Lbbb in mi
Download as PPTX, PDF11 likes782 views
This document discusses left bundle branch block (LBBB) and how it affects electrocardiogram (ECG) patterns, making the diagnosis of myocardial infarction (MI) more complicated. Key points: - LBBB alters the normal sequence of ventricular activation, masking typical Q wave changes seen with MI. - ST-T wave changes are usually discordant in LBBB (elevated in leads with negative Q waves, depressed in leads with positive Q waves). - "Hard signs" of MI in LBBB include new Q waves, ST elevation Ōēź0.1mV in direction of QRS, or ST/S ratio Ōēź25%. - Cabrera's sign (notching of
1 of 26
Downloaded 29 times














Recommended
Lbbb + sgarbossa



Lbbb + sgarbossachricres
╠²
The document discusses the Law of Discordance for left bundle branch block (LBBB), stating that in a normal LBBB the ST segments should be isoelectric or go in the opposite direction from the dominant part of the QRS. It then outlines the Modified Sgarbossa Criteria for diagnosing STEMI in the presence of LBBB, including concordant ST changes or discordant ST elevation greater than 1/4 the amplitude of the S wave. Finally, it notes that these criteria also apply to ventricular paced rhythms and stresses the importance of documentation for ECG interpretations.ECG: LBBB and Acute MI



ECG: LBBB and Acute MIStanley Medical College, Department of Medicine
╠²
The document discusses an ECG of a 75-year-old female patient presenting with chest pain. The initial ECG showed left bundle branch block (LBBB) and signs of an acute myocardial infarction (MI) in the left anterior descending artery. A repeat ECG after 24 hours showed signs of left ventricular hypertrophy and anterior and inferior wall ischemia. The document then discusses various criteria for diagnosing MI in patients presenting with LBBB, including the Sgarbossa criteria. It also describes different subtypes and variants of LBBB that can complicate the diagnosis of MI.Bundle branch blocks by Dr Sujith Chadala



Bundle branch blocks by Dr Sujith ChadalaDr Sujith Chadala
╠²
Right bundle branch block,Left bundle branch block,Fasicular blocks,Intraventricular conduction blocks,hemiblocks,bifasicular blocks,trifasicular blocks,qRBBB ecg,causes of rbbb,causes of lbbb,Sgarbossa criteria,incomplete blocks,LAFB,LPFB,RAD,LADLeft Bundle Branch Block (LBBB)



Left Bundle Branch Block (LBBB)Kerolus Shehata
╠²
- Left bundle branch block (LBBB) is caused by conditions that damage the left bundle branch, such as hypertension, dilated cardiomyopathy, and ischemic heart disease.
- LBBB is diagnosed based on criteria including a QRS duration of over 120ms and abnormal ST segment and T wave patterns.
- The prognosis of LBBB depends on any underlying heart conditions, with LBBB increasing the risk of mortality. LBBB may resolve temporarily following a premature ventricular contraction due to resetting of the conduction system.Life saving ecgs



Life saving ecgsPritom Das
╠²
Some slides are taken from different textbooks of medicine like Davidson, Kumar and Clark and Oxford, and some from other presentations made by respected tutors. I'm barely responsible for compilation of various resources per my interest. These resources are free for use, and I do not claim any copyright. Hoping knowledge remains free for all, forever.ECG: Anterolateral MI with LBBB



ECG: Anterolateral MI with LBBBStanley Medical College, Department of Medicine
╠²
1. The document discusses electrocardiogram (ECG) findings in a patient presenting with left bundle branch block (LBBB) and possible myocardial infarction (MI).
2. It outlines criteria like the Sgarbossa criteria that can help identify ST segment changes indicating MI in the setting of LBBB, though these have limited sensitivity.
3. Serial ECGs and cardiac enzyme levels are also useful to help diagnose MI in patients with LBBB due to the challenges of ECG interpretation.Mi in lbbb i.tammi raju



Mi in lbbb i.tammi rajuTammiraju Iragavarapu
╠²
This document discusses the diagnosis of myocardial infarction (MI) in the presence of bundle branch blocks. It notes that bundle branch blocks can make ECG diagnosis of MI more difficult by altering depolarization patterns. For right bundle branch block, the criteria for diagnosing a Q-wave MI are the same as normal conduction. For left bundle branch block, the Sgarbossa criteria (ST elevation concordant with QRS, ST depression in V1-V3, discordant ST elevation Ōēź5mm) have high specificity but low sensitivity for acute MI diagnosis. Certain ECG patterns like abnormal Q waves may suggest prior infarction despite left bundle branch block.Bundle branch blocks



Bundle branch blocksSonukurian
╠²
RBBB is characterized by a QRS duration Ōēź0.12s with an RSR' pattern in V1 and a wide S wave in V6. Causes include myocardial infarction, cardiomyopathy, and pulmonary embolism. LBBB has a QS or rS pattern in V1 and a late intrinsicoid deflection in V6. It is associated with ischemic heart disease and cardiomyopathy. New onset LBBB alone is no longer considered a STEMI equivalent. The Sgarbossa criteria help identify MI in the presence of LBBB. Left anterior and posterior fascicular blocks involve specific QRS and axis changes and help localize conduction system disease. Trifascicular block represents complete heart block with bifascicularLBBB



LBBBAswin Rm
╠²
1. Left bundle branch block (LBBB) is a conduction abnormality caused by impaired conduction in the left bundle branch or its fascicles.
2. LBBB can be chronic or intermittent and is often caused by coronary artery disease or hypertension.
3. On ECG, LBBB is characterized by a QRS duration Ōēź120ms and other abnormalities including broad R waves and abnormal ST-T wave patterns.
4. LBBB can make ECG diagnosis of myocardial infarction difficult and criteria like Sgarbossa scores are used to help identify MI in the setting of LBBB. ECG criteria for left bundle branch block



ECG criteria for left bundle branch blockhttps://aiimsbhubaneswar.nic.in/
╠²
The document defines left bundle branch block (LBBB) according to guidelines from the AHA/ACCF/HRS and Strauss et al. The AHA/ACCF/HRS defines LBBB as a QRS duration of 120 ms or greater with additional features including a broad notched R wave in certain leads and absence of q waves in others. Strauss et al defines LBBB as a QRS duration of 140 ms or greater in men and 130 ms or greater in women with additional features such as QS or rS patterns in leads V1 and V2. Guidelines from AHA/ACCF/HRS and ESC recommend cardiac resynchronization therapy for LBBB patients with a QRS duration of 150Bundle branch blocks



Bundle branch blocksAdarsh
╠²
Bundle branch blocks occur when the left or right bundle branch is blocked, preventing normal conduction of electrical impulses through the ventricles. Right bundle branch block is usually benign but can worsen prognosis in acute myocardial infarction by indicating occlusion of the proximal left anterior descending artery. Left bundle branch block is more serious as it can mask signs of myocardial infarction and worsen prognosis in acute infarction. The Sgarbossa criteria can help diagnose myocardial infarction in the presence of left bundle branch block. Left anterior and posterior hemiblocks involve conduction abnormalities localized to one side of the ventricles.ECG: RBBB with LAFB



