporarily block pain sensation during surgery or other procedures. It has a long history dating back to the 1850s with early experiments using cocaine. Local anesthetics work by inhibiting sodium ion channels in nerves, preventing the generation of action potentials. While useful for minor procedures, local anesthetics can cause adverse effects if too much enters the bloodstream, possibly interfering with heart function. Proper administration is important to avoid safety issues.Local anasthesia in dentistry
Local anasthesia in dentistryMohammed Rhael
Ã˝
This document discusses local anesthesia in dentistry. It defines key terms like pain, analgesia, anesthesia and paresthesia. It describes how local anesthesia works by depolarizing and repolarizing nerves. The requirements, uses, indications and contraindications of local anesthesia are outlined. Advantages are that no special preparation or equipment is needed, anesthesia lasts over an hour, and patients remain awake. The only disadvantage is if a patient has a contraindication like an allergy.Local Anaesthesia In Plastic Surgery
Local Anaesthesia In Plastic SurgeryDr Saurabh Garg
Ã˝
This document summarizes various techniques for anaesthesia in plastic surgery, including local anaesthetics, regional nerve blocks, and other methods. It describes the classification, mechanisms of action, dosing, and administration techniques for local anaesthetics like lidocaine, bupivacaine, and ropivacaine. It also provides details on performing regional nerve blocks for different areas of the body, including techniques for blocking nerves in the head, neck, upper and lower limbs. Complications of local anaesthetics and their management are also summarized.Pain control in oral surgery
Pain control in oral surgerywria zangana
Ã˝
This document discusses pain control in dentistry. It covers procedural pain from injections and treatments, as well as post-procedural pain management. Topical anesthetics like lidocaine or benzocaine gels can numb the surface before injections. Local anesthetics like lidocaine are commonly used during procedures. NSAIDs given before nerve blocks can improve anesthesia effectiveness. After procedures, over-the-counter NSAIDs like ibuprofen or acetaminophen combined with codeine can help manage pain. Non-pharmacological options like warm salt water rinses and cold compresses are also discussed.LOCAL ANESTHESIA IN ORAL AND MAXILLOFACIAL SURGERY
LOCAL ANESTHESIA IN ORAL AND MAXILLOFACIAL SURGERYARSHIYAGARG1
Ã˝
The document provides an extensive overview of local anesthesia, including its definition, properties, classification (by chemical structure and duration), mechanisms of action, and various techniques for administering anesthesia in oral maxillofacial surgery. It details equipment used, composition and dosages, terminologies, and techniques for maxillary and mandibular anesthesia, emphasizing safety, efficacy, and potential complications associated with each method. Key areas covered include specific nerve blocks, recommended dosages, and factors influencing anesthesia outcomes.la-141122030742-conversion-gate01.pdf
la-141122030742-conversion-gate01.pdfHaroonButt17
Ã˝
This document provides an overview of local anesthesia techniques for pediatric dental patients. It defines pain and local anesthesia, and describes topical anesthetics and the components of local anesthetic solutions. Techniques for mandibular and maxillary anesthesia are outlined, including nerve blocks and infiltration. Supplemental injection methods and maximum recommended doses are also discussed. Potential complications of local anesthesia are reviewed. Finally, some new techniques are mentioned, such as jet injection and computer-controlled delivery systems.Local anaesthesia in dentistry
Local anaesthesia in dentistryKirtiRanka1
Ã˝
This document provides information about local anesthesia. It defines local anesthesia as the loss of sensation in a circumscribed area caused by blocking nerve impulses. It discusses the requirements for local anesthetic agents, their structure and classifications. It also covers the theories of how local anesthetics work, common techniques used, and complications that can arise. Local anesthetics allow for reversible loss of sensation in a specific area and include agents such as lidocaine, benzocaine and bupivacaine.local anaesthesia used in dentistery ppt
local anaesthesia used in dentistery ppthtetmyat553419
Ã˝
The document provides an in-depth overview of local anesthesia, detailing its definition, properties, classifications, and techniques. It examines various local anesthetic agents, their compositions, application methods, and specialized techniques for maxillary and mandibular injections, along with potential complications. The conclusion emphasizes the importance of local anesthesia in dentistry as a safe and effective means for pain control during procedures.Localans 140906145706-phpapp02-160924162017
Localans 140906145706-phpapp02-160924162017Maryam Arbab
Ã˝
The document provides information on local anesthesia, including its definition, classifications, constituents, maximum recommended doses, techniques of administration, and complications. It defines local anesthesia as the transient loss of sensation in a circumscribed area caused by depression of nerve endings or inhibition of peripheral nerve conduction. It classifies local anesthetics based on their composition, amide group, duration of action, source, and potency. The key constituents include a local anesthetic agent, vasoconstrictors, reducing agents, preservatives, fungicides, and vehicles. Techniques of administration for maxillary and mandibular injections are described. Complications can arise from the method of drug deposition, drug dosage, or hypersensitivity reactions.Techniques of regional anesthesia
Techniques of regional anesthesiaDr. SHEETAL KAPSE
Ã˝
This document provides information on local anesthesia techniques. It begins with definitions of local anesthesia and contraindications. It then describes the basic injection technique in 19 steps, including using a sharp sterile needle, checking solution flow, warming cartridges if needed, positioning the patient, drying tissue, applying topical anesthetic, establishing a firm hand rest, making tissue taut, keeping the syringe out of view, slowly inserting and advancing the needle, slowly depositing solution, observing the patient, and documenting the injection. Finally, it discusses various regional anesthesia techniques for the maxilla and mandible, including infiltration, nerve blocks, and intraseptal injections.Local anaesthesia
Local anaesthesia Mohammed Haneef Farooq
Ã˝
This document provides a history of local anesthetics from ancient times to modern drugs like lidocaine and bupivacaine. It discusses the definition and classification of local anesthetics, how they work, and their mechanisms of action. Examples of commonly used local anesthetics are presented, including details about their onset, duration, dosing, and metabolism. The document also covers local anesthetic administration techniques and necessary armamentarium. In summary, it provides a comprehensive overview of the development and use of local anesthetics in oral and maxillofacial surgery.Local Anesthesia for pediatric dentistry
Local Anesthesia for pediatric dentistryRahaf Sn
Ã˝
This document discusses local anesthesia techniques for pediatric dental patients. It defines pain and local anesthesia, and describes the components of local anesthetic solutions. It provides details on topical anesthetics and various injection techniques for mandibular and maxillary teeth, including inferior alveolar nerve block, mental nerve block, and local infiltration. Supplemental techniques like periodontal ligament injections are also covered. The document discusses metabolism of local anesthetics, maximum recommended doses, and potential complications. It concludes by mentioning new techniques like jet injection and computer-controlled delivery systems.Local anaesthesia and techniques for pedodontics
Local anaesthesia and techniques for pedodonticskomal0506
Ã˝
The document provides an extensive overview of local anesthesia in pediatric dentistry, detailing its definition, classification, composition, and modes of action. It discusses various local anesthetic agents, maximum recommended doses, injection procedures, and potential complications, as well as recent advancements in administering anesthesia. The conclusion emphasizes the importance of research in pediatric pharmacology to enhance the safety and efficacy of local anesthetics.Long Island Periodontist presents "The Art and Science of the Painless Dental...
