Laws of thermodynamics
- 1. SME Unit 2 Laws of Thermodynamics 1 Laws of Thermodynamics, Concept of Heat Engine, Refrigerator and Heat Pump Prof.A.J.More Assistant Professor Engineering Sciences Department Email : amolmore@aissmsioit.org
- 2. Contents 1. Concept of thermodynamics 2. Application of thermodynamics 3. Definitions 4. Types of systems with example 5. Zeroth law statement 6. 1st law of thermodynamics 7. 1st law examples and Limitation 8. 2nd law of thermodynamics 9. Examples Heat Engine Refrigerator and Heat Pumps SME Unit 2 Laws of Thermodynamics 2
- 3. Concept of thermodynamics • Study of Heat and Work • Their effects on system • Under this topic learners will be able to explain effect thermal energy w.rt.KE of gases, temperature Pressure volume etc on system SME Unit 2 Laws of Thermodynamics 3 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/49583940_Probing_Thai_Freshmen_ Science_Students%27_Conceptions_of_Heat_and_Temperature_Using_Open- Ended_Questions_A_Case_Study
- 4. SME Unit 2 Laws of Thermodynamics 4
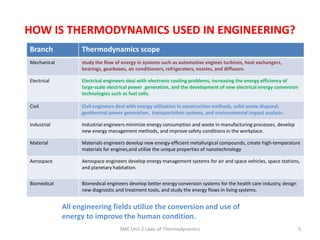
- 5. HOW IS THERMODYNAMICS USED IN ENGINEERING? SME Unit 2 Laws of Thermodynamics 5 Branch Thermodynamics scope Mechanical study the flow of energy in systems such as automotive engines turbines, heat exchangers, bearings, gearboxes, air conditioners, refrigerators, nozzles, and diffusers. Electrical Electrical engineers deal with electronic cooling problems, increasing the energy efficiency of large-scale electrical power generation, and the development of new electrical energy conversion technologies such as fuel cells. Civil Civil engineers deal with energy utilization in construction methods, solid waste disposal, geothermal power generation, transportation systems, and environmental impact analysis. Industrial Industrial engineers minimize energy consumption and waste in manufacturing processes, develop new energy management methods, and improve safety conditions in the workplace. Material Materials engineers develop new energy-efficient metallurgical compounds, create high-temperature materials for engines,and utilize the unique properties of nanotechnology Aerospace Aerospace engineers develop energy management systems for air and space vehicles, space stations, and planetary habitation. Biomedical Biomedical engineers develop better energy conversion systems for the health care industry, design new diagnostic and treatment tools, and study the energy flows in living systems. All engineering fields utilize the conversion and use of energy to improve the human condition.
- 6. Thermodynamics Thermodynamics is the study of the various processes that change energy from one form into another (such as converting heat into work) and uses variables such as temperature, volume, and pressure. *Can be defined as science of energy *Governs all energy consuming and transforming devices and systems. *Energy is ability to do work (cause changes) SME Unit 2 Laws of Thermodynamics 6
- 7. Thermodynamics is the science that deals with the relationship of heat and mechanical energy and conversion of one into the other. The Greek roots, therme, meaning heat, and dynamic, meaning power Thermodynamics means Heat Power 7SME Unit 2 Laws of Thermodynamics
- 8. Thermodynamic System 8SME Unit 2 Laws of Thermodynamics
- 9. SME Unit 2 Laws of Thermodynamics 9 • A system with mass and energy transfer across its boundaries is called Open system [Flow system]. • A system with energy transfer but without mass transfer across its boundaries is called Closed system [Non-flow system]. • If there is no mass and energy transfer between the system and its surroundings, the system is said to be an Isolated system. Types of Thermodynamic System
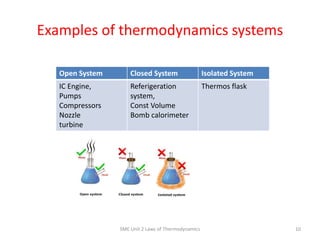
- 10. Examples of thermodynamics systems SME Unit 2 Laws of Thermodynamics 10 Open System Closed System Isolated System IC Engine, Pumps Compressors Nozzle turbine Referigeration system, Const Volume Bomb calorimeter Thermos flask
- 11. 11 • The property which is independent of Mass is called an Intensive Property. E.g. P, T, Density, Viscosity, etc. • It represents a point function. • The property which depends on the Size and Mass is called an Extensive Property. E.g. diameter,l×W,Volume, Heat, Work, Energy, Entropy etc. SME Unit 2 Laws of Thermodynamics Intensive and Extensive property
- 12. SME Unit 2 Laws of Thermodynamics 12 Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics This law deals with the Thermal Equilibrium and establishes a concept of Temperature. If two systems are in thermal equilibrium with a third system, then they are in thermal equilibrium with each other.
- 13. Thank You SME Unit 2 Laws of Thermodynamics 13








![SME Unit 2 Laws of Thermodynamics 9
• A system with mass and energy transfer
across its boundaries is called Open system
[Flow system].
• A system with energy transfer but without
mass transfer across its boundaries is called
Closed system [Non-flow system].
• If there is no mass and energy transfer
between the system and its surroundings, the
system is said to be an Isolated system.
Types of Thermodynamic System](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/v2-201206173728/85/Laws-of-thermodynamics-9-320.jpg)