ECG: RBBB with LAFBStanley Medical College, Department of Medicine
╠²
The ECG shows right bundle branch block (RBBB) and left anterior fascicular block (LAFB) in a 60-year-old hypertensive man. RBBB is characterized by a wide QRS complex with a terminal R wave in lead V1 and slurred S wave in lead V6. LAFB presents with left axis deviation and rS waves in lead III. The combination of RBBB and LAFB on an ECG suggests ischemia, as LAFB is commonly seen in acute anterior wall myocardial infarctions supplied by the left anterior descending artery.ECG #5 - ID 168 - Left bundle branch block 



ECG #5 - ID 168 - Left bundle branch block Anas Nader
╠²
A 58-year-old man followed for coronary artery disease presented with an ECG showing sinus rhythm at 88 beats per minute, a prolonged QRS duration of 145 milliseconds consistent with left bundle branch block, and no evidence of right or left ventricular hypertrophy or atrial enlargement. The left bundle branch block precludes diagnosing left ventricular hypertrophy and can mask underlying myocardial infarction.Bundlebranchblocks 



Bundlebranchblocks Suneth Weerarathna
╠²
1) Right bundle branch block (RBBB) is characterized by a QRS duration Ōēź 120ms and signs of delayed right ventricular activation. It is commonly benign but worsens prognosis when seen in acute myocardial infarction, especially of the proximal left anterior descending artery.
2) Left bundle branch block (LBBB) has a QRS duration Ōēź 120ms and signs of delayed left ventricular activation. New onset LBBB indicates the need for thrombolysis in myocardial infarction and worsens prognosis when seen in acute myocardial infarction.
3) Hemiblocks involve delayed activation of only one side of the ventricles. Left anterior hemiblock may mask inferior wall myocardial infarction. Left posterior hemiblock in anterior myocardial infarctionRBBB with STEMI



RBBB with STEMITaipei medical university, Wanfang Hospital
╠²
This document summarizes research on right bundle branch block (RBBB) in patients presenting with acute coronary syndrome (ACS). It finds that RBBB in ACS patients identifies a high-risk group with worse short- and long-term outcomes. The presence of RBBB in AMI is associated with more complex cases and obstructive coronary artery disease as well as higher rates of complications and mortality. Studies found 30-day mortality was 14% for AMI patients with RBBB compared to 2% for those without.WIDE COMPLEX ECGs : case presentation



WIDE COMPLEX ECGs : case presentationSMSRAZA
╠²
Left bundle branch block (LBBB) is a conduction abnormality with a prevalence of 0.2-2% that is commonly caused by myocardial infarction, coronary artery disease, hypertension, and cardiomyopathies. LBBB can occur transiently due to tachycardia, exercise, or other acute conditions. It involves delayed conduction in the left ventricle that can persist until heart rate slows. Patients with LBBB require cardiac evaluation and have a poorer prognosis, especially those with underlying heart failure or myocardial infarction who are at higher risk for underdiagnosis and lack of reperfusion therapy.Right bundle branch block



Right bundle branch blockRawalpindi Medical College
╠²
This document discusses right bundle branch block (RBBB) in the electrocardiogram (ECG). It begins by explaining normal ventricular conduction, then describes RBBB. Key points of RBBB include a QRS duration of over 110ms, an rSR' pattern or notched R wave in lead V1, and a wide and slurred S wave in leads I and V6. The document contrasts RBBB and left bundle branch block (LBBB) and provides illustrations of complete RBBB, incomplete RBBB, intermittent RBBB, and RBBB with left anterior fascicular block. It emphasizes using lead V1 and the direction of the terminal QRS force (upward for RBBB, downward for LBBB)Bundle Branch Block



Bundle Branch BlockYukta Wankhede
╠²
Right Bundle Branch Block, Left Bundle Branch Block , Left Anterior and Posterior Fasicular / Hemiblock. Rbbb final



Rbbb finalRawalpindi Medical College
╠²
1. Right bundle branch block (RBBB) results from a defect in the heart's electrical conduction system where there is a delay or failure of impulses traveling down the right bundle branch.
2. This causes the right ventricle to depolarize more slowly than usual, resulting in a characteristic wide and notched QRS complex on ECG.
3. RBBB is generally not treated unless it progresses to heart block, in which case further testing may be needed.Stemi criteria



Stemi criteriachricres
╠²
The document provides criteria for diagnosing ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) on electrocardiogram (ECG). It lists cut-off values for ST elevation in different leads used to identify STEMI based on the patient's age, sex and lead location. It cautions that baseline ECG abnormalities like left bundle branch block (LBBB) could obscure interpretation and provides examples of STEMI in different heart locations identified by affected leads on ECG.Ecg 101 with answers



Ecg 101 with answerschricres
╠²
This document provides an overview of ECG interpretation. It discusses key elements like rhythm, axis, intervals, complexes and segments. Specific conditions are highlighted like inferior posterior STEMI and RV infarct. The importance of systematic analysis is emphasized. Pattern recognition, trends over serial ECGs and correlating findings with the clinical scenario are important skills. Confirming posterior STEMI with lateral precordial lead placement is advised. Overall it is a comprehensive guide to the fundamentals of ECG interpretation and applications in patient care.STEMI Equivalent 



STEMI Equivalent Rashid Abuelhassan
╠²
This document provides an overview of various electrocardiogram (ECG) findings that can indicate acute myocardial infarction (AMI) or critical stenosis requiring intervention. It discusses ECG patterns seen in posterior MIs, left main coronary artery occlusions, De Winter's T waves, Wellen's syndrome, and Sgarbossa's criteria. Assessment of left ventricular ejection fraction is also reviewed, including fractional shortening, Simpson's method, and E-point septal separation. Limitations of certain methods in specific conditions are noted.Ecg in AMI



Ecg in AMIAdarsh
╠²
The document discusses how ECG can be used to diagnose acute myocardial infarction (AMI) and locate the culprit artery. It provides details on:
1) Common ECG patterns seen in AMI including ST elevation, Q waves, T wave changes.
2) How ECG patterns can localize the infarct region and suggest the underlying coronary artery, such as ST elevation in certain leads indicating right coronary or left anterior descending artery.
3) Limitations of ECG including inability to detect all AMIs and accurately estimate infarct size due to individual variations in anatomy and collateral circulation. ECG is not optimal for posterior wall infarcts.ECG diagnosis of chamber enlargement 



ECG diagnosis of chamber enlargement Magesh Vadivelu
╠²
This document outlines ECG criteria for detecting enlargement of the heart chambers, including the left ventricle, right ventricle, and atria. Several voltage-based criteria and point scoring systems are described for identifying left ventricular hypertrophy with sensitivities generally around 35-55% and specificities of 85-95%. Signs of right ventricular hypertrophy and chronic pulmonary disease on ECG are also summarized. Biventricular enlargement can be suggested based on meeting criteria for both left and right ventricular hypertrophy simultaneously. Atrial enlargement of the left or right atria is characterized by abnormalities in the P wave morphology and duration.Infarct localisation