Long Island Periodontist presents "The Art and Science of the Painless Dental...Edward Brant DDS, MS
Ã˝
The document discusses techniques and considerations for achieving painless injections in dental practice, focusing on local anesthetics (LAs) and their pharmacology. It outlines factors affecting injection success, maximum recommended dosages, and specific techniques for maximizing patient comfort, such as slow administration and anatomical considerations for injections in the maxillary and mandibular arches. Additionally, it addresses the implications of using epinephrine and safety measures for avoiding overdose and managing potential adverse effects.Local anesthesia IN PERIODONTICS DR.ANIZ.pptx
Local anesthesia IN PERIODONTICS DR.ANIZ.pptxPrasanthThalur
Ã˝
This document provides information on local anesthesia techniques used in periodontics. It defines local anesthesia and describes the composition, classification, and mechanism of action of local anesthetic drugs. It discusses various local anesthesia techniques for the maxillary and mandibular arches, including nerve block techniques and infiltration. Potential complications are outlined as well as maximum recommended doses. Recent advances in local anesthesia delivery methods are also mentioned.local anesthetic.ppt
local anesthetic.pptmuhammadmansooralamk1
Ã˝
This document provides information on local anesthesia. It begins by defining different types of anesthesia such as analgesia, anesthesia, general anesthesia, and local anesthesia. It then discusses the advantages of local anesthesia, such as the patient being awake and cooperative. It provides examples of indications and contraindications for local anesthesia. It classifies local anesthetics based on potency, chemical composition, and biological site of action. It discusses the basic structure of local anesthetic molecules and desirable properties of an ideal local anesthetic. It explains the mechanism of action of local anesthetics and lists common local anesthetic agents such as lidocaine and bupivacaine. It also discusses vasoconstrictors, reducing agents, preservatives, andLocal anaesthetics Dr.Vrushali
Local anaesthetics Dr.Vrushalivrushali83
Ã˝
The document provides an overview of local anesthetics. It defines local anesthesia as the loss of sensation in a circumscribed area caused by depression of nerve endings or inhibition of nerve conduction. Local anesthetics reversibly block action potentials in excitable membranes. They are classified based on their chemical structure and duration of action. Properties, composition, indications, contraindications and mechanisms of action are described. The calcium displacement theory and specific receptor theory are discussed in relation to the mechanism by which local anesthetics block nerve conduction.Pharmacotherapy of Local anaesthetic drugs
Pharmacotherapy of Local anaesthetic drugsManoj Kumar
Ã˝
Local anesthetics are drugs that reversibly block sensation, especially pain, in a localized area without loss of consciousness or control of vital functions. They can be administered topically, via injection, or infiltration. The ideal local anesthetic has rapid onset, sufficient duration, is potent, stable in solutions, and does not interfere with tissue healing or cause toxicity. Common techniques for local anesthesia include infiltration, field block, nerve block, spinal anesthesia, epidural anesthesia, and intravenous regional anesthesia. Proper administration and monitoring can prevent potential toxic effects on the central nervous system and cardiovascular system.Local anesthesia in children
Local anesthesia in children Dr. Nameeda K. S.
Ã˝
Local anaesthesia and exodontia in children is discussed. Key points include:
1. Local anaesthesia works by reversibly interrupting nerve conduction. The most accepted theory is that local anaesthetics bind to sodium channels on nerves, preventing sodium entry and conduction.
2. Techniques for anaesthetizing primary teeth include inferior alveolar nerve block, mental nerve block, infiltration and supraperiosteal injections.
