Leadership Academy 1
- 2. Research based on a national database of over 200,000 churches reveals that the overall population growth rate far outpaces the church’s rate of growth. Part 1 – Church Growth Statistics
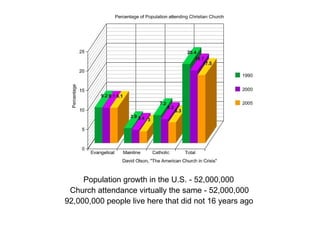
- 3. Population growth in the U.S. - 52,000,000 Church attendance virtually the same - 52,000,000 92,000,000 people live here that did not 16 years ago
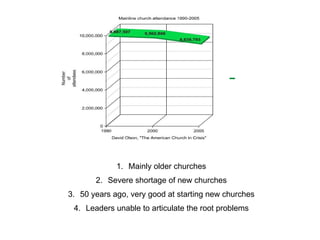
- 4. Mainly older churches Severe shortage of new churches 50 years ago, very good at starting new churches Leaders unable to articulate the root problems
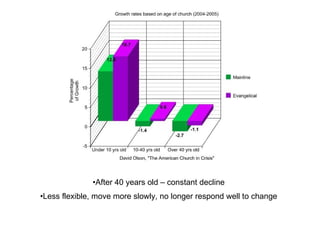
- 5. After 40 years old – constant decline Less flexible, move more slowly, no longer respond well to change
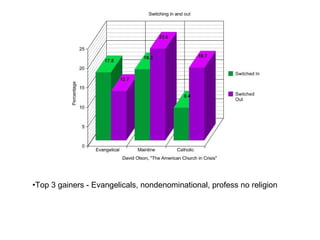
- 6. Top 3 gainers - Evangelicals, nondenominational, profess no religion
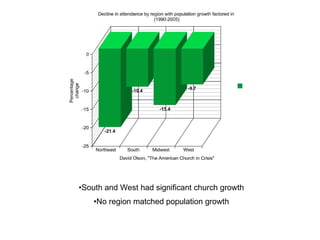
- 7. South and West had significant church growth No region matched population growth
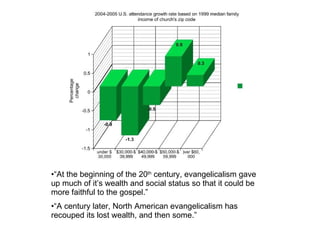
- 8. “At the beginning of the 20 th century, evangelicalism gave up much of it’s wealth and social status so that it could be more faithful to the gospel.” “A century later, North American evangelicalism has recouped its lost wealth, and then some.”
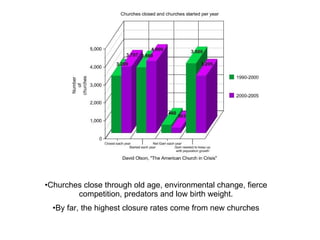
- 9. Churches close through old age, environmental change, fierce competition, predators and low birth weight. By far, the highest closure rates come from new churches
- 10. Part 2 – Root of the Problem – Cultural Change Three Critical Transitions Christian to Post-Christian Modern to Post-Modern Monoethnic to multiethnic
- 11. Part 2 – Root of the Problem – Cultural Change Christian Christendom Close relationship between church and culture Focus on institution needs of insiders most important People brought needs to church Preaching the Word, sacraments, pastoral care
- 12. Part 2 – Root of the Problem – Cultural Change Post-Christian Church needs to operate more like early church Needs of outsiders most important More like missionary work Equip to live mission of Jesus outside the church Not traditional vs. contemporary (dated) Missional – live the mission – not separate
- 13. Part 2 – Root of the Problem – Cultural Change Modern Main influence – Enlightenment Observation, logic, and reason Move from world of mythology to engage physical reality Science was king Self all-powerful Everything Discoverable National Park – Easum Image Neat and organized – clearly defined trails
- 14. Part 2 – Root of the Problem – Cultural Change Post-Modern Characterized by Uncertainty Skepticism and cynicism about over certainty Communal life replaces individualism History and tradition rise in value Spiritual curiosity is present Jungle – Video Game (Easum image) No clear rules – discover on own
- 15. Part 2 – Root of the Problem – Cultural Change Monoethnic to Multiethnic Previous church only had to understand own culture Limits gospel Acts 2 Gospel applies to all cultures Beef Stew All ingredients recognizable yet form something new
- 16. Part 3 – Ways to Read Those Changes Method For Reading Cultural Texts Locution Employs medium Illocution Act of Doing Something in Saying Perlocution Certain Effects
- 17. Part 3 – Ways to Read Those Changes Method For Reading Cultural Texts World Behind the Work Background Context World of the Work Way of doing life as embodied in text World in Front of the Work Make decision about What to Do
- 18. Part 3 – Ways to Read Those Changes From cell phones to mp3 players to the internet, no previous age has seen such profound change manifested so quickly. But these thrilling, dizzying transformations are forcing the church to decide where it fits in all this progress.
- 19. Part 3 – Ways to Read Those Changes Media Shapes the Message Way we tell the story is part of the story (Media we use) Doug Pagitt “Preaching Re-Imagined” Major medium of modern age Printed Word Major medium of post-modern age Electronic media
- 20. Part 3 – Ways to Read Those Changes Roots of Internet Age 1850-1900 Telegraph Radio Graphic Revolution
- 21. Part 3 – Ways to Read Those Changes Knowledge as Building Knowledge as Web Derived from Print Linear – bottom up Mirrors printed word Derived from Telegraph Conditioned by experience and truth claims Two way dialogue
- 22. Part 3 – Ways to Read Those Changes Radio – A Return to Tribal Campfires Shared songs, experiences and stories Ways of knowing corporate Reversal of individualism of printed word
- 23. Part 3 – Ways to Read Those Changes Graphic Revolution Dissolving dependence on literacy Corporate logos Preference for concrete, holistic, non-linear view of world Doesn’t eliminate need for print, just the bias towards
- 24. Part 3 – Ways to Read Those Changes The Girl is Sad
- 25. Part 3 – Ways to Read Those Changes
- 26. Part 3 – Ways to Read Those Changes Print Age Reductionist formulaic faith Importance of personal relationship Unlocked rational theology Electronic Age Power of truth and story Importance of following Jesus holistically not just believe Emphasizes corporate understanding of faith
- 27. Church 2.0 Need for Community Create Framework for User Contribution
- 28. Part 4 – Marketing Overview Put tools in hands of people when time is right will come Shape perceptions - outbound communication Live in overcommunicated world how can be heard Authenticity
- 29. Part 4 – Marketing Overview Brand Matters Promise (from church) Mental Picture (person) Perception is Reality Logo Influences Perception What People Think Of Perception is Brand Goal is to Carve out Position
- 30. Part 4 – Marketing Overview
- 31. Part 4 – Marketing Overview Roots - Mission, Vision, Values Direction to the Brand Trunk - Brand Positioning What’s Unique Who target / What About / Why Trust / Personality Branches - Identity Reminds of Message Name / Logo / Visual Style Using Same Phrases Shapes How People Talk About Church Leaves - Brand Expressions Every Interaction Shapes Perception Print / Web / Ambience of Site Buzz in Community
- 32. Part 4 – Marketing Overview Six Non-Negotiables Be Authentic Be Excellent Be Surprising Be Consistent Be Strategic Be Realistic
- 33. Part 4 – Marketing Overview Goals of Marketing Influence Perceptions Increase Awareness More sowing than Reaping Inviting to Action When Ready