Learning materials&odl 1
- 1. Planning and Writing Learning Materials for use in open and distance learning (ODL)
- 2. Open and distance learning (ODL) Remove barriers to education, Allow students to study what they want, when they want and where they want. Use of technology to mediate learning
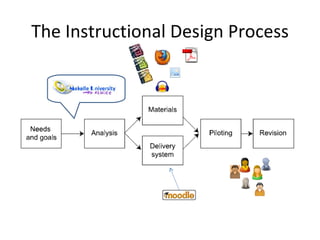
- 3. The Instructional Design Process
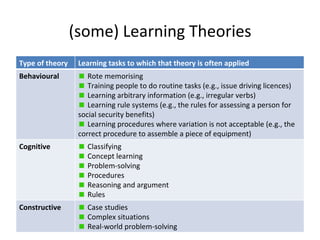
- 4. (some) Learning Theories Type of theory Learning tasks to which that theory is often applied Behavioural Rote memorising Training people to do routine tasks (e.g., issue driving licences) Learning arbitrary information (e.g., irregular verbs) Learning rule systems (e.g., the rules for assessing a person for social security benefits) Learning procedures where variation is not acceptable (e.g., the correct procedure to assemble a piece of equipment) Cognitive Classifying Concept learning Problem-solving Procedures Reasoning and argument Rules Constructive Case studies Complex situations Real-world problem-solving
- 5. Typical Learning Devices Associated with Behavioural Theory Learning devices used learning objectives stated task broken down into small steps most tasks have clear right or wrong answers learners assessed against the stated learning objectives the learning package prescribes what is to be learnt
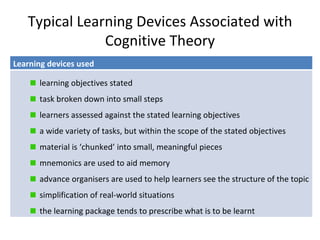
- 6. Typical Learning Devices Associated with Cognitive Theory Learning devices used learning objectives stated task broken down into small steps learners assessed against the stated learning objectives a wide variety of tasks, but within the scope of the stated objectives material is ŌĆśchunkedŌĆÖ into small, meaningful pieces mnemonics are used to aid memory advance organisers are used to help learners see the structure of the topic simplification of real-world situations the learning package tends to prescribe what is to be learnt
- 7. Typical Learning Devices Associated with Constructive Theory Learning devices used learner choice of task or situation authentic, real-world tasks case studies complexity of the real world presented in the tasks collaborative learning tasks opportunities to learn from observing others (e.g., trainee teaching as observer in a classroom) the learning package tends to be open-ended in terms of what is to be learnt self-evaluation rather than formal assessment
- 8. What Does an Instructional Designer Do? determine what the learners need to know develop learning outcomes; decide how learning will be assessed at the end of the course allocate outcomes to the various sections of the course (units); for each unit: decide the types of activity needed to achieve each outcome decide the examples needed to help learners learn each outcome identify any graphics needed plan any self-assessment needed for that unit; write the units; test and evaluate the materials; and revise to take account of the evaluation results.
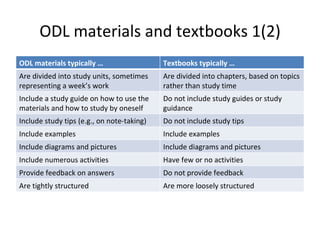
- 9. ODL materials and textbooks 1(2) ODL materials typically ŌĆ” Textbooks typically ŌĆ” Are divided into study units, sometimes representing a weekŌĆÖs work Are divided into chapters, based on topics rather than study time Include a study guide on how to use the materials and how to study by oneself Do not include study guides or study guidance Include study tips (e.g., on note-taking) Do not include study tips Include examples Include examples Include diagrams and pictures Include diagrams and pictures Include numerous activities Have few or no activities Provide feedback on answers Do not provide feedback Are tightly structured Are more loosely structured
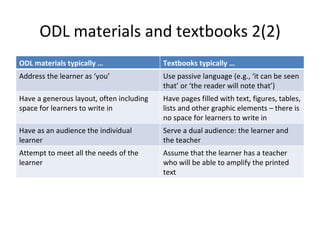
- 10. ODL materials and textbooks 2(2) ODL materials typically ŌĆ” Textbooks typically ŌĆ” Address the learner as ŌĆśyouŌĆÖ Use passive language (e.g., ŌĆśit can be seen thatŌĆÖ or ŌĆśthe reader will note thatŌĆÖ) Have a generous layout, often including space for learners to write in Have pages filled with text, figures, tables, lists and other graphic elements ŌĆō there is no space for learners to write in Have as an audience the individual learner Serve a dual audience: the learner and the teacher Attempt to meet all the needs of the learner Assume that the learner has a teacher who will be able to amplify the printed text
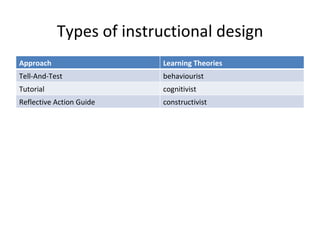
- 11. Types of instructional design Approach Learning Theories Tell-And-Test behaviourist Tutorial cognitivist Reflective Action Guide constructivist
- 12. Tell-And-Test Each topic: a piece of explanatory text (with diagrams and examples as needed) followed by a test to check whether the learners have learnt the material. Emphasis: memorising rather than understanding. Advantage: comparatively easy to produce and can easily be created from existing teaching notes or lecture notes.