3. Landmarks and techniques may need modification for paediatric patients due to anatomical differences compared to adults.LOCAL ANESTHESIA.pptx
LOCAL ANESTHESIA.pptxalpeshbista1
Ã˝
This document summarizes various local anesthesia techniques used in dentistry. It describes the basic atraumatic injection technique in 19 steps and provides details on various local anesthesia techniques including topical anesthetics, local infiltration, field blocks, and nerve blocks. It also discusses newer trends in pain control during local anesthesia administration such as safety syringes, computerized delivery systems, and vibration devices. Complications of local anesthesia and contraindications are briefly covered as well.local anesthesia: Uses, Types, Side effects and Safety
local anesthesia: Uses, Types, Side effects and SafetyPrachiRathi40
Ã˝
This document provides an overview of local anesthesia. It begins with definitions and an introduction. It then covers the historical background, classifications, components, mechanisms of action, techniques, and complications of local anesthesia. The classifications section divides local anesthetics based on their pharmacology, route of administration, biologic site and mode of action, and duration of action. Key local anesthetic agents like lidocaine, mepivacaine, articaine, bupivacaine, and topical anesthetics are also summarized. Maximum recommended doses and specific nerve block techniques for the maxillary nerve are outlined. In conclusion, the document reviews local anesthesia in detail.Local Anasthesia
Local AnasthesiaRajvi Nahar
Ã˝
The document discusses local anesthesia techniques used in dentistry. It begins with the history of local anesthesia, describing how early indigenous populations discovered numbing effects of coca leaves and how cocaine was later used as the first local anesthetic. It then defines local anesthesia and describes the ideal properties, classification, composition, mechanisms of action, and pharmacokinetics of local anesthetic drugs. The remainder of the document details the equipment used to administer local anesthesia such as syringes, needles, and cartridges, as well as various anesthesia techniques including infiltration, conduction block, and nerve block anesthesia.Local anaesthetics
Local anaesthetics John Milton
Ã˝
1. Local anesthetics work by blocking sodium ion channels in nerve cells, preventing the transmission of pain signals. They have various medical uses depending on their potency, duration, and route of administration.
2. Common local anesthetics include lidocaine, bupivacaine, prilocaine, and tetracaine. They can be administered via surface application, infiltration, nerve blocks, and other regional techniques. The addition of vasoconstrictors prolongs the duration of anesthesia.
3. Proper use of local anesthetics allows for painless minor procedures while avoiding loss of consciousness. Overdose can potentially cause cardiac or neurological toxicity.Maxillary injection techniques
Maxillary injection techniquesNishant Khurana
Ã˝
This document provides information on various maxillary injection techniques for local anesthesia. It discusses the composition of local anesthetic solutions and classifications of local anesthetics. It summarizes different maxillary injection techniques including the infraorbital nerve block, posterior superior alveolar nerve block, nasopalatine nerve block, and greater palatine nerve block. Advantages, disadvantages, anatomical landmarks, and areas of anesthesia are described for each technique. The document also covers topical anesthetics, their onset time, and examples like lidocaine and benzocaine.State of the Art LVAD Care: What Does the Year 2025 Bring?
State of the Art LVAD Care: What Does the Year 2025 Bring?Duke Heart
Ã˝
Elizabeth Volz, MD
University of North Carolina-Chapel HillDrugs Acting on the Autonomic Nervous System – Classification, Properties & Uses
Drugs Acting on the Autonomic Nervous System – Classification, Properties & UsesSajini
Ã˝
This presentation offers a comprehensive overview of drugs acting on the autonomic nervous system (ANS), including sympathomimetic, sympatholytic, parasympathomimetic, and anticholinergic agents. It explains the classification, mechanism of action, properties, formulation, brand names, and clinical uses of key drugs like adrenaline, dopamine, propranolol, atropine, and pilocarpine. Ideal for students and professionals in pharmacy, medicine, and healthcare.More Related Content
Similar to La (20)
LOCAL ANESTHESIA IN ORAL AND MAXILLOFACIAL SURGERY
LOCAL ANESTHESIA IN ORAL AND MAXILLOFACIAL SURGERYARSHIYAGARG1
Ã˝
The document provides an extensive overview of local anesthesia, including its definition, properties, classification (by chemical structure and duration), mechanisms of action, and various techniques for administering anesthesia in oral maxillofacial surgery. It details equipment used, composition and dosages, terminologies, and techniques for maxillary and mandibular anesthesia, emphasizing safety, efficacy, and potential complications associated with each method. Key areas covered include specific nerve blocks, recommended dosages, and factors influencing anesthesia outcomes.la-141122030742-conversion-gate01.pdf
la-141122030742-conversion-gate01.pdfHaroonButt17
Ã˝
This document provides an overview of local anesthesia techniques for pediatric dental patients. It defines pain and local anesthesia, and describes topical anesthetics and the components of local anesthetic solutions. Techniques for mandibular and maxillary anesthesia are outlined, including nerve blocks and infiltration. Supplemental injection methods and maximum recommended doses are also discussed. Potential complications of local anesthesia are reviewed. Finally, some new techniques are mentioned, such as jet injection and computer-controlled delivery systems.Local anaesthesia in dentistry
Local anaesthesia in dentistryKirtiRanka1
Ã˝
This document provides information about local anesthesia. It defines local anesthesia as the loss of sensation in a circumscribed area caused by blocking nerve impulses. It discusses the requirements for local anesthetic agents, their structure and classifications. It also covers the theories of how local anesthetics work, common techniques used, and complications that can arise. Local anesthetics allow for reversible loss of sensation in a specific area and include agents such as lidocaine, benzocaine and bupivacaine.local anaesthesia used in dentistery ppt
local anaesthesia used in dentistery ppthtetmyat553419
Ã˝
The document provides an in-depth overview of local anesthesia, detailing its definition, properties, classifications, and techniques. It examines various local anesthetic agents, their compositions, application methods, and specialized techniques for maxillary and mandibular injections, along with potential complications. The conclusion emphasizes the importance of local anesthesia in dentistry as a safe and effective means for pain control during procedures.Localans 140906145706-phpapp02-160924162017
Localans 140906145706-phpapp02-160924162017Maryam Arbab
Ã˝