Infarct localisationTammiraju Iragavarapu
╠²
This document discusses ECG patterns in ST-elevation acute coronary syndrome (ACS). It provides threshold values for defining ST elevation and discusses patterns corresponding to different infarct locations. Anterior STEMI results from LAD occlusion and involves the interventricular septum. Inferior STEMI is usually due to RCA occlusion but can also be from dominant LCx occlusion. Wellens' syndrome indicates high-grade LAD stenosis. Posterior MI accompanies inferior or lateral MI and implies a larger infarct size. The document also provides algorithms to localize the infarct artery based on ECG patterns.Stemi equivalents



Stemi equivalentsMohamed Hamoda
╠²
1) STEMI equivalents refer to patients with acutely occluded coronary arteries who do not present with classical ECG changes but have worse outcomes. Common equivalents include de Winter ST/T waves, Wellens' syndromes, ST elevation in aVR, new LBBB, isolated posterior MIs, and upright T waves in V1.
2) Wellens' syndromes present with progressive T wave inversions in leads V2-V3 and little cardiac marker elevation, indicating critical proximal LAD stenosis.
3) ST elevation in aVR with widespread ST depression indicates high-risk left main or three-vessel coronary disease requiring emergent angiography.Making Sense Through series of ECG signs.pptx



Making Sense Through series of ECG signs.pptxSadanand Indi
╠²
bundle branch blocks with LBBB and diagnosis of Myocardial infarction Myocardial infarction (MI) ecg localisation



Myocardial infarction (MI) ecg localisationMalleswara rao Dangeti
╠²
This document discusses various non-coronary causes of ST-elevation on electrocardiograms (ECGs) including ventricular aneurysms, pericarditis, early repolarization patterns, left ventricular hypertrophy, left bundle branch block, hypothermia, cardioversion, intraventricular hemorrhage, hyperkalemia, Brugada pattern, type 1C antiarrhythmic drugs, hypercalcemia, pulmonary embolism, hypothermia, myocarditis, and tumor invasion of the left ventricle. It then discusses left ventricular aneurysms, early repolarization, acute pericarditis, hyperkalemia, hypothermia, increased intracranial pressure, Brugada syndrome, TakVentricular tachycardia



Ventricular tachycardiaAkshay Chincholi
╠²
This document discusses ventricular tachycardia (VT), providing definitions and key characteristics. VT can be nonsustained (<30 seconds) or sustained (>30 seconds). ECG patterns include right bundle branch block (RBBB), left bundle branch block (LBBB), and various axis deviations. Idiopathic VT originates from the outflow tracts, mitral/tricuspid annuli, or fascicles. Specific VT types like bidirectional VT and torsades de pointes are also outlined. The document provides visual examples and differentiates VT from similar rhythms.More Related Content
What's hot (18)
LBBB



LBBBAswin Rm
╠²
1. Left bundle branch block (LBBB) is a conduction abnormality caused by impaired conduction in the left bundle branch or its fascicles.
2. LBBB can be chronic or intermittent and is often caused by coronary artery disease or hypertension.
3. On ECG, LBBB is characterized by a QRS duration Ōēź120ms and other abnormalities including broad R waves and abnormal ST-T wave patterns.
4. LBBB can make ECG diagnosis of myocardial infarction difficult and criteria like Sgarbossa scores are used to help identify MI in the setting of LBBB. ECG criteria for left bundle branch block



ECG criteria for left bundle branch blockhttps://aiimsbhubaneswar.nic.in/
╠²
The document defines left bundle branch block (LBBB) according to guidelines from the AHA/ACCF/HRS and Strauss et al. The AHA/ACCF/HRS defines LBBB as a QRS duration of 120 ms or greater with additional features including a broad notched R wave in certain leads and absence of q waves in others. Strauss et al defines LBBB as a QRS duration of 140 ms or greater in men and 130 ms or greater in women with additional features such as QS or rS patterns in leads V1 and V2. Guidelines from AHA/ACCF/HRS and ESC recommend cardiac resynchronization therapy for LBBB patients with a QRS duration of 150Bundle branch blocks



Bundle branch blocksAdarsh
╠²
Bundle branch blocks occur when the left or right bundle branch is blocked, preventing normal conduction of electrical impulses through the ventricles. Right bundle branch block is usually benign but can worsen prognosis in acute myocardial infarction by indicating occlusion of the proximal left anterior descending artery. Left bundle branch block is more serious as it can mask signs of myocardial infarction and worsen prognosis in acute infarction. The Sgarbossa criteria can help diagnose myocardial infarction in the presence of left bundle branch block. Left anterior and posterior hemiblocks involve conduction abnormalities localized to one side of the ventricles.ECG: RBBB with LAFB



ECG: RBBB with LAFBStanley Medical College, Department of Medicine
╠²
The ECG shows right bundle branch block (RBBB) and left anterior fascicular block (LAFB) in a 60-year-old hypertensive man. RBBB is characterized by a wide QRS complex with a terminal R wave in lead V1 and slurred S wave in lead V6. LAFB presents with left axis deviation and rS waves in lead III. The combination of RBBB and LAFB on an ECG suggests ischemia, as LAFB is commonly seen in acute anterior wall myocardial infarctions supplied by the left anterior descending artery.ECG #5 - ID 168 - Left bundle branch block 



ECG #5 - ID 168 - Left bundle branch block Anas Nader
╠²
A 58-year-old man followed for coronary artery disease presented with an ECG showing sinus rhythm at 88 beats per minute, a prolonged QRS duration of 145 milliseconds consistent with left bundle branch block, and no evidence of right or left ventricular hypertrophy or atrial enlargement. The left bundle branch block precludes diagnosing left ventricular hypertrophy and can mask underlying myocardial infarction.Bundlebranchblocks 



Bundlebranchblocks Suneth Weerarathna
╠²
1) Right bundle branch block (RBBB) is characterized by a QRS duration Ōēź 120ms and signs of delayed right ventricular activation. It is commonly benign but worsens prognosis when seen in acute myocardial infarction, especially of the proximal left anterior descending artery.
2) Left bundle branch block (LBBB) has a QRS duration Ōēź 120ms and signs of delayed left ventricular activation. New onset LBBB indicates the need for thrombolysis in myocardial infarction and worsens prognosis when seen in acute myocardial infarction.
3) Hemiblocks involve delayed activation of only one side of the ventricles. Left anterior hemiblock may mask inferior wall myocardial infarction. Left posterior hemiblock in anterior myocardial infarctionRBBB with STEMI



RBBB with STEMITaipei medical university, Wanfang Hospital
╠²
This document summarizes research on right bundle branch block (RBBB) in patients presenting with acute coronary syndrome (ACS). It finds that RBBB in ACS patients identifies a high-risk group with worse short- and long-term outcomes. The presence of RBBB in AMI is associated with more complex cases and obstructive coronary artery disease as well as higher rates of complications and mortality. Studies found 30-day mortality was 14% for AMI patients with RBBB compared to 2% for those without.WIDE COMPLEX ECGs : case presentation



