Landslide and volcanism
- 1. Presentation on Causes, Effects and Mitigation of Landslide and Volcanism
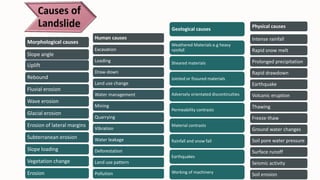
- 2. Human causes Excavation Loading Draw-down Land use change Water management Mining Quarrying Vibration Water leakage Deforestation Land use pattern Pollution Physical causes Intense rainfall Rapid snow melt Prolonged precipitation Rapid drawdown Earthquake Volcanic eruption Thawing Freeze-thaw Ground water changes Soil pore water pressure Surface runoff Seismic activity Soil erosion Geological causes Weathered Materials e.g heavy rainfall Sheared materials Jointed or fissured materials Adversely orientated discontinuities Permeability contrasts Material contrasts Rainfall and snow fall Earthquakes Working of machinery Morphological causes Slope angle Uplift Rebound Fluvial erosion Wave erosion Glacial erosion Erosion of lateral margins Subterranean erosion Slope loading Vegetation change Erosion
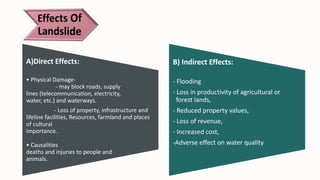
- 3. A)Direct Effects: • Physical Damage- - may block roads, supply lines (telecommunication, electricity, water, etc.) and waterways. - Loss of property, infrastructure and lifeline facilities, Resources, farmland and places of cultural importance. • Causalities deaths and injuries to people and animals. B) Indirect Effects: - Flooding - Loss in productivity of agricultural or forest lands, - Reduced property values, - Loss of revenue, - Increased cost, -Adverse effect on water quality
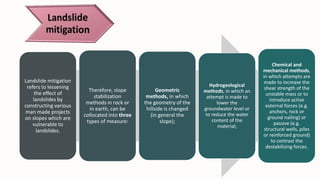
- 4. Landslide mitigation refers to lessening the effect of landslides by constructing various man made projects on slopes which are vulnerable to landslides. Therefore, slope stabilization methods in rock or in earth, can be collocated into three types of measure: Geometric methods, in which the geometry of the hillside is changed (in general the slope); Hydrogeological methods, in which an attempt is made to lower the groundwater level or to reduce the water content of the material; Chemical and mechanical methods, in which attempts are made to increase the shear strength of the unstable mass or to introduce active external forces (e.g. anchors, rock or ground nailing) or passive (e.g. structural wells, piles or reinforced ground) to contrast the destabilizing forces.
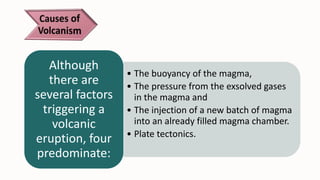
- 5. • The buoyancy of the magma, • The pressure from the exsolved gases in the magma and • The injection of a new batch of magma into an already filled magma chamber. • Plate tectonics. Although there are several factors triggering a volcanic eruption, four predominate:
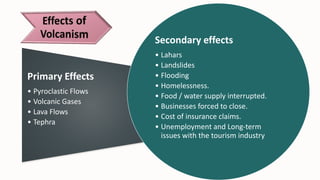
- 6. Primary Effects • Pyroclastic Flows • Volcanic Gases • Lava Flows • Tephra Secondary effects • Lahars • Landslides • Flooding • Homelessness. • Food / water supply interrupted. • Businesses forced to close. • Cost of insurance claims. • Unemployment and Long-term issues with the tourism industry
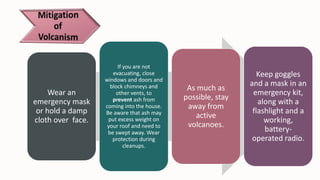
- 7. Wear an emergency mask or hold a damp cloth over face. If you are not evacuating, close windows and doors and block chimneys and other vents, to prevent ash from coming into the house. Be aware that ash may put excess weight on your roof and need to be swept away. Wear protection during cleanups. As much as possible, stay away from active volcanoes. Keep goggles and a mask in an emergency kit, along with a flashlight and a working, battery- operated radio.
- 8. Credits: – Dr. M Bodrozzoha Mia. – Edward A. Keller