The document provides information on local anesthesia, including its definition, classifications, constituents, maximum recommended doses, techniques of administration, and complications. It defines local anesthesia as the transient loss of sensation in a circumscribed area caused by depression of nerve endings or inhibition of peripheral nerve conduction. It classifies local anesthetics based on their composition, amide group, duration of action, source, and potency. The key constituents include a local anesthetic agent, vasoconstrictors, reducing agents, preservatives, fungicides, and vehicles. Techniques of administration for maxillary and mandibular injections are described. Complications can arise from the method of drug deposition, drug dosage, or hypersensitivity reactions.Techniques of regional anesthesia
Techniques of regional anesthesiaDr. SHEETAL KAPSE
Ã˝
This document provides information on local anesthesia techniques. It begins with definitions of local anesthesia and contraindications. It then describes the basic injection technique in 19 steps, including using a sharp sterile needle, checking solution flow, warming cartridges if needed, positioning the patient, drying tissue, applying topical anesthetic, establishing a firm hand rest, making tissue taut, keeping the syringe out of view, slowly inserting and advancing the needle, slowly depositing solution, observing the patient, and documenting the injection. Finally, it discusses various regional anesthesia techniques for the maxilla and mandible, including infiltration, nerve blocks, and intraseptal injections.Local anaesthesia
Local anaesthesia Mohammed Haneef Farooq
Ã˝
This document provides a history of local anesthetics from ancient times to modern drugs like lidocaine and bupivacaine. It discusses the definition and classification of local anesthetics, how they work, and their mechanisms of action. Examples of commonly used local anesthetics are presented, including details about their onset, duration, dosing, and metabolism. The document also covers local anesthetic administration techniques and necessary armamentarium. In summary, it provides a comprehensive overview of the development and use of local anesthetics in oral and maxillofacial surgery.Local Anesthesia for pediatric dentistry
Local Anesthesia for pediatric dentistryRahaf Sn
Ã˝
This document discusses local anesthesia techniques for pediatric dental patients. It defines pain and local anesthesia, and describes the components of local anesthetic solutions. It provides details on topical anesthetics and various injection techniques for mandibular and maxillary teeth, including inferior alveolar nerve block, mental nerve block, and local infiltration. Supplemental techniques like periodontal ligament injections are also covered. The document discusses metabolism of local anesthetics, maximum recommended doses, and potential complications. It concludes by mentioning new techniques like jet injection and computer-controlled delivery systems.Local anaesthesia and techniques for pedodontics
Local anaesthesia and techniques for pedodonticskomal0506
Ã˝
The document provides an extensive overview of local anesthesia in pediatric dentistry, detailing its definition, classification, composition, and modes of action. It discusses various local anesthetic agents, maximum recommended doses, injection procedures, and potential complications, as well as recent advancements in administering anesthesia. The conclusion emphasizes the importance of research in pediatric pharmacology to enhance the safety and efficacy of local anesthetics.Long Island Periodontist presents "The Art and Science of the Painless Dental...
Long Island Periodontist presents "The Art and Science of the Painless Dental...Edward Brant DDS, MS
Ã˝
The document discusses techniques and considerations for achieving painless injections in dental practice, focusing on local anesthetics (LAs) and their pharmacology. It outlines factors affecting injection success, maximum recommended dosages, and specific techniques for maximizing patient comfort, such as slow administration and anatomical considerations for injections in the maxillary and mandibular arches. Additionally, it addresses the implications of using epinephrine and safety measures for avoiding overdose and managing potential adverse effects.Local anesthesia IN PERIODONTICS DR.ANIZ.pptx
Local anesthesia IN PERIODONTICS DR.ANIZ.pptxPrasanthThalur
Ã˝
This document provides information on local anesthesia techniques used in periodontics. It defines local anesthesia and describes the composition, classification, and mechanism of action of local anesthetic drugs. It discusses various local anesthesia techniques for the maxillary and mandibular arches, including nerve block techniques and infiltration. Potential complications are outlined as well as maximum recommended doses. Recent advances in local anesthesia delivery methods are also mentioned.local anesthetic.ppt
local anesthetic.pptmuhammadmansooralamk1
Ã˝
This document provides information on local anesthesia. It begins by defining different types of anesthesia such as analgesia, anesthesia, general anesthesia, and local anesthesia. It then discusses the advantages of local anesthesia, such as the patient being awake and cooperative. It provides examples of indications and contraindications for local anesthesia. It classifies local anesthetics based on potency, chemical composition, and biological site of action. It discusses the basic structure of local anesthetic molecules and desirable properties of an ideal local anesthetic. It explains the mechanism of action of local anesthetics and lists common local anesthetic agents such as lidocaine and bupivacaine. It also discusses vasoconstrictors, reducing agents, preservatives, andLocal anaesthetics Dr.Vrushali
Local anaesthetics Dr.Vrushalivrushali83
Ã˝
The document provides an overview of local anesthetics. It defines local anesthesia as the loss of sensation in a circumscribed area caused by depression of nerve endings or inhibition of nerve conduction. Local anesthetics reversibly block action potentials in excitable membranes. They are classified based on their chemical structure and duration of action. Properties, composition, indications, contraindications and mechanisms of action are described. The calcium displacement theory and specific receptor theory are discussed in relation to the mechanism by which local anesthetics block nerve conduction.Pharmacotherapy of Local anaesthetic drugs
Pharmacotherapy of Local anaesthetic drugsManoj Kumar
Ã˝
Local anesthetics are drugs that reversibly block sensation, especially pain, in a localized area without loss of consciousness or control of vital functions. They can be administered topically, via injection, or infiltration. The ideal local anesthetic has rapid onset, sufficient duration, is potent, stable in solutions, and does not interfere with tissue healing or cause toxicity. Common techniques for local anesthesia include infiltration, field block, nerve block, spinal anesthesia, epidural anesthesia, and intravenous regional anesthesia. Proper administration and monitoring can prevent potential toxic effects on the central nervous system and cardiovascular system.Local anesthesia in children
Local anesthesia in children Dr. Nameeda K. S.