WIDE COMPLEX ECGs : case presentationSMSRAZA
╠²
Left bundle branch block (LBBB) is a conduction abnormality with a prevalence of 0.2-2% that is commonly caused by myocardial infarction, coronary artery disease, hypertension, and cardiomyopathies. LBBB can occur transiently due to tachycardia, exercise, or other acute conditions. It involves delayed conduction in the left ventricle that can persist until heart rate slows. Patients with LBBB require cardiac evaluation and have a poorer prognosis, especially those with underlying heart failure or myocardial infarction who are at higher risk for underdiagnosis and lack of reperfusion therapy.Right bundle branch block



Right bundle branch blockRawalpindi Medical College
╠²
This document discusses right bundle branch block (RBBB) in the electrocardiogram (ECG). It begins by explaining normal ventricular conduction, then describes RBBB. Key points of RBBB include a QRS duration of over 110ms, an rSR' pattern or notched R wave in lead V1, and a wide and slurred S wave in leads I and V6. The document contrasts RBBB and left bundle branch block (LBBB) and provides illustrations of complete RBBB, incomplete RBBB, intermittent RBBB, and RBBB with left anterior fascicular block. It emphasizes using lead V1 and the direction of the terminal QRS force (upward for RBBB, downward for LBBB)Bundle Branch Block



Bundle Branch BlockYukta Wankhede
╠²
Right Bundle Branch Block, Left Bundle Branch Block , Left Anterior and Posterior Fasicular / Hemiblock. Rbbb final



Rbbb finalRawalpindi Medical College
╠²
1. Right bundle branch block (RBBB) results from a defect in the heart's electrical conduction system where there is a delay or failure of impulses traveling down the right bundle branch.
2. This causes the right ventricle to depolarize more slowly than usual, resulting in a characteristic wide and notched QRS complex on ECG.
3. RBBB is generally not treated unless it progresses to heart block, in which case further testing may be needed.Stemi criteria



Stemi criteriachricres
╠²
The document provides criteria for diagnosing ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) on electrocardiogram (ECG). It lists cut-off values for ST elevation in different leads used to identify STEMI based on the patient's age, sex and lead location. It cautions that baseline ECG abnormalities like left bundle branch block (LBBB) could obscure interpretation and provides examples of STEMI in different heart locations identified by affected leads on ECG.Ecg 101 with answers



Ecg 101 with answerschricres
╠²
This document provides an overview of ECG interpretation. It discusses key elements like rhythm, axis, intervals, complexes and segments. Specific conditions are highlighted like inferior posterior STEMI and RV infarct. The importance of systematic analysis is emphasized. Pattern recognition, trends over serial ECGs and correlating findings with the clinical scenario are important skills. Confirming posterior STEMI with lateral precordial lead placement is advised. Overall it is a comprehensive guide to the fundamentals of ECG interpretation and applications in patient care.STEMI Equivalent 



STEMI Equivalent Rashid Abuelhassan
╠²
This document provides an overview of various electrocardiogram (ECG) findings that can indicate acute myocardial infarction (AMI) or critical stenosis requiring intervention. It discusses ECG patterns seen in posterior MIs, left main coronary artery occlusions, De Winter's T waves, Wellen's syndrome, and Sgarbossa's criteria. Assessment of left ventricular ejection fraction is also reviewed, including fractional shortening, Simpson's method, and E-point septal separation. Limitations of certain methods in specific conditions are noted.Ecg in AMI



Ecg in AMIAdarsh
╠²
The document discusses how ECG can be used to diagnose acute myocardial infarction (AMI) and locate the culprit artery. It provides details on:
1) Common ECG patterns seen in AMI including ST elevation, Q waves, T wave changes.
2) How ECG patterns can localize the infarct region and suggest the underlying coronary artery, such as ST elevation in certain leads indicating right coronary or left anterior descending artery.
3) Limitations of ECG including inability to detect all AMIs and accurately estimate infarct size due to individual variations in anatomy and collateral circulation. ECG is not optimal for posterior wall infarcts.ECG diagnosis of chamber enlargement 



ECG diagnosis of chamber enlargement Magesh Vadivelu
╠²
This document outlines ECG criteria for detecting enlargement of the heart chambers, including the left ventricle, right ventricle, and atria. Several voltage-based criteria and point scoring systems are described for identifying left ventricular hypertrophy with sensitivities generally around 35-55% and specificities of 85-95%. Signs of right ventricular hypertrophy and chronic pulmonary disease on ECG are also summarized. Biventricular enlargement can be suggested based on meeting criteria for both left and right ventricular hypertrophy simultaneously. Atrial enlargement of the left or right atria is characterized by abnormalities in the P wave morphology and duration.Infarct localisation



Infarct localisationTammiraju Iragavarapu
╠²
This document discusses ECG patterns in ST-elevation acute coronary syndrome (ACS). It provides threshold values for defining ST elevation and discusses patterns corresponding to different infarct locations. Anterior STEMI results from LAD occlusion and involves the interventricular septum. Inferior STEMI is usually due to RCA occlusion but can also be from dominant LCx occlusion. Wellens' syndrome indicates high-grade LAD stenosis. Posterior MI accompanies inferior or lateral MI and implies a larger infarct size. The document also provides algorithms to localize the infarct artery based on ECG patterns.Stemi equivalents



Stemi equivalentsMohamed Hamoda
╠²
1) STEMI equivalents refer to patients with acutely occluded coronary arteries who do not present with classical ECG changes but have worse outcomes. Common equivalents include de Winter ST/T waves, Wellens' syndromes, ST elevation in aVR, new LBBB, isolated posterior MIs, and upright T waves in V1.
2) Wellens' syndromes present with progressive T wave inversions in leads V2-V3 and little cardiac marker elevation, indicating critical proximal LAD stenosis.
3) ST elevation in aVR with widespread ST depression indicates high-risk left main or three-vessel coronary disease requiring emergent angiography.Similar to Lbbb in mi (20)
Making Sense Through series of ECG signs.pptx



Making Sense Through series of ECG signs.pptxSadanand Indi
╠²
bundle branch blocks with LBBB and diagnosis of Myocardial infarction Myocardial infarction (MI) ecg localisation



Myocardial infarction (MI) ecg localisationMalleswara rao Dangeti
╠²
This document discusses various non-coronary causes of ST-elevation on electrocardiograms (ECGs) including ventricular aneurysms, pericarditis, early repolarization patterns, left ventricular hypertrophy, left bundle branch block, hypothermia, cardioversion, intraventricular hemorrhage, hyperkalemia, Brugada pattern, type 1C antiarrhythmic drugs, hypercalcemia, pulmonary embolism, hypothermia, myocarditis, and tumor invasion of the left ventricle. It then discusses left ventricular aneurysms, early repolarization, acute pericarditis, hyperkalemia, hypothermia, increased intracranial pressure, Brugada syndrome, TakVentricular tachycardia



Ventricular tachycardiaAkshay Chincholi
╠²
This document discusses ventricular tachycardia (VT), providing definitions and key characteristics. VT can be nonsustained (<30 seconds) or sustained (>30 seconds). ECG patterns include right bundle branch block (RBBB), left bundle branch block (LBBB), and various axis deviations. Idiopathic VT originates from the outflow tracts, mitral/tricuspid annuli, or fascicles. Specific VT types like bidirectional VT and torsades de pointes are also outlined. The document provides visual examples and differentiates VT from similar rhythms.Vt in normal and abnormal hearts my ppt copy



