lab5 .ppt.pdf
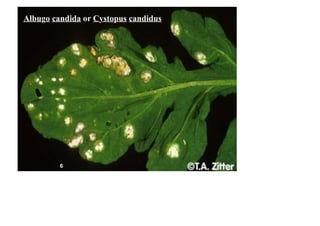
- 1. K.: Mycetae D.: Eumycota Sub D.: Mastigomycotina Class: Oomycetes Order (2): Peronosporales Family (2): Albuginaceae ex: Albugo candida or Cystopus candidus Cause: white rust disease of crucifer (radish).
- 2. Albugo candida 1- Obligate parasitic fungus which attacks several species of crucifers causing the white rust. 2- The hyphae are intercellular and feed by haustoria which penetrate the walls of the host cells and enlarge inside it as spherical structure. 3- Asexual reproduction takes place by sporangia produced in chains from the tips of short, club-shaped hyphae called the sporangiophores.
- 3. 1. Both the growth of the mycelium and the production of numerous sporangia exert a pressure from below on the host epidermis, causing rupture. So, the sporangia are released and form a white rust on the surface of the host. 2. Zoospores are released from sporangia, Encystment, and then germinated and infects the host. 3. Oogonia and antheridia are formed within the tissues of the host and the type of sexual reproduction is gametangial contact
- 4. Albugo candida or Cystopus candidus 6
- 8. Family (3): Peronosporaceae Ex: Plasmopora viticola (Cause: downy mildew on grape). Ex: Peronspora spp. (Cause: downy mildew on radish). Ex: Bremia lactucae (Cause: downy mildew on Lettuce).
- 9. Family: Peronosporaceae This is the most highly specialized family in the peronosporales, all species are obligate parasites of vascular Plants causing diseases called downy mildews. The family include a number of common genera differentiated chiefly by the branching of their sporangiophores.
- 10. Plasmopora viticola The branches and their subdivision occur at right angles. Causes D.M. on Grape.
- 11. Plasmopora viticola (Cause: downy mildew on grape).
- 12. Peronospora: The sporangiophores are dichotomously branched at acute angles with curved pointed tips on which sporangia are borne. This genus causes D.M. on Radish.
- 13. Peronspora spp. (Cause: downy mildew on radish)
- 14. Bremia lactucae Is similar to Peronospora except that the tips of the branches are expanded into cup-shaped apophyses with four sterigmata each bearing the sporangium
- 15. Bremia lactucae (Cause: downy mildew on Lettuce).
- 16. Sub D.: Zygomycotina Class: Zygomycetes Order (1): Mucorales Family: Mucoraceae Ex.: Mucor spp. Ex.: Rhizopus nigricans (Cause: soft mold on fruits). Ex.: Rhizopus stolonifer (Cause: Bread mold).
- 17. Class: Zygomycetes 1-The class zygomycetes derives its name from the thick-walled resting spores. 2-The hyphal walls are composed of chitin & chitosan. 3-Asexual reproduction by production sporangiospore or aplanospore. 4-Sexual reproduction by gametangial copulation. Produced a thick walled zygospore . 5-Most of zygomycetes are saprobes, some of them are parasite and obligate parasite. 6-Economically important, some of them used in fermentation of food, produced enzymes, acids, and other are saprophytic spoil food.
- 18. Order: Mucorales: (Black mold) Asexual reproduction: Take place by non motile sporangiospores which produced in large number within globose columellate sporangia borne on tips of simple or branched sporangiophores. Sexual reproduction: Occurred by gametangial copulation, two short, side branches the progametangia arise from hyphae by zygophores, grow towards each other and come to contact end to end. A small terminal multinucleate cell called gametangium cut off by septum at the tip of each progametangium, the remainder called suspensor. The wall dissolves between gametangia then karyogamy to produce zygospore.
- 20. Family: Mucoraceae It include two important and best known genera the Mucor and Rhizopus
- 21. Rhizopus: The mycelium during the vegetative phase is a white fluffy mass, coenocytic (aseptate) hyphae consist of stolon hyphae and rhizoidal hyphae. The sporangiophores arise in the air from the stolon, bearing sporangia which are multinucleate non-motile sporangiospore.
- 27. Rhizopus spp.
- 28. Rhizoids Aseptate hyphae Stolon hyphae a white fluffy mass
- 30. Mucor Rhizopus Mycelium consist of only one kind of hyphae The mycelium is differentiated into stolon, rhizoids and sporangiophores Sporangiophores arise from any point in the mycelium. Sporangiophores the nodes junction of rhizoids and stolon. Spores in Mucor are not easily disseminated and remain adhered to columella Spores easily blown away. No change columella Columella become umbrella shaped after sporangial dehiscence.
- 32. Mucor spp.