Ã˝
Local anaesthesia and exodontia in children is discussed. Key points include:
1. Local anaesthesia works by reversibly interrupting nerve conduction. The most accepted theory is that local anaesthetics bind to sodium channels on nerves, preventing sodium entry and conduction.
2. Techniques for anaesthetizing primary teeth include inferior alveolar nerve block, mental nerve block, infiltration and supraperiosteal injections.
3. Landmarks and techniques may need modification for paediatric patients due to anatomical differences compared to adults.LOCAL ANESTHESIA.pptx
LOCAL ANESTHESIA.pptxalpeshbista1
Ã˝
This document summarizes various local anesthesia techniques used in dentistry. It describes the basic atraumatic injection technique in 19 steps and provides details on various local anesthesia techniques including topical anesthetics, local infiltration, field blocks, and nerve blocks. It also discusses newer trends in pain control during local anesthesia administration such as safety syringes, computerized delivery systems, and vibration devices. Complications of local anesthesia and contraindications are briefly covered as well.local anesthesia: Uses, Types, Side effects and Safety
local anesthesia: Uses, Types, Side effects and SafetyPrachiRathi40
Ã˝
This document provides an overview of local anesthesia. It begins with definitions and an introduction. It then covers the historical background, classifications, components, mechanisms of action, techniques, and complications of local anesthesia. The classifications section divides local anesthetics based on their pharmacology, route of administration, biologic site and mode of action, and duration of action. Key local anesthetic agents like lidocaine, mepivacaine, articaine, bupivacaine, and topical anesthetics are also summarized. Maximum recommended doses and specific nerve block techniques for the maxillary nerve are outlined. In conclusion, the document reviews local anesthesia in detail.Local Anasthesia
Local AnasthesiaRajvi Nahar
Ã˝
The document discusses local anesthesia techniques used in dentistry. It begins with the history of local anesthesia, describing how early indigenous populations discovered numbing effects of coca leaves and how cocaine was later used as the first local anesthetic. It then defines local anesthesia and describes the ideal properties, classification, composition, mechanisms of action, and pharmacokinetics of local anesthetic drugs. The remainder of the document details the equipment used to administer local anesthesia such as syringes, needles, and cartridges, as well as various anesthesia techniques including infiltration, conduction block, and nerve block anesthesia.Local anaesthetics
Local anaesthetics John Milton
Ã˝
1. Local anesthetics work by blocking sodium ion channels in nerve cells, preventing the transmission of pain signals. They have various medical uses depending on their potency, duration, and route of administration.
2. Common local anesthetics include lidocaine, bupivacaine, prilocaine, and tetracaine. They can be administered via surface application, infiltration, nerve blocks, and other regional techniques. The addition of vasoconstrictors prolongs the duration of anesthesia.
3. Proper use of local anesthetics allows for painless minor procedures while avoiding loss of consciousness. Overdose can potentially cause cardiac or neurological toxicity.Maxillary injection techniques
Maxillary injection techniquesNishant Khurana
Ã˝
This document provides information on various maxillary injection techniques for local anesthesia. It discusses the composition of local anesthetic solutions and classifications of local anesthetics. It summarizes different maxillary injection techniques including the infraorbital nerve block, posterior superior alveolar nerve block, nasopalatine nerve block, and greater palatine nerve block. Advantages, disadvantages, anatomical landmarks, and areas of anesthesia are described for each technique. The document also covers topical anesthetics, their onset time, and examples like lidocaine and benzocaine.Long Island Periodontist presents "The Art and Science of the Painless Dental...
Long Island Periodontist presents "The Art and Science of the Painless Dental...Edward Brant DDS, MS
Ã˝
Recently uploaded (20)
State of the Art LVAD Care: What Does the Year 2025 Bring?
State of the Art LVAD Care: What Does the Year 2025 Bring?Duke Heart
Ã˝
Elizabeth Volz, MD
University of North Carolina-Chapel HillDrugs Acting on the Autonomic Nervous System – Classification, Properties & Uses
Drugs Acting on the Autonomic Nervous System – Classification, Properties & UsesSajini
Ã˝
This presentation offers a comprehensive overview of drugs acting on the autonomic nervous system (ANS), including sympathomimetic, sympatholytic, parasympathomimetic, and anticholinergic agents. It explains the classification, mechanism of action, properties, formulation, brand names, and clinical uses of key drugs like adrenaline, dopamine, propranolol, atropine, and pilocarpine. Ideal for students and professionals in pharmacy, medicine, and healthcare.COUGH AND THIER DRUGS AND MODE OF ACTION.pptx
COUGH AND THIER DRUGS AND MODE OF ACTION.pptxPackialakshmiP
Ã˝
COUGH AND THIER DRUGS AND MODE OF ACTIONELECTROMYOGRAPHY.pptX by GOKULAKRISHNAN.
ELECTROMYOGRAPHY.pptX by GOKULAKRISHNAN.GOKULAKRISHNAN JANARTHANAN
Ã˝
Electromyography is basically the study of motor unit activity.
In electromyography, the study of the electrical activity of contracting muscle provides information concerning the structure and function of the motor units.
Theories of Learning and Teaching.......
Theories of Learning and Teaching.......Avantika Gupta
Ã˝
Definition of Teaching:
“Teaching is a form of interpersonal influence aim at changing the behavior potential of another person”.