Vt in normal and abnormal hearts my ppt copyRahul Chalwade
╠²
This document discusses ventricular tachycardia (VT) in normal and abnormal hearts. It begins by defining VT and describing its classification based on ECG morphology, duration, mechanism, and etiology. In normal hearts, VT can be due to reentry, automaticity, or triggered activity. Common types of idiopathic VT in normal hearts include outflow tract VT, fascicular VT, and automatic VT. Outflow tract VT often originates from the right ventricular outflow tract and has a good prognosis. Fascicular VT originates from the left posterior fascicle. In abnormal hearts post-myocardial infarction, VT is commonly due to reentry within scar tissue. The 12-lead ECG can provideEcg basics



Ecg basicsSnehal Jayaram
╠²
Genesis of vectors,normal wave forms, segments and intervals.
differential diagnosis of pathological wave formsECG in Acute Myocardial Infarction



ECG in Acute Myocardial InfarctionChetan Ganteppanavar
╠²
1. The document discusses ECG patterns in acute myocardial infarction, describing ST segment elevations, depressions, and T wave changes associated with occlusions of the left anterior descending, left circumflex, and right coronary arteries.
2. Mechanisms of ECG changes during acute MI including systolic and diastolic currents of injury are explained.
3. Criteria for diagnosing acute MI based on ECG findings are provided.7th part ECG Basics: ECG changes in IHD Dr Salah Mabrouk



7th part ECG Basics: ECG changes in IHD Dr Salah MabroukDr Salah Mabrouk Khallaf
╠²
This document provides information on ECG changes seen in ischemic heart disease. It discusses the blood supply of the heart and how different coronary artery occlusions can cause specific ECG changes. These include ST segment elevation or depression, T wave changes, and pathologic Q waves indicating injury, ischemia or necrosis in different heart regions. Examples are provided of ECG tracings demonstrating myocardial infarction patterns involving the inferior, lateral, anterior and posterior walls. It also discusses non-Q wave infarction and pseudoinfarction ECG patterns that can mimic myocardial injury. The effects of conditions like electrolyte abnormalities, drugs, and cardiac syndromes on the ECG are summarized.ecg_systemic_approach_12-lead_compressed.pdf



ecg_systemic_approach_12-lead_compressed.pdfjiregnaetichadako
╠²
This document discusses the analysis of a 12-lead EKG. It begins by describing the components that should be assessed, including rhythm, rate, axis, and grouped lead analysis. Specific abnormalities are then discussed in detail such as ST segment changes, bundle branch blocks, Q waves, and more. The overall goal is to systematically analyze all aspects of the 12-lead EKG to evaluate for any cardiac abnormalities.ST SEGMENT IN ECG,ST ELEVATION AND ST DEPRESSION



ST SEGMENT IN ECG,ST ELEVATION AND ST DEPRESSIONDR Venkata Ramana
╠²
The document discusses the ST segment of the ECG and various abnormalities that can occur. It notes that the ST segment represents the interval between ventricular depolarization and repolarization. ST segment elevation or depression can indicate myocardial ischemia or infarction. Various conditions are described that can cause ST segment changes, including myocardial infarction in different coronary artery territories, coronary vasospasm, pericarditis, early repolarization, and others. The morphology and patterns of ST segment abnormalities are discussed for evaluating these conditions.ECG-2 RAMA.pptx



ECG-2 RAMA.pptxmanishadya
╠²
The document discusses the basics of electrocardiography (ECG), including the 12-lead ECG system and cardiac rhythms. It explains that a standard ECG uses 6 limb leads (I, II, III, aVR, aVL, aVF) and 6 precordial/chest leads (V1-V6). It describes Einthoven's triangle and law. It discusses normal sinus rhythm, cardiac intervals, axis determination, hypertrophy, ischemia, blocks, arrhythmias, and bundle branch blocks. Key points are made about rate, regularity, P waves, PR interval, and QRS duration for interpreting rhythms.3rd part ECG Basics QRS complex Dr Salah Mabrouk Khallaf



3rd part ECG Basics QRS complex Dr Salah Mabrouk KhallafDr Salah Mabrouk Khallaf
╠²
This document provides an overview of QRS complexes and abnormalities seen on electrocardiograms (ECGs). It defines the components of the QRS complex and discusses causes of low or high voltage QRS complexes. Specific conditions that can cause left or right ventricular hypertrophy are described. Various conduction abnormalities are also summarized, including right and left bundle branch blocks, fascicular blocks, and bifascicular blocks. Causes of wide QRS complexes like hyperkalemia and certain drugs are mentioned. The document aims to educate on interpreting and analyzing QRS complexes on ECGs.Ecg made easy



Ecg made easyhttps://aiimsbhubaneswar.nic.in/
╠²
An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) records the electrical signal from your heart to check for different heart conditions. Electrodes are placed on your chest to record your heart's electrical signals, which cause your heart to beat. The signals are shown as waves on an attached computer monitor or printerCardiology 2.1. ECG or EKG - by Dr. Farjad Ikram



Cardiology 2.1. ECG or EKG - by Dr. Farjad IkramFarjad Ikram
╠²
A brief introduction to mechanism of ECG, interpretation of ECG, features of a normal ECG, and ECG seen with limb lead reversal.ECG



ECGLokender Yadav
╠²
This document summarizes key information about interpreting electrocardiograms (ECGs):
1. It discusses how to recognize normal sinus rhythm, 13 common arrhythmias, and acute myocardial infarction on ECGs.
2. It explains the differences between ST elevation and non-ST elevation myocardial infarctions and how they present differently on ECGs over time with ischemia, infarction, and fibrosis.
3. It also reviews how left ventricular hypertrophy and bundle branch blocks present on ECGs, noting that LVH causes increased QRS voltage while bundle branch blocks cause widened QRS duration and distinct morphology changes.BUNDLE BRANCH BLOCK WITH AMI latest.pptx



BUNDLE BRANCH BLOCK WITH AMI latest.pptxSiti Syahida
╠²
This document discusses left bundle branch block (LBBB) in the context of acute myocardial infarction (AMI). It provides an overview of LBBB and challenges in diagnosing AMI when LBBB is present. Several criteria are discussed for identifying AMI in the setting of LBBB, including the original Sgarbossa criteria from 1996, modified Sgarbossa criteria from 2012, and the Barcelona algorithm from 2020. The Barcelona algorithm achieved the highest sensitivity while maintaining good specificity for diagnosing AMI when LBBB is present. An ECG example is also provided to demonstrate positive Sgarbossa criteria.The electrocardiogram (ecg)