- 13. Tutorial Some form of input (e.g., text, diagram, case study) and an activity on it The activity seeks to help the learner understand the material being taught. A complete unit consists of a succession of input-activity sequences. The material mimics the teacher who gives some input and then asks a question or sets a task in the classroom.
- 14. ╠²
- 15. Reflective Action Guide To support learning from their own experiences (e.g., at work) Typically such materials will: specify broadly defined aims but no precise learning outcomes; set projects; set tasks that require the learners to engage with others encourage the learners to record and reflect on their own experience (e.g., by keeping a learning journal); use case studies; set activities often being based on the learnersŌĆÖ own experiences.
- 16. ╠²
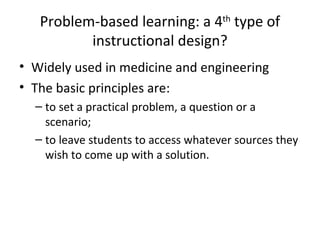
- 17. Problem-based learning: a 4 th type of instructional design? Widely used in medicine and engineering The basic principles are: to set a practical problem, a question or a scenario ; to leave students to access whatever sources they wish to come up with a solution.
- 18. Mixing Instructional Design Types The most common mix: a combination of tutorial to cover outcomes associated with well-defined material, and reflective action guide to cover less well-defined material.
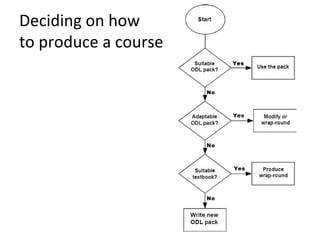
- 19. Adapt or Create? 3 basic ways to produce an ODL course: write it from scratch (time and cost...) adapt an existing ODL course, or produce a wrap-round guide to an existing resource such as a textbook.
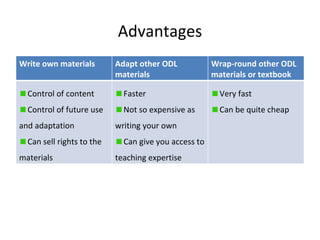
- 20. Advantages Write own materials Adapt other ODL materials Wrap-round other ODL materials or textbook Control of content Control of future use and adaptation Can sell rights to the materials Faster Not so expensive as writing your own Can give you access to teaching expertise Very fast Can be quite cheap
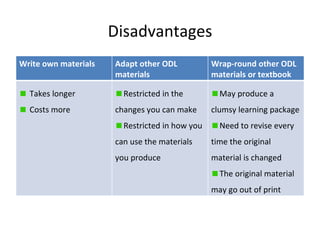
- 21. Disadvantages Write own materials Adapt other ODL materials Wrap-round other ODL materials or textbook Takes longer Costs more Restricted in the changes you can make Restricted in how you can use the materials you produce May produce a clumsy learning package Need to revise every time the original material is changed The original material may go out of print
- 22. Deciding on how to produce a course
- 23. What You Might Add Study advice Activities Examples Self-tests Summaries Assessment material Links to local resources Case studies Media elements: audio, video, a web site.
- 24. Issues in Adapting Copyright Changes in the original version Going out of print
- 25. Evaluate and Adapt Existing Materials Commonwealth of Learning: www.col.org/resources/weblinks/resources_edtech.htm Distance Learning Course Finder: www.dlcoursefinder.com Resources in Distance Education (RIDE, Athabasca University, Canada): http://ccism.pc.athabascau.ca/html/ccism/deresrce/de.htm The International Centre for Distance Learning: www-icdl.open.ac.uk/ UK distance learning courses: www.distance-learning.co.uk/ World Wide Learn: www.worldwidelearn.com/index.html (mostly North American institutions)