Nature and Characteristics of Teaching:
ÔÉò Teaching is giving information.
ÔÉò Teaching is causing to learn.
ÔÉò Teaching is a matter of helping the child to respond to his environment in an effective manner.
ÔÉò Teaching is helping a child to adjust himself to his environment.
ÔÉò Teaching is stimulation and encouragement.
ÔÉò Teaching is guidance.
ÔÉò Teaching is Training the emotions of the child.
ÔÉò Teaching is a mean of preparation.
ÔÉò Teaching is an art and science.
General Theory of Teaching:
The General Theory of Teaching, also known as the "Theory of Teaching" or "General Theory of Instruction," is a comprehensive framework that outlines the fundamental principles and processes of teaching.
Benefits of the General Theory of Teaching:
• Improved Student Learning
• Increased Teacher Efficacy
• Enhanced Teacher Professional Development
• Better Student Engagement
CONCLUSION
• Teaching theory is prescriptive.
• Teachers and pupils are the major variables of teaching theory.
• It is narrow and specific.
• It is based upon learning theory, learning conditions and learning components.
• While learning theory are formulated by conducting experiments on animals teaching theory is developed by dealing with human subjects in normal situations.
• It is concerned with effective learning and development of pupils.
Learning is a complex and multifaceted process that involves the acquisition, processing, and retention of knowledge, skills, and attitudes.
The relatively permanent change in a person's knowledge or behavior due to experience.
Characteristics of Learning:
• Learning is Growth.
• Learning is adjustment.
• Learning is purposeful.
• Learning is intelligent.
• Learning is active.
• Learning is both individual and social.
• Learning is the product of the environment.
• Learning is experience.
Learning Theory: Learning theory refers to the body of knowledge that explains how people learn and acquire new knowledge, skills, and attitudes.
Types of Teaching Theory:
1.Formal Theory of Teaching
• Meutic Theory of teaching.
• Communication theory of teaching.
• Moulding theory of teaching.
• The mutual enquiry theory.
2.Descriptive theory of teaching
• Theories of instruction
• Prescriptive theory of teaching
3.Normative theory of teaching
• Cognitive theory of teaching
• Theory of teacher behaviour
• Psychological theory of teaching
• General theory of teaching
FORMAL THEORY OF TEACHING
Formal theory of teaching is also known as philosophical theory. The theory which is based upon certain logic, certain metaphysical, epistemological assumptions and propositions is known as formal theory of teaching.
1.Meutic Theory of Teaching:
• This theory conceives that teaching process helps to recollect or unfold that knowledge with questioning techniques.
• The Socratic’s method is an essential for this theory.
• The heredity plays an importAspirin powder or Acetyl salicylic acid powder.docx
Aspirin powder or Acetyl salicylic acid powder.docxkopalsharma85
Ã˝
pharmacy exercise on aspirin powderGAIT in Biomechanics along with abnormal gait
GAIT in Biomechanics along with abnormal gaitNerusu sai priyanka
Ã˝
Gait , ab normal gait,normal biomechanics,pathomechanics of gait,unilateral stance,factors affectoing gait When is the Right Time to Refer to (Advanced) Heart Failure?
When is the Right Time to Refer to (Advanced) Heart Failure?Duke Heart
Ã˝
Adam DeVore, MD, MHS
Duke University THE EYELID PPT FOR 1ST YEAR BSC OPTOMETRY
THE EYELID PPT FOR 1ST YEAR BSC OPTOMETRYnihalanichz
Ã˝
THIS IS THE NOTES FOR EYELID ANATOMY AND SOME PHYSIOLOGY WHICH WILL HELP FOR 1ST YEAR OF BSC OPTOMETRY Ophthalmic Techniques HSSC-1 | Federal Board Past Paper | 2025 Preparation.pdf
Ophthalmic Techniques HSSC-1 | Federal Board Past Paper | 2025 Preparation.pdfazkaimran130
Ã˝
üìò HSSC-1 Ophthalmic Technology | Federal Board Past Paper Solved üëÅÔ∏è
Welcome to our channel! In this video, we cover the Federal Board Ophthalmic Techniques Past Paper for HSSC-1, including:
✅ Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) – Section A (20 Marks)
✅ Short Questions – Section B (50 Marks)
✅ Long Questions – Section C (30 Marks)
üìÖ Latest Exam Pattern | 2025 Preparation Guide
‚è∞ Time Management Tips Included!
This video is perfect for students preparing for HSSC-1 Ophthalmic Technology exams under the Federal Board of Intermediate and Secondary Education (FBISE).
üîî Don‚Äôt forget to like, share, and subscribe for more solved papers and exam tips!
#OphthalmicTechnology #FBISE #HSSC1 #PastPaper #MedicalTechnology #OphthalmicTechniques #FederalBoard #MCQs #ShortQuestions #LongQuestions #BoardExam2025whooping cough community health nursing.
whooping cough community health nursing.ASWIN S
Ã˝
Whooping cough for BSC 5th sem community health nursing..
This includes
Introduction
Definition
Incidence
Incubation period
Causes
Clinical manifestations
Diagnostic evaluation
Treatment
Prevention
Complications
Of whooping cough....Devices in the Management of Acute Heart Failure (or) Cardiogenic Shock
Devices in the Management of Acute Heart Failure (or) Cardiogenic ShockDuke Heart
Ã˝
M. Imran Aslam, MD
Duke University Exomind in General Aesthetics - with June 10, 2025 updates
Exomind in General Aesthetics - with June 10, 2025 updateslcadymd1
Ã˝
Hi. This is Dr. Cady writing. This is the updated presentation compared to the original one given in Hong Kong on June 3rd. The rationale behind the update is my further reflection on the interesting concept of "mental wellness" which has been identified as a treatment target with a modified TMS protocol developed by BTL. It should be clearly noted that this device is definitely approved in the USA for the treatment of depression according to old TMS protocols. The "depression protocol" involves a minimum of 30 treatments, administered over 5 - 6 weeks, with one treatment typically on every weekday (M-F).