The electrocardiogram (ecg)Endegena Abebe
╠²
The ECG is a diagnostic tool that measures electrical currents in the heart during the cardiac cycle using electrodes placed on the body. It provides information about heart rate and rhythm, as well as signs of conditions like myocardial infarction, chamber enlargement, and conduction delays or blocks. Key aspects of the ECG include the P wave, QRS complex, T wave, and intervals between them like the PR interval. Abnormal rhythms and conduction patterns seen on ECG can help diagnose conditions affecting the heart's electrical system.ventricular tachycardia (VT) Localisation



ventricular tachycardia (VT) LocalisationMalleswara rao Dangeti
╠²
This document discusses techniques for localizing the site of origin of ventricular tachycardia based on electrocardiogram characteristics. It describes that right ventricular outflow tract tachycardias typically present with left bundle branch block morphology while left ventricular sites may present with either right or left bundle branch block depending on exit site. Specific leads are discussed that can provide clues about anterior vs posterior, septal vs free wall origin within the outflow tracts. Other areas like fascicles, papillary muscles and mitral/tricuspid annuli are also summarized.QRS axis change during ventricualr tachycardia (VT)



QRS axis change during ventricualr tachycardia (VT)Malleswara rao Dangeti
╠²
1) The QRS axis during ventricular tachycardia (VT) depends on the site of origin of the arrhythmia within the ventricles.
2) A change in axis of more than 40 degrees left or right from the normal range of -30 to 90 degrees is suggestive of VT.
3) The axis can help identify the site of origin, with apical VT showing a left axis and basal VT showing a right axis.APPROACH TO WIDE QRS COMPLEXTACHYCARDIA.pptx



APPROACH TO WIDE QRS COMPLEXTACHYCARDIA.pptxPDT DM CARDIOLOGY
╠²
Wide QRS tachycardia requires differentiating between ventricular tachycardia (VT) and supraventricular tachycardia with aberrancy (SVT-A). The document discusses various algorithms and criteria for making this distinction using the electrocardiogram. These include Wellens' criteria, Brugada criteria, Vereckei's aVR algorithm, and analyzing features such as QRS morphology and the presence of atrioventricular dissociation. No single algorithm is perfect, so electrophysiological testing may be needed in some cases to make a definitive diagnosis and guide appropriate treatment.Recently uploaded (20)
Asthma: Causes, Types, Symptoms & Management ŌĆō A Comprehensive Overview



Asthma: Causes, Types, Symptoms & Management ŌĆō A Comprehensive OverviewDr Aman Suresh Tharayil
╠²
This presentation provides a detailed yet concise overview of Asthma, a chronic inflammatory disease of the airways. It covers the definition, etiology (causes), different types, signs & symptoms, and common triggers of asthma. The content highlights both allergic (extrinsic) and non-allergic (intrinsic) asthma, along with specific forms like exercise-induced, occupational, drug-induced, and nocturnal asthma.
Whether you are a healthcare professional, student, or someone looking to understand asthma better, this presentation offers valuable insights into the condition and its management.BIOMECHANICS OF THE MOVEMENT OF THE SHOULDER COMPLEX.pptx



BIOMECHANICS OF THE MOVEMENT OF THE SHOULDER COMPLEX.pptxdrnidhimnd
╠²
The shoulder complex acts as in coordinated fashion to provide the smoothest and greatest range of motion possible of the upper limb.
Combined motion of GH and ST joint of shoulder complex helps in:
Distribution of motion between other two joints.
Maintenance of glenoid fossa in optimal position.
Maintenance of good length tension
Although some amount of glenohumeral motion may occur while the other shoulder articulations remain stabilized, movement of the humerus more commonly involves some movement at all three shoulder joints.
DIAGNOSIS OF PREGNANCY PPT IN ALL TRIMESTER



DIAGNOSIS OF PREGNANCY PPT IN ALL TRIMESTERdaminipatel37
╠²
Diagnosis of all three trimester of pregnancy Presentaci├│ "Projecte Benestar". MWC 2025



Presentaci├│ "Projecte Benestar". MWC 2025Badalona Serveis Assistencials
╠²
Presentaci├│ que va acompanyar la demostraci├│ pr├Āctica de metge d'Innovaci├│ Jos├® Ferrer sobre el projecte Benestar de BSA, nom d'IDIAP Pere Gol, el 5 de mar├¦ de 2025 a l'estand de XarSMART al Mobible Word Congress. Optimization in Pharmaceutical Formulations: Concepts, Methods & Applications



Optimization in Pharmaceutical Formulations: Concepts, Methods & ApplicationsKHUSHAL CHAVAN
╠²
This presentation provides a comprehensive overview of optimization in pharmaceutical formulations. It explains the concept of optimization, different types of optimization problems (constrained and unconstrained), and the mathematical principles behind formulation development. Key topics include:
Methods for optimization (Sequential Simplex Method, Classical Mathematical Methods)
Statistical analysis in optimization (Mean, Standard Deviation, Regression, Hypothesis Testing)
Factorial Design & Quality by Design (QbD) for process improvement
Applications of optimization in drug formulation
This resource is beneficial for pharmaceutical scientists, R&D professionals, regulatory experts, and students looking to understand pharmaceutical process optimization and quality by design approaches.Regulation of tubular reabsorption _AntiCopy.pdf



Regulation of tubular reabsorption _AntiCopy.pdfMedicoseAcademics
╠²
Title: Regulation of Tubular Reabsorption ŌĆō A Comprehensive Overview
Description:
This lecture provides a detailed and structured explanation of the mechanisms regulating tubular reabsorption in the kidneys. It explores how different physiological and hormonal factors influence glomerular filtration and reabsorption rates, ensuring fluid and electrolyte balance in the body.
¤öŹ Who Should Read This?
This presentation is designed for:
Ō£ö’ĖÅ Medical Students (MBBS, BDS, Nursing, Allied Health Sciences) preparing for physiology exams.
Ō£ö’ĖÅ Medical Educators & Professors looking for structured teaching material.
Ō£ö’ĖÅ Healthcare Professionals (doctors, nephrologists, and physiologists) seeking a refresher on renal physiology.
Ō£ö’ĖÅ Postgraduate Students & Researchers in the field of medical sciences and physiology.
¤ōī What YouŌĆÖll Learn:
Ō£ģ Local Regulation of Tubular Reabsorption
Ō£ö’ĖÅ Glomerulo-Tubular Balance ŌĆō its mechanism and clinical significance
Ō£ö’ĖÅ Net reabsorptive forces affecting peritubular capillaries
Ō£ö’ĖÅ Role of peritubular hydrostatic and colloid osmotic pressures
Ō£ģ Hormonal Regulation of Tubular Reabsorption
Ō£ö’ĖÅ Effects of Aldosterone, Angiotensin II, ADH, and Natriuretic Peptides
Ō£ö’ĖÅ Clinical conditions like AddisonŌĆÖs disease & Conn Syndrome
Ō£ö’ĖÅ Mechanisms of pressure natriuresis and diuresis
Ō£ģ Nervous System Regulation
Ō£ö’ĖÅ Sympathetic Nervous System activation and its effects on sodium reabsorption
¤®║ Clinical Correlations & Case Discussions
Ō£ö’ĖÅ How renal regulation is altered in hypertension, hypotension, and proteinuria
Ō£ö’ĖÅ Comparison of Glomerulo-Tubular Balance vs. Tubulo-Glomerular Feedback
This presentation provides detailed diagrams, flowcharts, and calculations to enhance understanding and retention. Whether you are studying, teaching, or practicing medicine, this lecture will serve as a valuable resource for mastering renal physiology.
¤ōó Keywords for Easy Search:
#Physiology #RenalPhysiology #TubularReabsorption #GlomeruloTubularBalance #HormonalRegulation #MedicalEducation #NephrologyMLS 208 - UNIT 4 A - Tissue Processing - ETANDO AYUK - SANU 1 - Secured.pdf



