Lab3 aggregating data
- 1. AGGREGATING DATA USING GROUP FUNCTIONS Structured Query Language
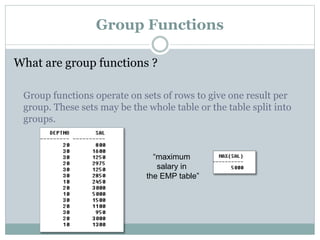
- 2. Group Functions What are group functions ? Group functions operate on sets of rows to give one result per group. These sets may be the whole table or the table split into groups. âmaximum salary in the EMP tableâ
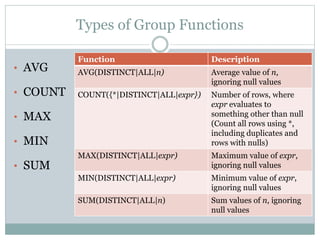
- 3. Types of Group Functions âĒ AVG âĒ COUNT âĒ MAX âĒ MIN âĒ SUM Function Description AVG(DISTINCT|ALL|n) Average value of n, ignoring null values COUNT({*|DISTINCT|ALL|expr}) Number of rows, where expr evaluates to something other than null (Count all rows using *, including duplicates and rows with nulls) MAX(DISTINCT|ALL|expr) Maximum value of expr, ignoring null values MIN(DISTINCT|ALL|expr) Minimum value of expr, ignoring null values SUM(DISTINCT|ALL|n) Sum values of n, ignoring null values
- 4. Using Group Functions ï Syntax: SELECT [column, ] group_function(column) FROM table [WHERE condition] [GROUP BY column] [ORDER BY column];
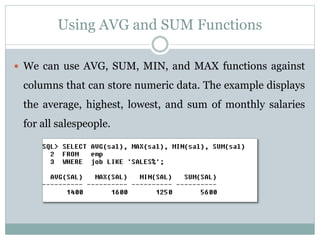
- 5. Using AVG and SUM Functions ï We can use AVG, SUM, MIN, and MAX functions against columns that can store numeric data. The example displays the average, highest, lowest, and sum of monthly salaries for all salespeople.
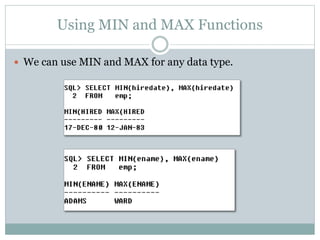
- 6. Using MIN and MAX Functions ï We can use MIN and MAX for any data type.
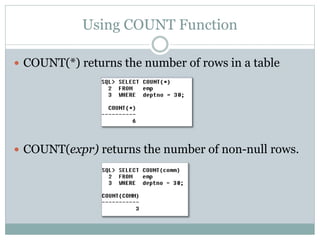
- 7. Using COUNT Function ï COUNT(*) returns the number of rows in a table ï COUNT(expr) returns the number of non-null rows.
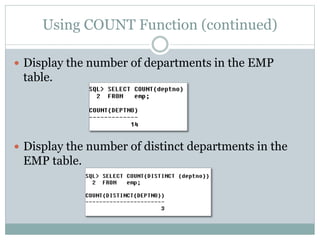
- 8. Using COUNT Function (continued) ï Display the number of departments in the EMP table. ï Display the number of distinct departments in the EMP table.
- 9. Creating Groups of Data ï We have used the group functions on the tables as one large group of information. At times we need to divide the table into smaller groups. This can be done by using GROUP BY clause. EMP âaverage salary in EMP table for each departmentâ 2916.6667 2175 1566.6667
- 10. Creating Groups of Data: GROUP BY Clause ï Divide rows in a table into smaller groups by using th GROUP BY clause. SELECT [column, ] group_function(column) FROM table [WHERE condition] [GROUP BY group_by_expression] [ORDER BY column]; ïĄ group_by_expression specifies columns whose values determine the basis for grouping rows.
- 11. Using the GROUP BY Clause ï All columns int the SELECT list that are not in group functions must by in the GROUP BY clause. ï The GROUP BY column does not have to be in the SELECT list.
- 12. Grouping by More Than One Column EMP âsum salaries in the EMP table for each job, grouped by departmentâ âĒ Display the total salary being paid to each job title, within each department.
- 13. Using the GROUP BY Clause on Multiple Columns âĒ Display the total salary being paid to each job title, within each department.
- 14. Illegal Queries Using Group Functions ï Any column or expression in the SELECT list that is not an aggregate function, must be in the GROUP BY clause. ï Display the number of employees in each department.
- 15. Illegal Queries Using Group Functions ï We cannot use the WHERE clause to restrict groups. ï We use the HAVING clause to restrict groups. ï Display the average salaries of those departments that have an average salary greater than $2000.
- 16. Excluding Group Results ï In the same way that we use the WHERE clause to restrict rows that we select, we use the HAVING clause to restrict groups. ï To find the maximum salary of each department, but show only the departments that have maximum salary more than $2900, we need to do the following: ïĒ Find the maximum salary for each department by grouping by department number. ïĒ Restrict the groups to those departments with a maximum salary greater than $2900.
- 17. Excluding Group Results EMP 5000 3000 2850 âmaximum salary per department greater than $2900â
- 18. Excluding Group Results: Having Clause ï Use the HAVING clause to restrict groups ïĄ Rows are grouped. ïĄ The group function is applied. ïĄ Groups matching the HAVING clause are displayed. SELECT column, group_function FROM table [WHERE condition] [GROUP BY group_by_expression] [HAVING group_condition] [ORDER BY column];
- 19. Using the HAVING Clause ï Display department numbers and maximum salary for those department whose maximum salary is greater than $2900.
- 20. ï Display the job title and total monthly salary for each job title with a total payroll exceeding $5000. Exclude salespeople and sort the list by the total monthly salary. Using the HAVING Clause
- 21. Nesting Group Functions ï Display the maximum average salary.
- 22. Summary SELECT column, group_function(column) FROM table [WHERE condition] [GROUP BY group_by_expression] [HAVING group_condition] [ORDER BY column]; Order of evaluation of the clauses: ï· WHERE clause ï· GROUP BY clause ï· HAVING clause