In contrast, the "wellness protocol" developed by BTL for this device has been successfully used in a study on "mental wellness" with just FOUR treatments administered, and in the study for food cravings and self control with just SIX treatments administered. Additionally, I demonstrate in this presentation the remarkable power of this TMS device to eliminate depression and anxiety in two patients presented after just two back to back treatments.
It should be clearly noted that this is not an official BTL protocol, nor the position of the company, and the use of this device for mental wellness is not "FDA approved." It is also not FDA approved for the aggressive treatment protocol I share in this presentation. Given that this device is used per physician discretion, and given that the scientific literature supports the idea that the more pulses or treatments delivered in a day increase the effectiveness of the treatment and the rapidity of onset, this aggressive treatment seemed to me to be scientifically valid, and safe. Scrupulous informed consent was obtained from the patients prior to administering the treatments in the manner I have illustrated herein. I am not necessasrily recommending tretments in this manner. But I include them and note them because they reveal, dramatically, the capability of this device to change people's lives with the most serious cases. The impact, therefore, on just "lack of mental wellness" or "food cravings and impulse control is very reasonable.
It is my belief that 4 - 6 treatments in a general aesthetic or "wellness" practice should be sufficient. For the harder cases that a psychiatrist would see, there is some argument that even six treatments, administered with three "couplet" or "paired" treatments, could be remarkably beneficial.
In this presentation, I review the epidemiology of depression, anxiety and the topic of simply being "mentally unwell" while not being necessarily diagnosed with depression or anxiety. It is the lack of mental wellness and addressing it with this helpful modality that is so tremendously exciting.
A rough comparison of the relative treatment potency and effects of the Exomind versus older technology is included, pointing the way toward the logical assumption that, indeed, merely a few treatments (4 - 6) could have significant benefits in our patients.Multidisciplinary Strategies in GDMT Implementation
Multidisciplinary Strategies in GDMT ImplementationDuke Heart
Ã˝
Aferdita Spahillari, MD
Duke University Guideline Directed Medical Therapy: What is the Best Approach?
Guideline Directed Medical Therapy: What is the Best Approach?Duke Heart
Ã˝
Benjamin Trichon, MD
Duke University5-Lift Analysis in ergonomics focuses on evaluating the safety and efficienc...
5-Lift Analysis in ergonomics focuses on evaluating the safety and efficienc...Bolan University of Medical and Health Sciences ,Quetta
Ã˝
Lift Analysis in ergonomics focuses on evaluating the safety and efficiency of manual lifting tasks in the workplace. It involves assessing the physical demands placed on the human body during lifting activities to prevent musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs), particularly lower back injuries5-Lift Analysis in ergonomics focuses on evaluating the safety and efficienc...
5-Lift Analysis in ergonomics focuses on evaluating the safety and efficienc...Bolan University of Medical and Health Sciences ,Quetta
Ã˝
Ad
La
- 1. DEFINITIONS • ANAESTHESIA – This is loss of all forms of sensation including pain, touch, temperature and pressure sensation which may be accompanied by impairment of motor function. • ANALGESIA – Loss of pain sensation unaccompanied by loss of other forms of sensibility.
- 2. IDEAL PROPERTIES OF LA AGENT • POTENCY AND RELIABILITY- Should effectively produce analgesia when administered in adequate dosage. • REVERSIBILITY OF ACTION- Must be completely reversible within predictable time. • SAFETY- Should not be toxic. Therapeutic Lethal dose(LD50) ratio = Effective dose(ED50) The higher the ratio the greater the safety margin. • LACK OF IRRITATION- It should be isotonic with a pH compatible to that of the tissues.
- 3. IDEAL PROPERTIES- Contd • RAPIDITY OF ONSET- Ideally, injection should be followed by immediate onset of LA. • DURATION OF EFFECT – The effect last till the completion of treatment. • STERILITY • ADEQUATE SHELF LIFE- Average is 2-2.5 years. • PENETRATION OF MUCOUS MEMBRANE- It should have penetrating ability.
- 4. CONSTITUENTS OF LOCAL ANAESTHETIC SOLUTIONS • Local anaesthetic agent • Vasoconstrictor • Reducing agent • Preservative • Fungicide • vehicle
- 5. • LA AGENT  ESTER LINKAGE- e.g. Procaine, Cocaine, Tetracaine.  AMIDE LINKAGE – e.g. Lignocaine, Prilocaine, Mepivacaine, Articaine, Etidocaine, Bupivacaine.  Short acting 3% Mepivacaine (20-40mins) 4% Prilocaine (5-10mins)
- 6. – Long acting a) 2% Lidocaine with VC (60mins) b) 0.5% Bupivacaine with VC (>90mins) c) 1.5% Ethidocaine with VC (>90mins) d) 4% Articaine (60mins) e) 4% Prilocaine with VC (60-90mins)
- 7. CONSTITUENTS OF LA AGENT Contd. • VASOCONSTRICTORS a. Adrenaline-A synthetic substance similar to that secreted in human body b. Felypressin- A synthetically produced polypeptide similar to that secreted from human posterior pituitary gland. It is contraindicated in pregnant women because it is believed to have an oxytocin-like effect. c. Noradrenaline- The common concentrations of adrenaline or noradrenaline are;1:50,000 1:80,000 1:100,000. Felypressin is only available in citanest in a concentration of 0.031U/ml.