MLS 208 - UNIT 4 A - Tissue Processing - ETANDO AYUK - SANU 1 - Secured.pdfEswatini Medical Christian University - EMCU / Southern Nazarene University - SANU
╠²
The course covers the steps undertaken from tissue collection, reception, fixation,
sectioning, tissue processing and staining. It covers all the general and special
techniques in histo/cytology laboratory. This course will provide the student with the
basic knowledge of the theory and practical aspect in the diagnosis of tumour cells
and non-malignant conditions in body tissues and for cytology focusing on
gynaecological and non-gynaecological samples.PARIS SYSTEM FOR URINE CYTOLOGY paris system of reporting urine slidespptx



PARIS SYSTEM FOR URINE CYTOLOGY paris system of reporting urine slidespptxDrDivitasaxena1
╠²
Paris system for reporting urine cytologyFlag Screening in Physiotherapy Examination.pptx



Flag Screening in Physiotherapy Examination.pptxBALAJI SOMA
╠²
Flag screening is a crucial part of physiotherapy assessment that helps in identifying medical, psychological, occupational, and social barriers to recovery. Recognizing these flags ensures that physiotherapists make informed decisions, provide holistic care, and refer patients appropriately when necessary. By integrating flag screening into practice, physiotherapists can optimize patient outcomes and prevent chronicity of conditions.OBSTRUCTIVE JAUNDICE- Problem Oriented Approach.pptx



OBSTRUCTIVE JAUNDICE- Problem Oriented Approach.pptxSelvaraj Balasubramani
╠²
Here discussing various cases of Obstructive jaundice namely Choledocholithiassis, Biliary atresia, Carcinoma Pancreas, Periampullary Carcinoma and Cholangiocarcinoma.Biography of Dr. Vincenzo Giordano



Biography of Dr. Vincenzo GiordanoDr. Vincenzo Giordano
╠²
Dr. Vincenzo Giordano began his medical career 2011 at Aberdeen Royal Infirmary in the Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery. Here, he performed complex adult cardiothoracic surgical procedures, significantly enhancing his proficiency in patient critical care, as evidenced by his FCCS certification.Sudurpaschim logsewa aayog Medical Officer 8th Level Curriculum



Sudurpaschim logsewa aayog Medical Officer 8th Level CurriculumDr Ovels
╠²
Sudurpaschim province psc ( lok sewa aayog) medical officer 8th level syllabusBest Sampling Practices Webinar ŌĆō USP <797> Compliance & Environmental Monito...



Best Sampling Practices Webinar ŌĆō USP <797> Compliance & Environmental Monito...NuAire
╠²
Best Sampling Practices Webinar ŌĆō USP <797> Compliance & Environmental Monitoring
Are your cleanroom sampling practices USP <797> compliant? This webinar, hosted by Pharmacy Purchasing & Products (PP&P Magazine) and sponsored by NuAire, features microbiology expert Abby Roth discussing best practices for surface & air sampling, data analysis, and compliance.
¤ÆĪ Key Topics Covered:
Ō£ö’ĖÅ Viable air & surface sampling best practices
Ō£ö’ĖÅ USP <797> requirements & compliance strategies
Ō£ö’ĖÅ How to analyze & trend viable sample data
Ō£ö’ĖÅ Improving environmental monitoring in cleanrooms
¤Äź Watch Now: https://www.nuaire.com/resources/best-sampling-practices-cleanroom-usp-797
¤ōó Stay informedŌĆöfollow Abby Roth on LinkedIn for more cleanroom insights!Op-eds and commentaries 101: U-M IHPI Elevating Impact series



Op-eds and commentaries 101: U-M IHPI Elevating Impact seriesKara Gavin
╠²
A slide set about writing opinion and commentary pieces, created for the University of Michigan Institute for Healthcare Policy and Innovation in Jan. 2025SAPIENT Medi-trivia Quiz (FINALS) | TRI-ORTA 2025



SAPIENT Medi-trivia Quiz (FINALS) | TRI-ORTA 2025Dr. Anindya
╠²
Final Round of SAPIENT Medi-trivia quiz
Part of TRI-ORTA 2025
Venue: GLT, Medical College Kolkata
Date: 25-02-2025MLS 208 - UNIT 4 A - Tissue Processing - ETANDO AYUK - SANU 1 - Secured.pdf



