Lean manufacturing
- 1. VIRTUAL LEAN MANUFACTURING Dr. V. RAMESH PROFESSOR SJCE, MYSORE
- 3. Functional layout Cellular layout Askin G.G & Standridge C.R. (1993) Modelling and Analysis of Manufacturing Systems, John Wiley ISBN 0-471-57369-8
- 4. ÂĐ Siemens Power Generation Systems Functional layout
- 5. Manufacturing cells ÂĐ Siemens Power Generation Systems
- 6. VIRTUAL LEAN MANUFACTURING PRACTICES FOR LEAN MANUFACTURING, LINE BALANCING, KAIZEN, FLOW PATH ANALYSIS, SMED, ERGONOMICS, SCHEDULING ANALYSIS WORKPRO FOR LAYOUT OPTIMIZATION PROMODEL FOR PROBLEM SOLVING INNOVATIVE WORK BENCH SIMULATION MODELLING ARENA
- 7. WORKPRO
- 8. WORKPRO â ERGO STUDIES
- 9. PROMODEL
- 13. Lean Manufacturing? âĒ Large batches âĒ Excessive inventory âĒ Long lead times âĒ Excessive work in progress âĒ Disorganized shop floor with no space âĒ High costs âĒ Low percent of on-time deliveries âĒ Difficulty in meeting customer needs âĒ Not competitiveâhaving selling price too high
- 14. POINT OF USE STORAGE
- 17. Linked Cell Manufacturing System
- 18. Lean Production As Linked Cell
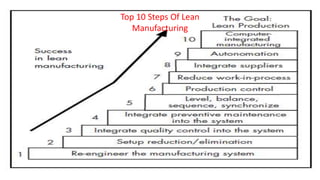
- 20. Top 10 Steps Of Lean Manufacturing
- 21. The Principles of a Lean Manufacturing System âĒ ValueâCustomerâs willingness to pay for your product. âĒ Value StreamâAdd-ons to a product or process. âĒ FlowâThe movement of your product through a single piece flow or work cells rather than production lines. âĒ PullâHaving the right amount of materials to manufacture the product, and at the same time, having a small or no inventory. âĒ Continuous ImprovementâGetting rid of waste on a constant basis.
- 22. Light Duty Lean Manufacturing
- 28. Parts Organizers
- 29. Cross Tub Racks
- 30. Howardell Seven Skills âĒ Customer consciousness, âĒ Enterprise thinking. âĒ Adaptation, âĒ Taking initiative, âĒ Innovation, âĒ Collaboration
- 31. Hence, Lean Manufacturing Aims at, âĒ Less labor and floor space. âĒ Fewer design hours for product development. âĒ Less stock on hand. âĒ Fewer defects. âĒ Quality. âĒ Faster delivery. âĒ Improved ergonomics. âĒ Maximum flexibility in product types and styles produced.
- 32. Lean and Ergonomics Safety and ergonomics should be one of the core values of the lean process âĒ Identify work process to improve âĒ Stakeholder involvement âĒ Ergonomics training âĒ Ergonomic design âĒ Quantifying the impact of ergonomic changes âĒ Creating shared belief for the benefit of ergonomics
- 33. Waste Waste of motion that does not add value âĒ Can lead to muscle fatigue Waste of manual effort âĒ Can lead to muscle fatigue Waste of movements to transport material âĒ Can lead to muscle fatigue and strains Waste of time to rework, repair, or scrap âĒ May be related to fatigue, strains or sprains âĒ Focus on self and not on job
- 34. Multifunction double gantry mill ÂĐ Siemens Power Generation Systems A single machine acting as a cell
- 35. Group Technology / Cellular Manufacturing âĒ Improved material flow âĒ Reduced queuing time âĒ Reduced inventory âĒ Improved use of space âĒ Improved team work âĒ Reduced waste âĒ Increased flexibility
- 36. Waller, D.L., 2003,âOperations Management: a Supply Chain Perspective 2nd Editionâ, Thompson, London