- 8. • Advantages; • Reduces toxic effect by retarding the absorption of the constituents. • By confining the local anaesthetic agent to a localised area, it increases the depth and duration of anaesthesia. • Produces a bloodless field of operation for surgical procedures.
- 9. DILUTION OF VASOCONSTRICTOR • Dilution of vasoconstrictor is commonly referred to as a ratio of 1:1000. • A conc. Of 1:1000 means that 1gram (1000mg) of solute (drug) contained in 1000ml of solution. ie 1:1000 dilution contains 1000mg in 1000ml or 1.0mg/ml of solution.
- 10. Maximum safest dose of lidocaine adult dose • Lidocaine without vasoconstrictor is 300mg • Lidocaine with vasoconstrictor is 500mg. • 2% of lidocaine=20mg/ml • ie 20mg=1ml • X=1.8ml • X=1.8x20 • X=36mg of lidocaine in one ampule. • Number of ampules that can be safely used for the pt in one visit=500mg/36, 14mg/ml.
- 11. Weight (more accurate) • Lidocaine without vasoconstrictor =4.4mg/kg • Lidocaine with vasoconstrictor= 7mg/kg
- 12. Children dose(clark’s rule) • Always deals with weight of pt. Dose of child=weight of child in pounds/150×adult dose. Young’s rule • Always deals with age of pt. • Age of pt × adult dose/age of pt×12
- 13. Healthy patient • 0.2mg of epinephrine • In pt with cardiac problem=0.04mg
- 14. • REDUCING AGENT – Sodium bimetasulphite in small quantity is included in the solution to prevents oxidation of the vasoconstrictors as they are unstable in solution, especialy on exposure to sunlight.
- 15. CONSTITUENTS Contd. • PRESERVATIVE – Caprylhydrocupreinotoxin in xylotox helps to maintain sterility of the solution and also increases its shelf life. • FUNGICIDE – Thymol prevents proliferation of minute fungae which cause cloudiness of the solution.
- 16. • VEHICLE – Ringer’s solution(modified) is an isotonic solution in which all the other constituents are dissolved to minimize discomfort during injection of the LA.
- 17. MODE OF ACTION • LA agent is made up of a weak base and strong acid which is hydrolyzed in the alkaline medium of human tissues to liberate the alkaloid base. • This stabilizes the axonal limiting membrane of the nerve fibres thereby preventing the inflow of sodium ions into the cell and the resultant depolarization of the cell membrane. • Impulse conduction is thus prevented so that pain stimulus is not transmitted.
- 18. Tips for painless injection Control Communication Confidence slow injection[slower still in tense tissue] Pre-anesthesia Needle insertion[sharp &slow] Distraction Small guage needles Solution warming
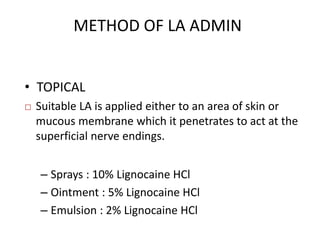
- 19. METHOD OF LA ADMIN • TOPICAL  Suitable LA is applied either to an area of skin or mucous membrane which it penetrates to act at the superficial nerve endings. – Sprays : 10% Lignocaine HCl – Ointment : 5% Lignocaine HCl – Emulsion : 2% Lignocaine HCl
- 20. • INFILTRATION – Submucous injection : the solution is deposited just beneath the mucous membrane. This method is used for anaesthetizing the long buccal nerve. – Sub-periosteal injection: The solution is deposited between periosteum and cortical plate of bone. E.g in palate.
- 21. ÔÇ® Supra-periosteal injection: The solution is deposited outside the periosteum. Most frequently used in the maxilla where the cortical plate of the alveolar bone is thin and perforated by tiny vascular canals.
- 22. METHOD CONTD – Intraosseous-The solution is deposited within the medullary bone. – Intraseptal- The solution is deposited into the soft bone of the alveolar crest.
- 23. • REGIONAL BLOCK – This is deposited near the nerve trunk and blocks the areas supplied by the nerve trunk. It is reliable in the mandible due to the thickness of the bone.
- 24. LA IN MAXILLA MAXILLARY Posterior superior alveolar nerve block: The upper 3rd,2nd and the distobuccal and palatal roots of the 1st molar are innervated by posterior superior alveolar nerve. ÔÇß LA is deposited between the 2nd and 3rd molars. Serves the three maxillary molars and related buccal soft tissue (except the MB root of 1st molar).
- 25. METHODS Contd.  Anterior and middle superior alveolar nerve – The mesiobuccal root of the 1st molar, both pre molars are supplied by this nerve.  LA is deposited just above the upper limit of the attached gingivae with the needle in-line with the long axis of the tooth. Serves premolars, all anterior teeth and overlying buccal mucosa and bone.
- 26. LA IN MAX CONTD • GREATER PALATINE NERVE – This is given over the estimated area of the apex of the root and should never be deposited distal to the 2nd molar because it will produce anaesthesia of the soft palate and uvular area making swallowing difficult for the patient. NASOPALATINE NERVE – This is deposited beneath the incisive papilla at a site lateral to central rugae and deposited slowly to reduce discomfort. Provides anaesthesia of hard and soft tissue of the pre maxilla as far as the distal aspect of the 1st premolar.
- 27. LA IN MANDIBLE • Due to the density of the buccal plate of bone infilteration technics are of limited value in the mandible and regional or block anaesthesia is most frequently used. E g inferior alveolar nerve block is done in the pterygomandibular space. PTERYGOMANDIBULAR SPACE Anaesthesia in the mandible is achieved by deposition of the solution around the inferior alveolar and lingual nerve in the pterygo-mandibular space.