MLS 208 - UNIT 4 A - Tissue Processing - ETANDO AYUK - SANU 1 - Secured.pdfEswatini Medical Christian University - EMCU / Southern Nazarene University - SANU
╠²
Lbbb in mi
- 1. MI IN LBBB
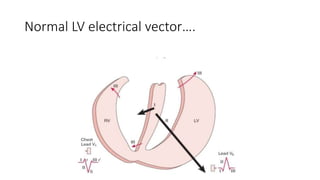
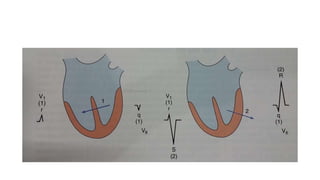
- 2. Normal LV electrical ▒╣▒│”│┘┤Ū░∙ŌĆ”.
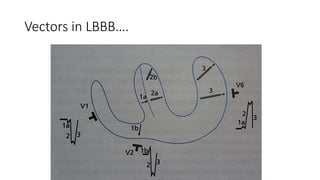
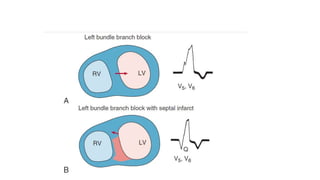
- 5. LBBBŌĆ” ŌĆó Initial septal activation with LBBB typically occurs on the right (rather than on the left) septal surface, leading to right to left (rather than left to right) activation of the septum, so that normal septal q waves are absent. ŌĆó Left ventricular activation then typically begins on the left septal surface, with a delay of 40 milliseconds or longer caused by slow transseptal spread from the right ventricular side of the septum. ŌĆó The subsequent activation of the ventricular free wall is highly variable, depending on the type, location, and extent of the underlying cardiac disease. ŌĆó Most commonly, the region of block is located anteriorly, and the lateral and posterolateral portions of the left ventricle are activated by wave fronts moving around the apex and across the inferior wall in a U-shaped pattern.
- 6. ŌĆó Irregular spread predominantly through working muscle fibers rather than the specialized conduction system results in notching and slurring of the wide QRS complex. ŌĆó Overall activation may then require more than 180 milliseconds, depending on the functional status of the distal left bundle and Purkinje systems and on the speed of propagation through working cardiac muscle; activation of portions of the left ventricle may not occur until well beyond the end of the QRS complex.
- 7. ST T CHANGES in LBBBŌĆ” ŌĆó The discordant ST-T wave pattern is a reflection of the altered pattern of ventricular activation. ŌĆó With LBBB, the right ventricle is activated and recovers earlier than the left, so recovery vectors are directed toward the right and away from the left ventricle. ŌĆó Hence positive ST-T waves will be registered in leads over the right ventricle that show S waves and negative ones over the left ventricle with prominent R waves. ŌĆó ST-T wave changes are prominent with LBBB. In most cases, the ST segment and T wave are discordant with the QRS complex. That is, the ST segment is depressed and the T wave is inverted in leads with positive QRS waves (e.g., leads I, aVL, V5, and V6), and the ST segment is elevated and the T wave is upright in leads with predominantly negative QRS complexes (e.g., leads V1 and V2). ŌĆó These ST-T wave changes are referred to secondary ST-T abnormalities because they are generated by abnormalities in conduction
- 8. ST T changes in LBBBŌĆ” ŌĆó ST-segment elevation with tall, positive T waves frequently is seen in the right precordial leads with uncomplicated LBBB. ŌĆó Secondary T wave inversions are characteristically seen in the lateral precordial leads. ŌĆó However, the appearance of ST-segment elevations in the lateral leads or ST- segment depressions or deep T wave inversions in leads V1 to V3 strongly suggests underlying ischemi. ŌĆó More marked ST-segment elevations (>0.5 mV) in leads with QS or rS waves also may be caused by acute ischemia. ŌĆó Use of the ratio of the amplitude of ST-segment elevation to S wave magnitude, determined in any relevant lead, has been proposed, with a value of less than 0.25 reported as having greater accuracy than that of the original criterion.
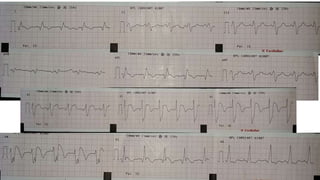
- 10. Electromechanical dissociation. ŌĆó Septal and lateral wall moves in dys synchrony. ŌĆó More than 60 msec of dyssynchrony is commom and as much as 120 to 150 msec out of phase contractions can occur between lateral and septal wall.
- 11. ŌĆóMI IN LBBB
- 12. The diagnosis of myocardial infarction may be obscured ŌĆó LBBB can mask or mimic MI. ŌĆó emergence of abnormal Q waves with infarction is dependent on a normal initial sequence of ventricular activation, which is absent with LBBB. ŌĆó In addition, ECG patterns of LBBB, including low R wave amplitude in the midprecordial leads and ST-T wave changes, can mimic anterior infarct patterns.
- 13. ŌĆó The diagnosis of infarction in the presence of LBBB is considerably more complicated and confusing, because LBBB alters the early and the late phases of ventricular depolarization and produces secondary ST-T changes. ŌĆó These changes may mask and/or mimic myocardial infarction findings. ŌĆó Infarction of the left ventricular free (or lateral) wall ordinarily results in abnormal Q waves in the midprecordial to lateral precordial leads (and selected limb leads). ŌĆó However, the initial septal depolarization forces with LBBB are directed from right to left. These leftward forces produce an initial R wave in the midprecordial to lateraprecordial leads, usually masking the loss of electrical potential (Q waves) caused by the infarction. ŌĆó Thereforeacute or chronic left ventricular free wall infarction by itself will not produce diagnostic Q waves in the presence of LBBB
- 14. Hard signs of MI in LBBBŌĆ” ŌĆó The presence of QR complexes in leads I, V5, or V6 or in II, III, and avf with LBBB strongly suggests underlying infarction. ŌĆó Chronic infarction also is suggested by notching of the ascending part of a wide S wave in the midprecordial leads or the ascending of a wide R wave in lead I, aVL, V5, or V6.
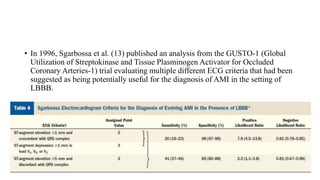
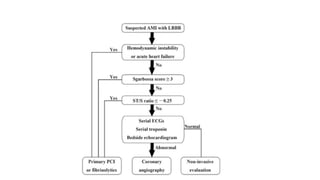
- 16. ŌĆó In 1996, Sgarbossa et al. (13) published an analysis from the GUSTO-1 (Global Utilization of Streptokinase and Tissue Plasminogen Activator for Occluded Coronary Arteries-1) trial evaluating multiple different ECG criteria that had been suggested as being potentially useful for the diagnosis of AMI in the setting of LBBB.
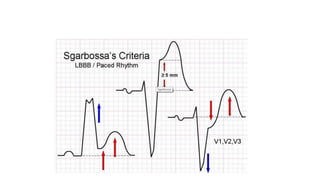
- 18. SMITH modification of Sgarbossa criteriaŌĆ” ŌĆó A new criterion from Smith et al. significantly increases the sensitivity (up to 90%) ŌĆó ST elevation or depression in the opposite direction as the QRS with a ST/S ratio of ŌłÆ0.25 or less (ie that the ST deviation is bigger than 25% of the S wave amplitude) In summary ŌĆó All those criteria can be put together like this: ŌĆó ST deviation ŌĆó ŌĆō Ōēź0.1 mV in the same direction as the QRS or ŌĆó ŌĆō ST/S ratio Ōēź 25%
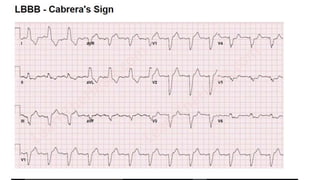
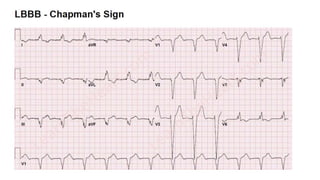
- 19. ŌĆó Cabrera's sign ŌĆó CabreraŌĆÖs sign is used to diagnose an acute myocardial infarction in the setting of a left bundle branch block and consists of notching at 40 milliseconds in the upslope of the S wave in lead V3 and V4. This has a poor sensitivity of 27% for myocardial infarction
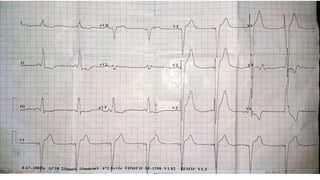
- 22. ŌĆó Mohammad kunju 65/m ŌĆó Known case of CAD, DCM, HTN ŌĆó MI 4 years back. ŌĆó ED III for 4 months. ŌĆó Elective PCI to prox LAD 3 months back. ŌĆó Presented with chest pain.. ŌĆó ECG was taken.
- 26. Refrences.. ŌĆó Braunwalds text book of Heart Diseases 10th edition. ŌĆó Leo scamroth ,An introduction to Electrocardiography 8th edi. ŌĆó Evolving Considerations in the Management of Patients With Left Bundle Branch Block and Suspected Myocardial Infarction JACC Vol. 60, No. 2, 2012 Neeland et al. 99 July 10, 2012:96ŌĆō10 ŌĆó Diagnosis of ST-elevation myocardial infarction in the presence of left bundle branch block with the ST-elevation to S-wave ratio in a modified Sgarbossa rule. Smith et al Ann Emer Med 2012 Dec;60(6):766-76