![Using Group Functions
ï Syntax:
SELECT [column, ] group_function(column)
FROM table
[WHERE condition]
[GROUP BY column]
[ORDER BY column];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab3-aggregatingdata-210914205441/85/Lab3-aggregating-data-4-320.jpg)

![Creating Groups of Data:
GROUP BY Clause
ï Divide rows in a table into smaller groups by using th
GROUP BY clause.
SELECT [column, ] group_function(column)
FROM table
[WHERE condition]
[GROUP BY group_by_expression]
[ORDER BY column];
ïĄ group_by_expression specifies columns whose values
determine the basis for grouping
rows.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab3-aggregatingdata-210914205441/85/Lab3-aggregating-data-10-320.jpg)







![Excluding Group Results:
Having Clause
ï Use the HAVING clause to restrict groups
ïĄ Rows are grouped.
ïĄ The group function is applied.
ïĄ Groups matching the HAVING clause are displayed.
SELECT column, group_function
FROM table
[WHERE condition]
[GROUP BY group_by_expression]
[HAVING group_condition]
[ORDER BY column];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab3-aggregatingdata-210914205441/85/Lab3-aggregating-data-18-320.jpg)



![Summary
SELECT column, group_function(column)
FROM table
[WHERE condition]
[GROUP BY group_by_expression]
[HAVING group_condition]
[ORDER BY column];
Order of evaluation of the clauses:
ï· WHERE clause
ï· GROUP BY clause
ï· HAVING clause](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab3-aggregatingdata-210914205441/85/Lab3-aggregating-data-22-320.jpg)